Visual Construction:Low-Code and No-Code Integration for Charts in Data Visualization
I. Overview
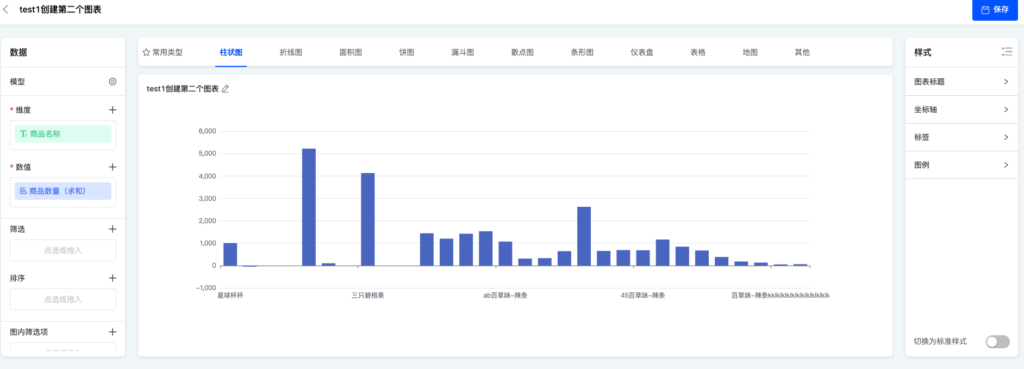
Data visualization provides the function of custom chart templates to meet business requirements that cannot be satisfied by existing chart templates.
II. How to Use
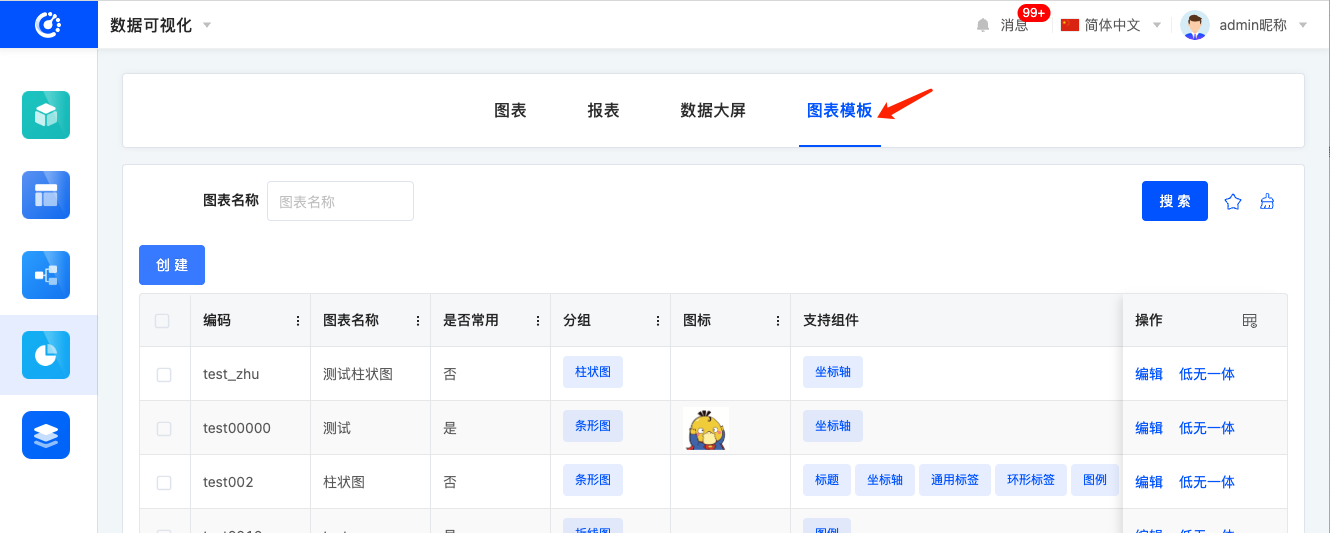
- Click "Chart Templates" at the top of the data visualization page
- Click the
Createbutton to pop up the chart template form, fill it in and submit for saving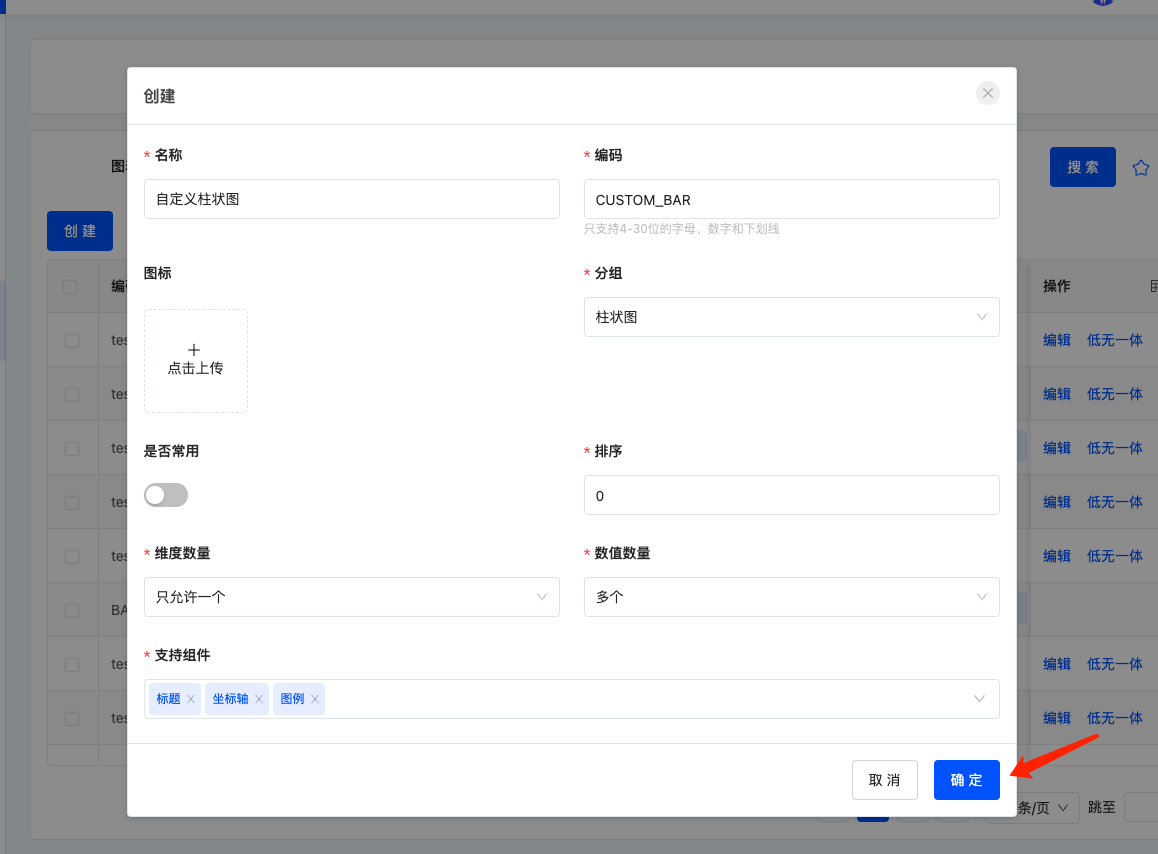
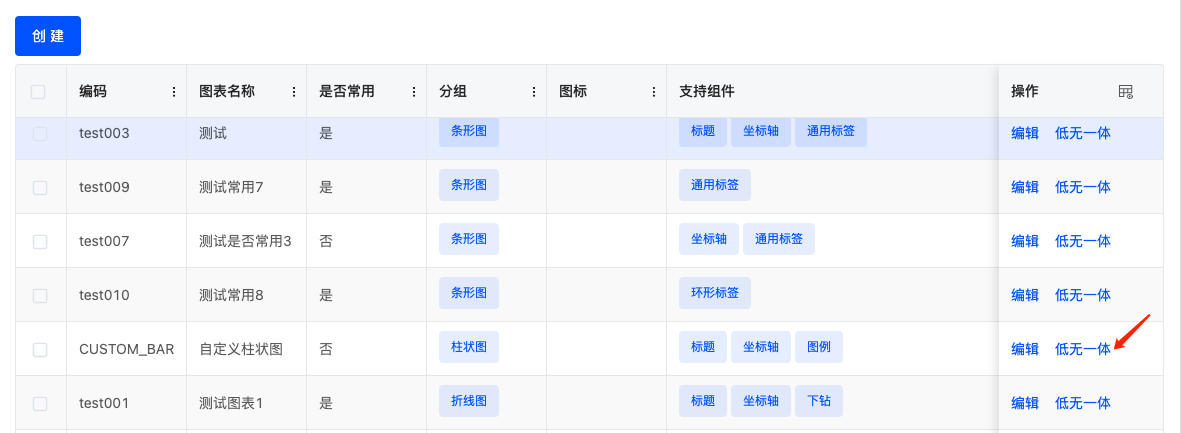
- Locate the newly created chart template and click the "Low-Code & No-Code Integration" button in the operation bar
- Click the "Generate SDK" button at the bottom of the pop-up window
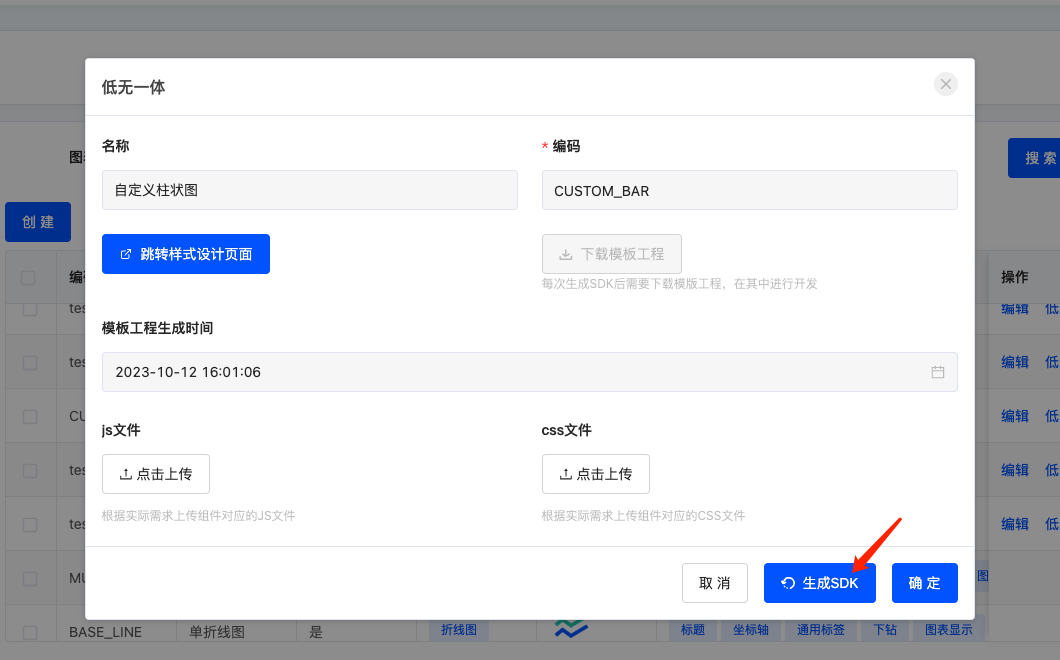
