Workflow
I. Overview
This document introduces the Oinone workflow-related APIs, aiming to enhance the flexibility and configurability of workflows at runtime.
II. Dependency Setup
The workflow runtime requires dependencies on related modules.
(Ⅰ) pom.xml Dependency Description
Add relevant dependency packages to the API project
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.workflow</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-workflow-api</artifactId>
</dependency>Start the project and add the relevant dependency packages
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.workflow</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-workflow-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.core</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-sql-record-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.core</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-trigger-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.core</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-trigger-bridge-tbschedule</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.framework</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-connectors-event-rocketmq</artifactId>
</dependency>Process overview and metrics dependent
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.workflow</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-workflow-datavi-core</artifactId>
</dependency>(Ⅱ) application.yml Configuration Description
spring:
rocket-mq:
# Do not configure when enabled is false
namesrv-addr: 192.168.6.2:19876
...
pamirs:
...
record:
sql:
# Modify to your own path
store: /opt/pamirs/logs
...
boot:
init: true
sync: true
modules:
...
- sql_record
- trigger
- workflow
...
sharding:
define:
data-sources:
ds:
pamirs
models:
"[trigger.PamirsSchedule]":
tables: 0..13
event:
enabled: true
schedule:
enabled: true
# ownSign differentiates different applications
ownSign: demo
trigger:
auto-trigger: trueProcess Overview Configuration description
pamirs:
workflow:
dashboard:
cache-time: 10 # Process overview Cache refresh time in minutes, 10 minutes by default
page-size: 10 # The 4 charts of the process running analysis show the number, and the first 10 data are queried by default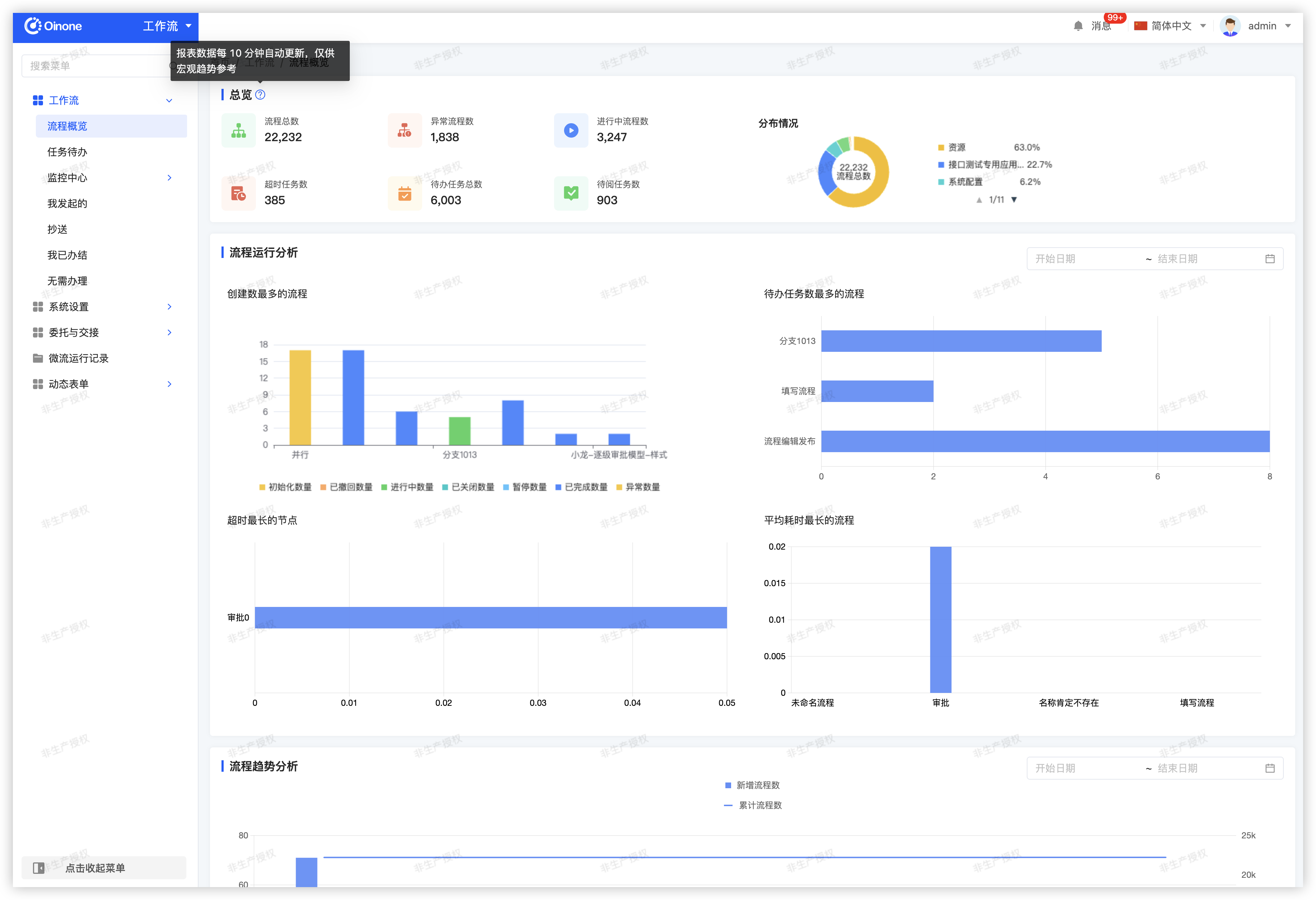