- After completing the above operation, the page will refresh. Locate the data again, click the "Low-Code & No-Code Integration" button. Now the "Download Template Project" button is clickable. Click it to download the sample code package
kunlun-chart-sdk.zipfor the custom chart template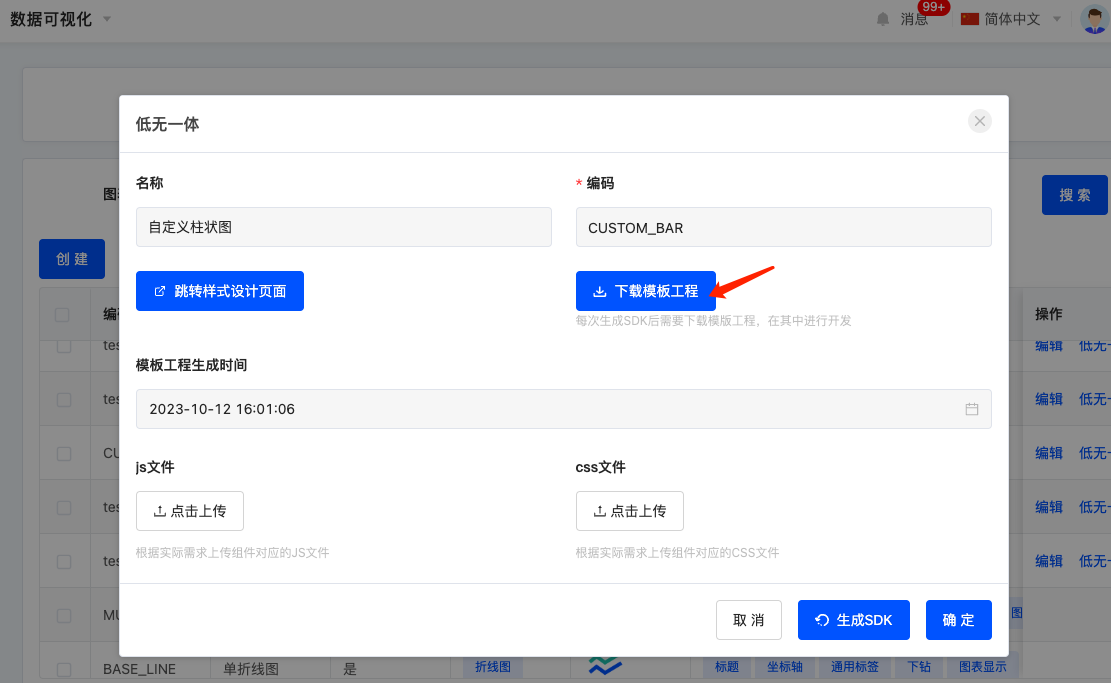
- After unzipping
kunlun-chart-sdk.zip, view the project structure. Executenpm iin the root directory to install dependencies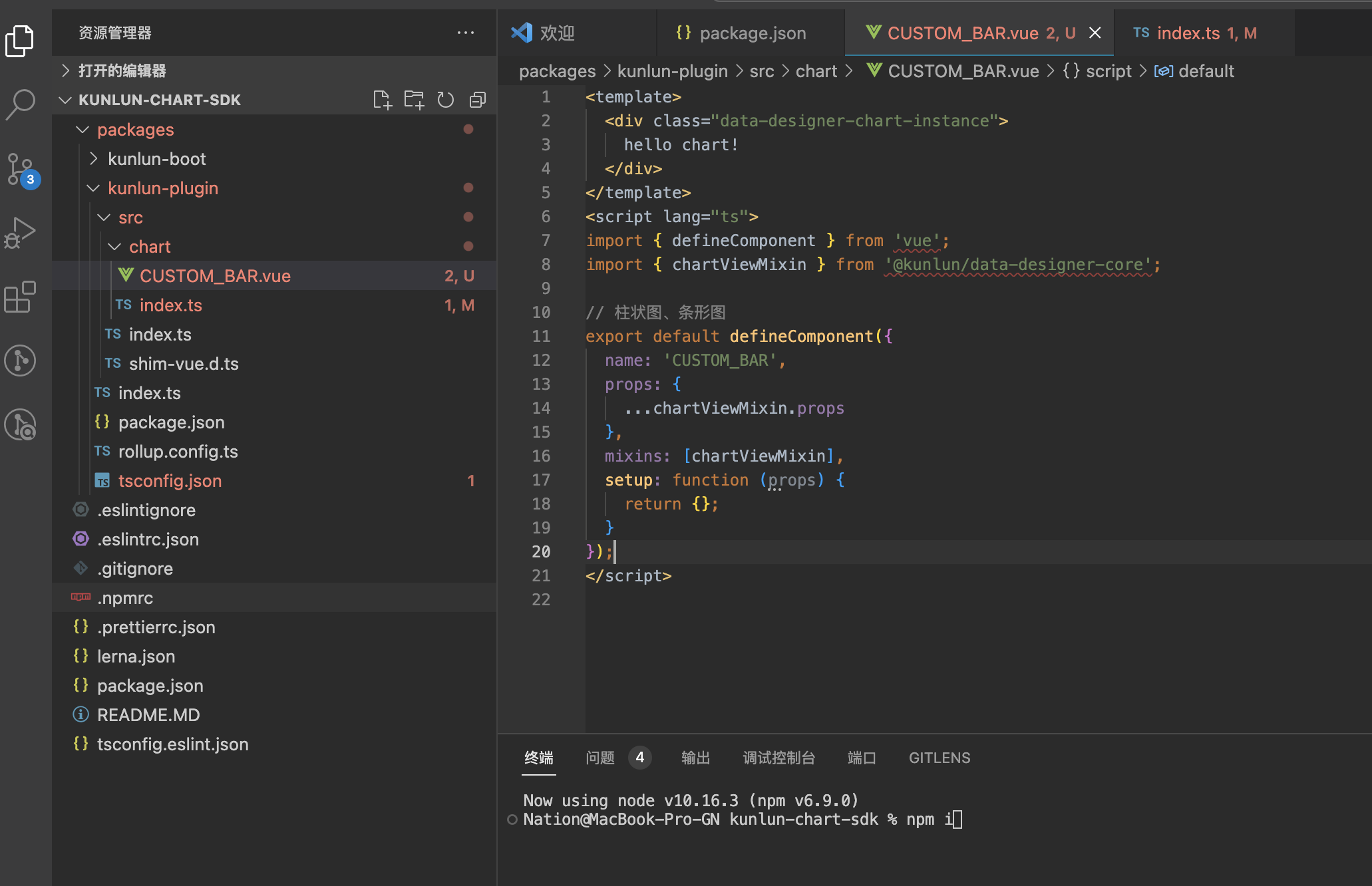
- The custom chart Vue component is located at
packages/kunlun-plugin/src/chart/CUSTOM_BAR.vue, where you can modify the custom display and logical processing - After completing the custom code, run
npm run buildin the root directory to package the code. The packaged JS and CSS files will be found inpackages/kunlun-plugin/dist(CSS file will not be generated if there is no CSS in the template, which can be ignored)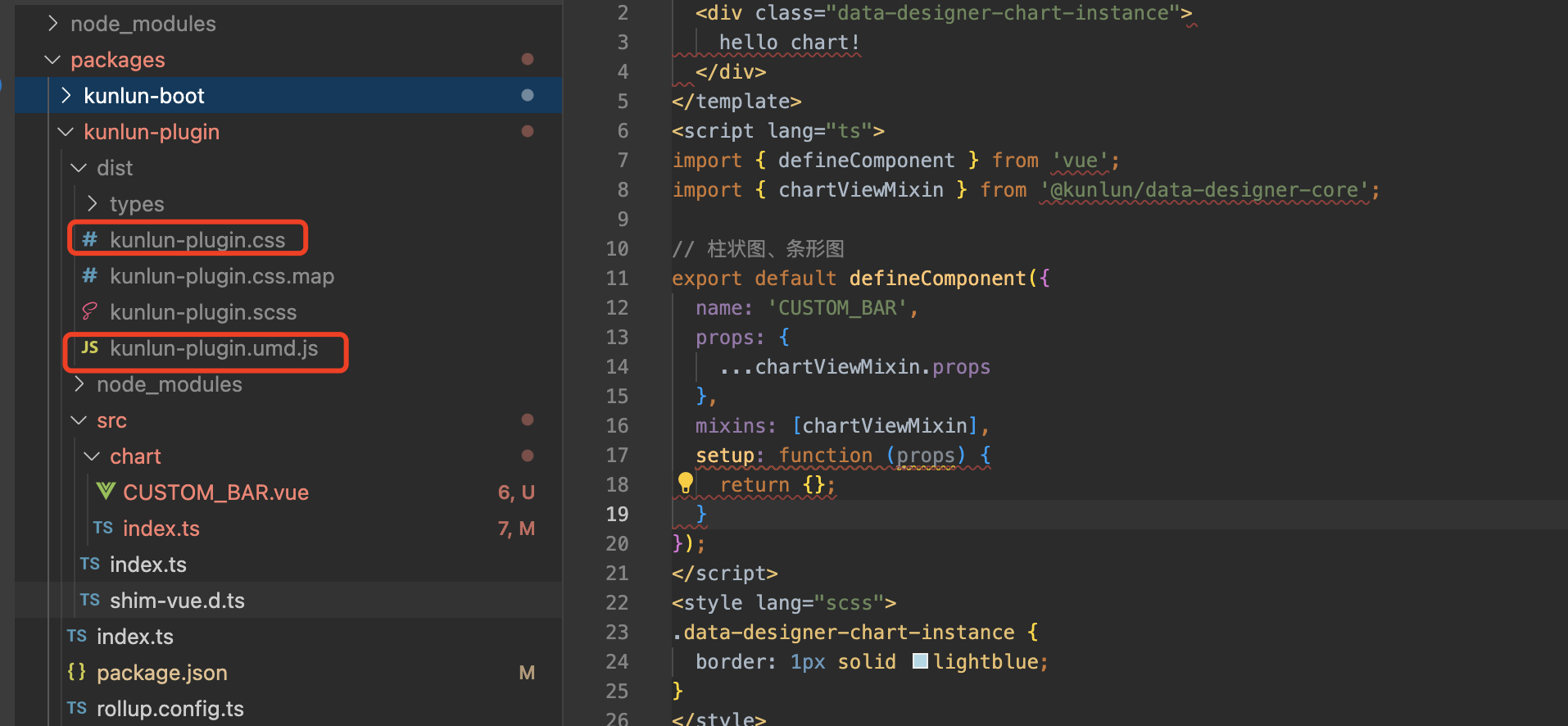
- Return to the management page of custom chart templates, locate the corresponding data row, click the "Low-Code & No-Code Integration" button again. Upload the generated
kunlun-plugin.umd.jsandkunlun-plugin.cssfiles in the pop-up window, then click "Confirm" at the bottom to save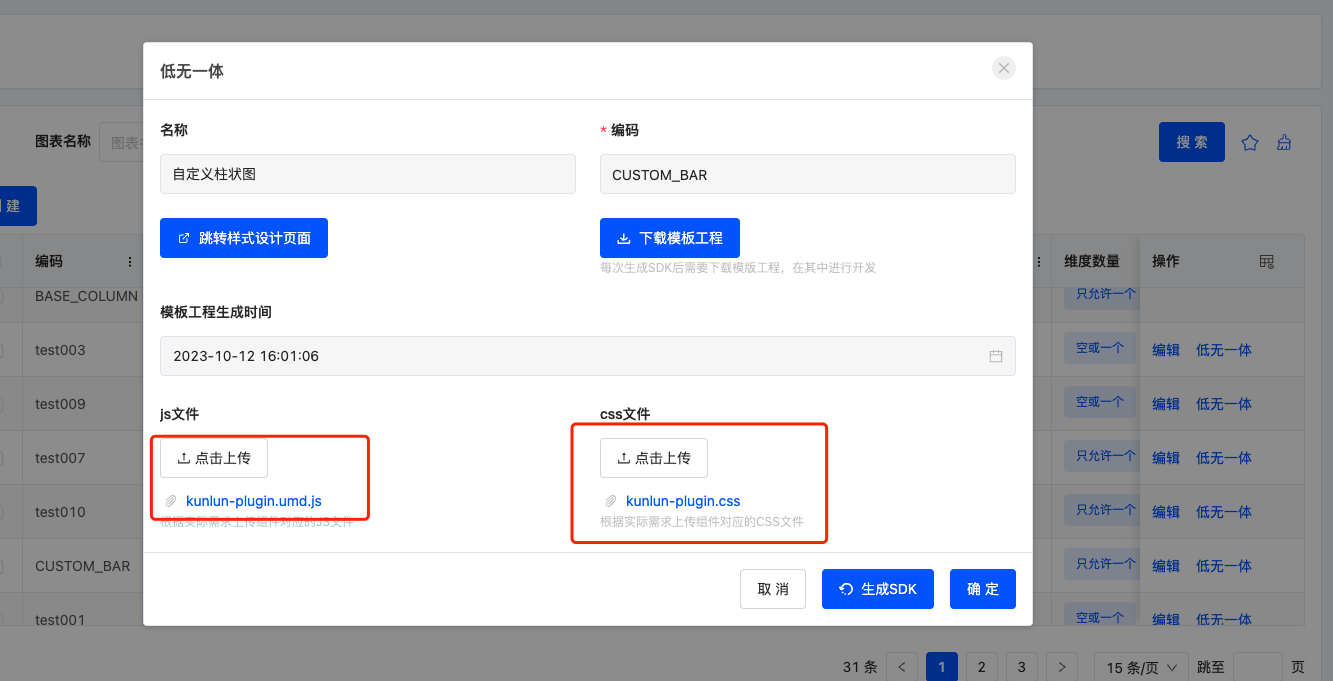
- Enter the chart editing page, and in the chart category selection, you can see the newly added subcategory "Custom Bar Chart" under the bar chart category. Click to switch
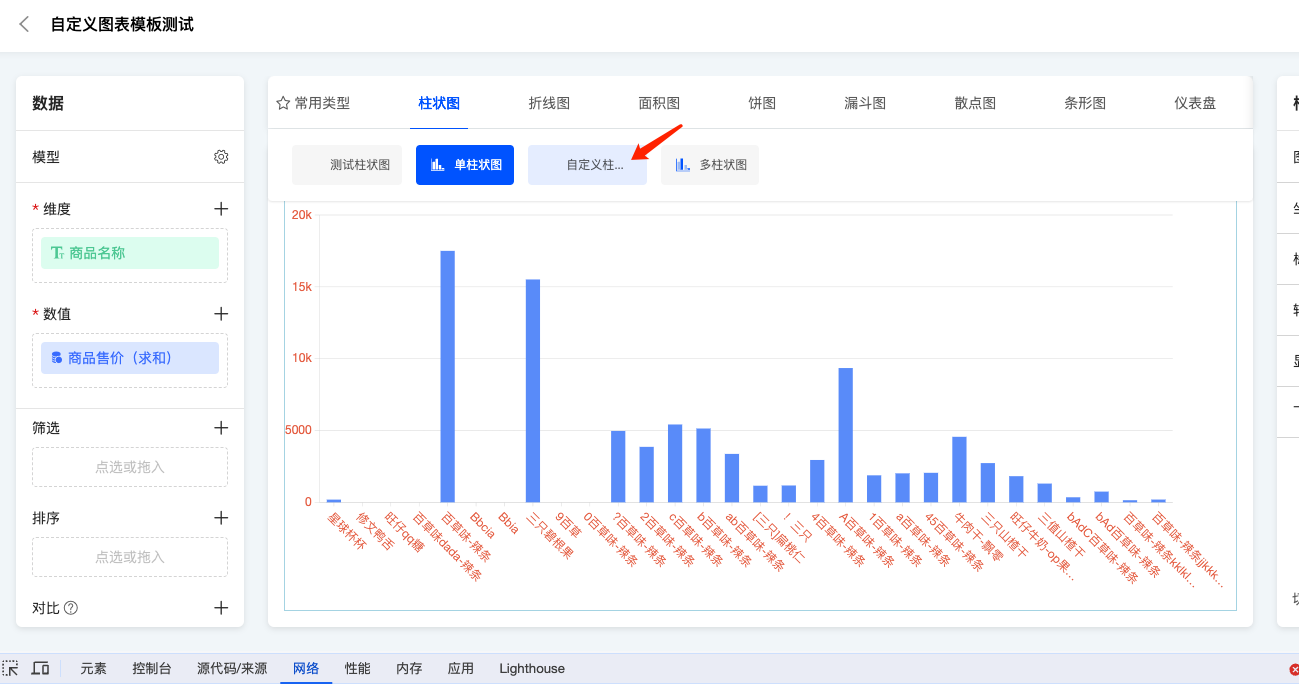
- After switching, the chart will change from the default bar chart to the custom chart with a blue border and the text
hello chartinside.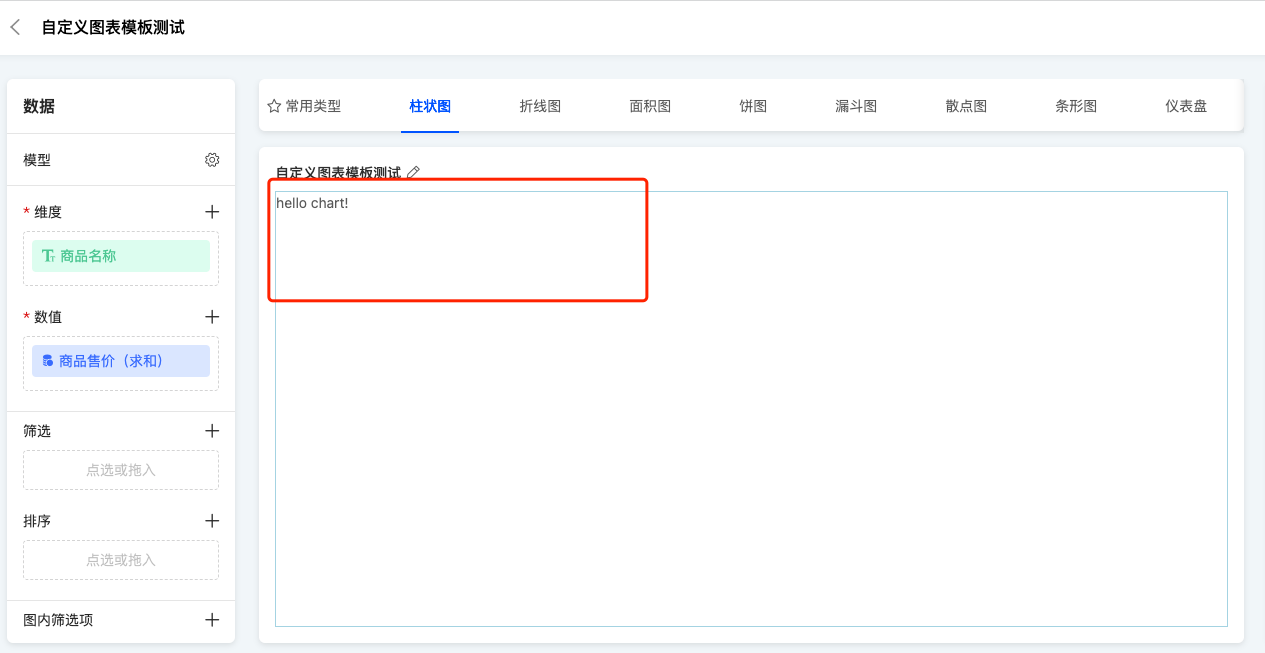