III. Workflow API Introduction
Note
The following API descriptions all involve models triggering workflows, where the model is the workflow triggering business model.
(Ⅰ) Manual Workflow Triggering
Manually trigger workflows for scenarios that are not automatically triggered.
1. Implement Manual Triggering
/**
* Manual triggering
*
* Replace <TriggerModel> in the code with your own process triggering business model
*
* @param workflowD WorkflowD workflow definition
* @param modelData Business data for user-triggered workflow
* @return Boolean status
*/
public Boolean startWorkflow(WorkflowD workflowD, IdModel modelData) {
WorkflowDefinition workflowDefinition = new WorkflowDefinition().queryOneByWrapper(
Pops.<WorkflowDefinition>lambdaQuery()
.from(WorkflowDefinition.MODEL_MODEL)
.eq(WorkflowD::getModel, <TriggerModel>.MODEL_MODEL)
.eq(WorkflowDefinition::getWorkflowCode, workflowD.getCode())
.eq(WorkflowDefinition::getActive, 1)
);
if (null == workflowDefinition) {
// No running instance of the process
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
String model = Models.api().getModel(modelData);
// Workflow context
WorkflowDataContext wdc = new WorkflowDataContext();
wdc.setDataType(WorkflowVariationTypeEnum.ADD);
wdc.setModel(model);
wdc.setWorkflowDefinitionDefinition(workflowDefinition.parseContent());
wdc.setWorkflowDefinition(workflowDefinition);
wdc.setWorkflowDefinitionId(workflowDefinition.getId());
// Data snapshot
IdModel copyData = KryoUtils.get().copy(modelData);
// Manually triggered action flow, set the operator as the current user as the process initiator
copyData.setCreateUid(PamirsSession.getUserId());
copyData.setWriteUid(PamirsSession.getUserId());
String jsonData = JsonUtils.toJSONString(copyData.get_d());
// Trigger workflow - onCreateManual for creation, onUpdateManual for update
Fun.run(WorkflowModelTriggerFunction.FUN_NAMESPACE, "onCreateManual", wdc, "0", jsonData);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}2. Business Invocation for Manual Triggering
Obtain the workflow definition based on business relevance in the code. The example below finds it by workflow code.