II. Example Custom Chart Component
This example implements a bar chart using the echarts library, while the framework's built-in bar chart uses the G2 library. demo-echarts-bar.vue
<template>
<div class="data-designer-chart-instance demo-echarts-bar" ref="designerChartViewRef">
<div class="data-designer-chart-container" ref="designerChartViewInnerRef"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, onMounted, ref, watch } from 'vue';
import DataSet from '@antv/data-set';
import * as echarts from 'echarts/core';
import { ECharts, EChartsCoreOption } from 'echarts/core';
import { GridComponent } from 'echarts/components';
import { BarChart, BarSeriesOption } from 'echarts/charts';
import { CanvasRenderer } from 'echarts/renderers';
import { deepClone } from '@oinone/kunlun-dependencies';
import {
filterDimensionScaleColumns,
isSameObj,
ChartTypeEnum,
IChartData,
IChartDataResult,
chartViewMixin,
isNeedRerenderChart,
isShowChatView,
watchEchartsSize,
ChartRenderEngine
} from '@oinone/kunlun-data-designer-core';
echarts.use([GridComponent, BarChart, CanvasRenderer]);
export default defineComponent({
props: {
...chartViewMixin.props
},
data() {
return {
engine: ChartRenderEngine.ECHARTS,
chartType: [ChartTypeEnum.MAP_CHINA]
};
},
mixins: [chartViewMixin],
setup(props, { emit }) {
const chart = ref<ECharts>();
const designerChartViewRef = ref<HTMLElement>(null as any);
const designerChartViewInnerRef = ref<HTMLElement>(null as any);
onMounted(() => {
initChart();
});
let option = {} as EChartsCoreOption;
function initChart() {
chart.value = echarts.init(designerChartViewInnerRef.value);
option = {
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
}
};
}
let oldChartData = {} as IChartData;
watch(
() => props.chartData,
(newVal) => {
if (!newVal || !chart.value) {
return;
}
if (!isNeedRerenderChart(newVal, oldChartData)) {
oldChartData = deepClone(newVal);
return;
}
render(chart.value!, newVal, props.chartDataResult);
oldChartData = deepClone(newVal);
},
{
immediate: true,
deep: true
}
);
let oldChartDataResult = {} as IChartDataResult;
function watchDataList(chartData: IChartData, chartDataResult: IChartDataResult) {
oldChartDataResult = deepClone(props.chartDataResult);
if (!chart.value) {
initChart();
}
render(chart.value!, chartData, chartDataResult);
}
// 监听数据的变动自动重新渲染
watch(
() => props.chartDataResult.data,
() => {
if (isSameObj(oldChartDataResult, props.chartDataResult)) {
return;
}
if (!designerChartViewRef.value) {
onMounted(() => {
watchDataList(props.chartData, props.chartDataResult);
});
} else {
watchDataList(props.chartData, props.chartDataResult);
}
},
{ immediate: true, deep: true }
);
/**
* 自定义渲染逻辑
* @param chart echarts图表对象
* @param chartData 图表模板的定义
* @param chartDataResult chartDataResult.data存放的是后端返回的图表数据
*/
function render(chart: ECharts, chartData: IChartData, chartDataResult: IChartDataResult) {
if (!isShowChatView(chartData)) {
return;
}
if (!isSameObj(chartData, chartDataResult.chartData)) {
return;
}
const {
scales = [],
dimensions = [],
} = filterDimensionScaleColumns(chartData);
const dataList = !scales.length || !dimensions.length ? [] : ((chartDataResult.data! || []) as any[]);
dataList.forEach((a) => {
if (dimensions.length && !a.name) {
a.name = a[dimensions[0].chartField.displayName];
}
if (scales.length && !a.value) {
a.value = a[scales[0].chartField.displayName] || null;
}
});
const dv = new DataSet.DataView().source(dataList);
option.xAxis = {
type: 'category',
data: dv.rows?.map((a) => a?.name)
};
option.series = [
{
type: 'bar',
data: dv.rows?.map((a) => a?.value)
} as BarSeriesOption
];
chart.setOption(option);
}
// 监听图表容器大小
watchEchartsSize(props, chart!);
return { designerChartViewRef, designerChartViewInnerRef, chart };
}
});
</script>(Ⅰ) Registering the Template
import { ChartRenderEngine, ChartRenderType, registerChartComponent } from '@oinone/kunlun-data-designer-core';
import component from './demo-echarts-bar.vue';
registerChartComponent({
engine: ChartRenderEngine.ECHARTS,
render: ChartRenderType.CANVAS,
chartTemplateCode: 'test002'
},
{
component
} as any
);(Ⅲ) Effect Display