@Action(displayName = "Trigger Workflow")
public <TriggerModel> triggerWorkflow(<TriggerModel> data) {
// Example: Find workflow metadata by workflow code
WorkflowD workflowD = new WorkflowD();
workflowD.setCode("WF0000000000003000");
// Invoke the manual trigger workflow implementation in the above context
startWorkflow(workflowD, data);
return data;
}(Ⅱ) Customize Process Participants
Customize workflow approvers through configuration functions to achieve flexible runtime configuration of process participants (including transfer, cc, add signature, fill, and notifier).
/*
* Customize process participants
* @param nodePersonList Current node participants
* @param nodeModel Current node and model-related metadata
* @param workflowContext Process context
*
* @return Customized process participant list
*/
@Function(openLevel = {FunctionOpenEnum.API})
@Function.Advanced(
type = FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY,
displayName = "Customize Process Participants",
// Must set the function group to CUSTOM_DESIGNER
category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER
)
public List<NodePerson> customPerson(List<NodePerson> nodePersonList, NodeModel nodeModel, WorkflowContext workflowContext) {
List<NodePerson> newNodePersonList = new ArrayList<>();
String nodeModelId = nodeModel.getId();
Object nodeData = workflowContext.get(nodeModelId);
// Deserialize business data
BuissModel inputBuissModel = JsonUtils.parseObject(JsonUtils.toJSONString(nodeData), BUISSMODEL_TR);
// Reverse query business data
BuissModel buissModel = new BuissModel().setId(inputBuissModel.getId()).queryById();
buissModel.fieldQuery(BuissModel::getZmEmployee);
BxEmployee zmEmployee = buissModel.getZmEmployee();
if (zmEmployee == null) {
log.error("Reimbursement form ID:{}, Name:{}, Approver is empty", buissModel.getId(), buissModel.getName());
return newNodePersonList;
}
NodePersonUser personUser = new NodePersonUser();
List<NodePersonUser> nodePersonUsers = new ArrayList<>();
NodePerson person = new NodePerson();
person.setId(zmEmployee.getBindingUserId() + "");
person.setType(NodePersonTypeEnum.USER);
personUser.setUserId(zmEmployee.getBindingUserId());
nodePersonUsers.add(personUser);
person.setNodePersonUsers(nodePersonUsers);
newNodePersonList.add(person);
return newNodePersonList;
}(Ⅲ) Custom Pre-Approval Execution Function
Use Case: When custom logic processing is required after the approval node task is initialized but before the task starts, this extension is used.
Execution Time: This extension is executed after the approval to-do task is initialized and before the approval is executed.
/**
* After the approval node is initialized, execute the pre-function
* @param approvalNode Approval node data
* @param context Workflow context
* @param taskInstance Workflow to-do instance
*/
@Function(name = "approvalCustomStartFun",openLevel = FunctionOpenEnum.API)
@Function.Advanced(type= FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY,displayName = "Pre-Approval Execution Processing",category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER )
public void approvalCustomStartFun(ApprovalNode approvalNode, WorkflowContext context, WorkflowTaskInstance taskInstance) {
// TODO: 2024/2/23 You can process business logic according to the result
}(Ⅳ) Custom Pre-Fill Execution Function
Use Case: When custom logic processing is required after the fill node task is initialized but before the task starts, this extension is used.
Execution Time: This extension is executed after the fill to-do task is initialized and before the fill result is executed.
/**
* Pre-fill execution processing
*
* @param taskInstance Workflow to-do instance
* @param writeNode Fill node data
* @param context Workflow context
*/
@Function(name = "writeCustomStartFun", openLevel = FunctionOpenEnum.API)
@Function.Advanced(type = FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY, displayName = "Pre-Fill Execution Processing", category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER)
public void writeCustomStartFun(WorkflowTaskInstance taskInstance, WriteNode writeNode, WorkflowContext context) {
System.out.println("Pre-fill execution processing");
}(Ⅴ) Post-Todo Operation Submission Function
Use Case: When additional logic needs to be executed during the operation of approval or fill to-do tasks, such as updating database records related to the current user's operation after submission.
Execution Time: This extension is executed after saving the to-do task and before asynchronously executing the approval or fill result.
/**
* Post-transfer operation function, selected in the process designer's approval and fill node extension settings - post-fill operation submission function
*
* @param userTask User to-do record
* @return User to-do
*/
@Function(name = "transformEndFun",openLevel = FunctionOpenEnum.API)
@Function.Advanced(type= FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY,displayName = "Post-Transfer Operation Function",category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER )
public WorkflowUserTask transformEndFun(WorkflowUserTask userTask) {
// Filter by operation type
// After transfer operation
if (!WorkflowUserTaskOperateTypeEnum.APPROVE_TRANGER.equals(userTask.getOperateType())) {
return userTask;
}
// TODO: 2023/11/21 Customize supplementary business logic, userTask data is the submitted T data
// In the case of approval agreement
if (WorkflowUserTaskOperateTypeEnum.APPROVE_AGREE.equals(userTask.getOperateType())) {
// TODO
}
// In the case of approval rejection
if (WorkflowUserTaskOperateTypeEnum.APPROVE_REJUST.equals(userTask.getOperateType())) {
// TODO
}
return userTask;
}(Ⅵ) Approval Operation Data Function
Use Case: During approval or fill execution, when additional business data logic needs to be changed (e.g., modifying associated data status after approval), this extension is used.
Execution Time: This extension is executed after the business data is saved following approval agreement or fill submission during approval or fill execution.
/**
* Post-approval data processing
* @param approvalNode Approval node
* @param context Context
* @param dataJson Submitted approval data
* @param result Approval result
*/
@Function(name = "approvalDataProcessFun",openLevel = FunctionOpenEnum.API)
@Function.Advanced(type= FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY,displayName = "Post-Approval Data Processing",category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER )
public void approvalDataProcessFun(ApprovalNode approvalNode, WorkflowContext context, String dataJson, Boolean result) {
// Approval data submission content
Map<String, Object> data = JsonUtils.parseMap(dataJson);
Long id = ParamUtils.createLong(data.get("id"));
// Process custom data based on approval result - approved
if(result != null && result){
// TODO: 2024/2/23 Process business logic according to the result
}
// Rejected
if(result != null && !result){
// TODO: 2024/2/23 Process business logic according to the result
}
}(Ⅶ) [Recall] Callback Hook
Use Case: When the process instance is recalled, this callback hook can be used to change other business data logic.
Note
The namespace of this function needs to be set to the process triggering model.
/**
* The corresponding return does not affect the process context
* @param data The input parameter is the business data at the time of triggering, as a JsonString
* @return Optional return
*/
@Function
public <ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel> recall(String data) {
// TODO: Convert data to a business object based on actual business logic
BusinessModel object = JsonUtils.parseObject(data, new TypeReference<BusinessModel>(){});
// TODO: Add custom business logic
return new <ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel>();
}(Ⅷ) [Rollback] Callback Hook
Use Case: When a rollback operation is performed on a workflow to-do, this callback hook can be used to change other business data logic.
Note
The namespace of this function needs to be set to the process triggering model.
/**
* The corresponding return does not affect the process context
* @param data The input parameter is the business data at the time of triggering, as a JsonString
* @return Optional return
*/
@Function
public <ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel> fallBack(String data) {
// TODO: Convert data to an object based on actual business logic
BusinessModel object = JsonUtils.parseObject(data, new TypeReference<BusinessModel>(){});
// TODO: Add custom business logic
return new <ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel>();
}(Ⅸ) [Reject] Callback Hook
Use case: This callback hook can be used when the process backlog is rejected and additional business data logic needs to be changed.
Note
The namespace of this function needs to be set to the process triggering model.
/**
* XXX is the triggering model when the current process triggering method is model triggering
* Callback hook
*
* @param data The input parameter is the business data at the time of triggering, as a JsonString
* @return Optional return
*/
@Function
public <ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel> reject(String data) {
// TODO: Convert data to an object based on actual business logic
BusinessModel object = JsonUtils.parseObject(data, new TypeReference<BusinessModel>(){});
// TODO: Add custom business logic
return new <ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel>();
}(X) [Retract] Callback Hook
Usage scenario: This callback hook can be used when additional business data logic needs to be modified during the retract operation of a pending workflow task.
Note
The namespace of this function needs to be set to the process trigger model.
@Function
@Function.fun(WorkflowBizCallConstants.retract)
public void retract(WorkflowUserTask workflowUserTask) {
// Get the process instance
workflowUserTask.fieldQuery(WorkflowUserTask::getInstance);
WorkflowInstance instance = workflowUserTask.getInstance();
// Get the user task instance
WorkflowUserInstance userInstance = new WorkflowUserInstance()
.setId(workflowUserTask.getWorkflowUserInstanceId())
.queryById();
// ID of the user who performed the retract
Long userId = workflowUserTask.getUserId();
// ID of the node where the retract occurred
String nodeId = workflowUserTask.getNodeId();
}(XI) Custom Approval Method
Use Case: Set the approval method at workflow runtime via code.
@Model.model(ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel.MODEL_MODEL)
@Component
public class ReplacedByProcessTriggerModelAction {
/**
* Custom approval method
* @param json Json is the business data, which can be converted using JsonUtils
* @return Return parameters:
* COUNTERSIGN_ONEAGREE_ONEREJUST (One approver's agreement or rejection is sufficient)
* COUNTERSIGN_ALLAGREE_ONEREJUST (All approvers must agree for approval, one rejection for rejection)
* COUNTERSIGN_ONEAGREE_ALLREJUST (One approver's agreement for approval, all rejections for rejection)
* SINGLE (Single person)
*/
@Function
@Function.Advanced(
category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER,
displayName = "Test Custom Approval Type"
)
public WorkflowSignTypeEnum signType(String json) {
// The incoming json is business data, which can be converted to business model data using JsonUtils to obtain business data context
// BusinessModel object = JsonUtils.parseObject(data, new TypeReference<BusinessModel>(){});
// TODO: Add custom business logic
return WorkflowSignTypeEnum.COUNTERSIGN_ONEAGREE_ONEREJUST;
}
}(XII) Custom Approval Node Name
Use Case: Dynamically set the workflow approval node name via code.
@Model.model(ReplacedByProcessTriggerModel.MODEL_MODEL)
@Component
public class ReplacedByProcessTriggerModelAction {
/**
* Custom approval node name
* @return String
*/
@Function
@Function.Advanced(
category = FunctionCategoryEnum.CUSTOM_DESIGNER,
displayName = "Test Custom Approval Name"
)
public String customApprovalName() {
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
}(XIII) Custom-defined Workflow Designer Approver Company List
When opening the pop-up window, the first company returned will be selected by default. ALL_COMPANY indicates all companies.
@Order(10)
@Component
@SPI.Service
public class CustomWorkflowCompanyQueryApi implements WorkflowCompanyQueryApi {
@Override
public Pagination<PamirsCompany> queryPage(Pagination<PamirsCompany> page, IWrapper<PamirsCompany> queryWrapper) {
// Example: Only display all companies
Pagination<PamirsCompany> pageResult = new Pagination<>();
pageResult.setContent(Lists.newArrayList(ALL_COMPANY));
pageResult.setTotalPages(1);
return pageResult;
}
//@Override
//public Pagination<PamirsCompany> queryPage(Pagination<PamirsCompany> page, IWrapper<PamirsCompany> queryWrapper) {
// // Example: Do not display all companies
// return new PamirsCompany().queryPage(page, queryWrapper);
//}
}