R&D Paradigm:R&D Process
I. Frontend-Backend Separation Architecture
In software development, the frontend-backend separation architecture is an efficient model that clearly separates the user interface (frontend) from business logic and data processing (backend), enabling independent development, testing, and deployment.
The frontend is responsible for user interaction, presentation, and input reception, composed of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Complex projects often use frameworks like React or Vue.js to improve development efficiency. The backend focuses on business logic and data storage, implemented using languages and frameworks such as Python (with Django), Java (e.g., Spring Boot), or Node.js (with Express). The backend interacts with databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL and provides data to the frontend via APIs, typically following RESTful or GraphQL specifications.
This architecture offers significant advantages. Development teams can divide tasks based on expertise, improving efficiency and code quality. Frontend and backend can be deployed and updated independently, reducing maintenance costs and risks, and facilitating cross-platform development. E-commerce platforms are typical applications, where the frontend displays products and shopping carts, and the backend handles inventory and order logic.
In summary, the frontend-backend separation architecture, with its clear responsibility division, efficient development, and good maintainability, has become an important model for modern software construction.
Shushi Oinone's frontend uses Vue.js, the backend adopts a Java technology stack, and APIs follow GraphQL specifications.
II. Evolution of Development Process
Tip: The Shushi Oinone framework takes the frontend-backend separation development model a step further
Frontend development work is only carried out when components fail to meet requirements or when developing specialized business components. This not only retains the benefits of the frontend-backend separation architecture but also reduces unnecessary communication between frontend and backend during business development, greatly improving efficiency.
Example: Improving Your Frontend-Backend Development Division with Oinone (Optional Recommendation)
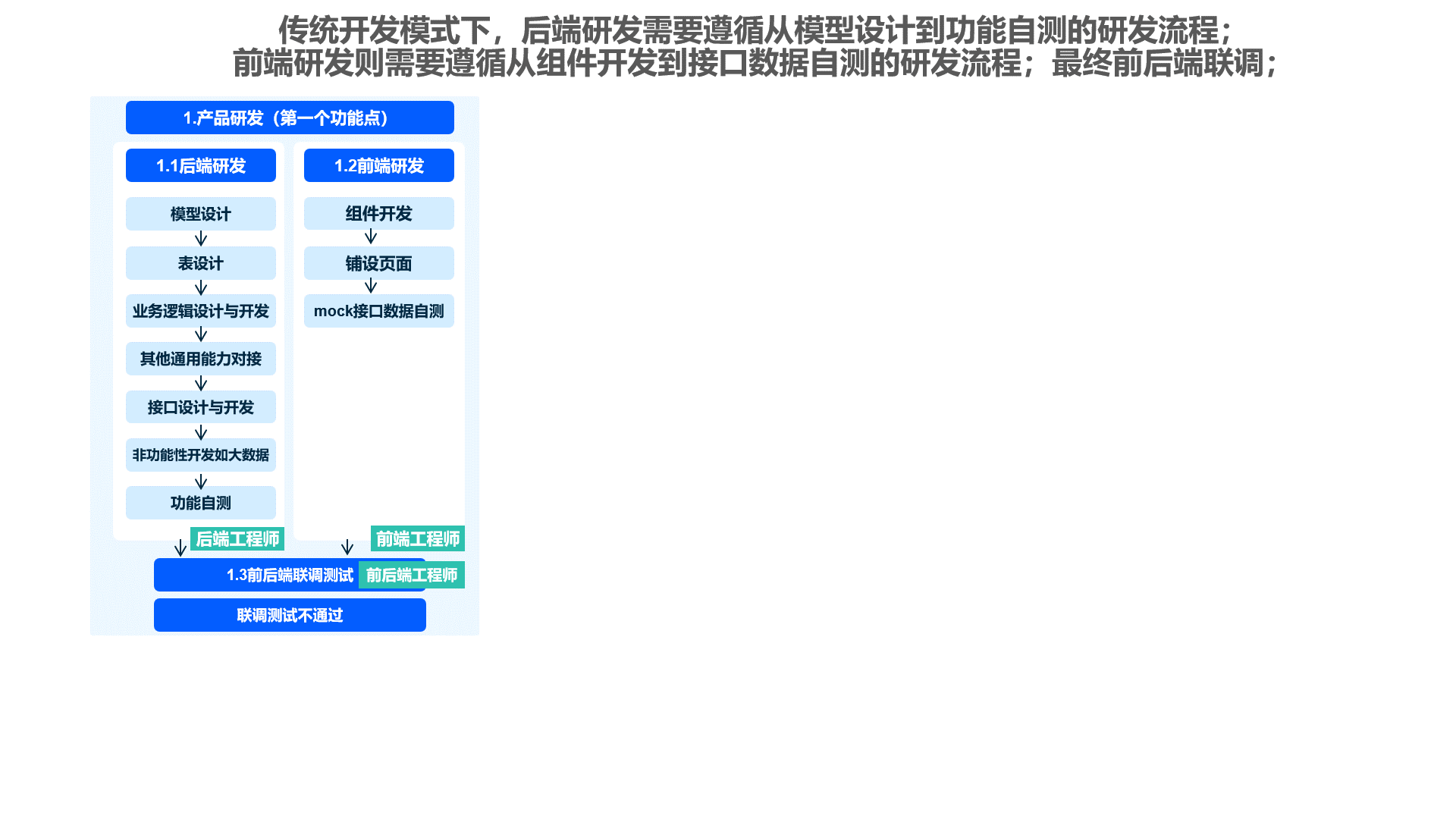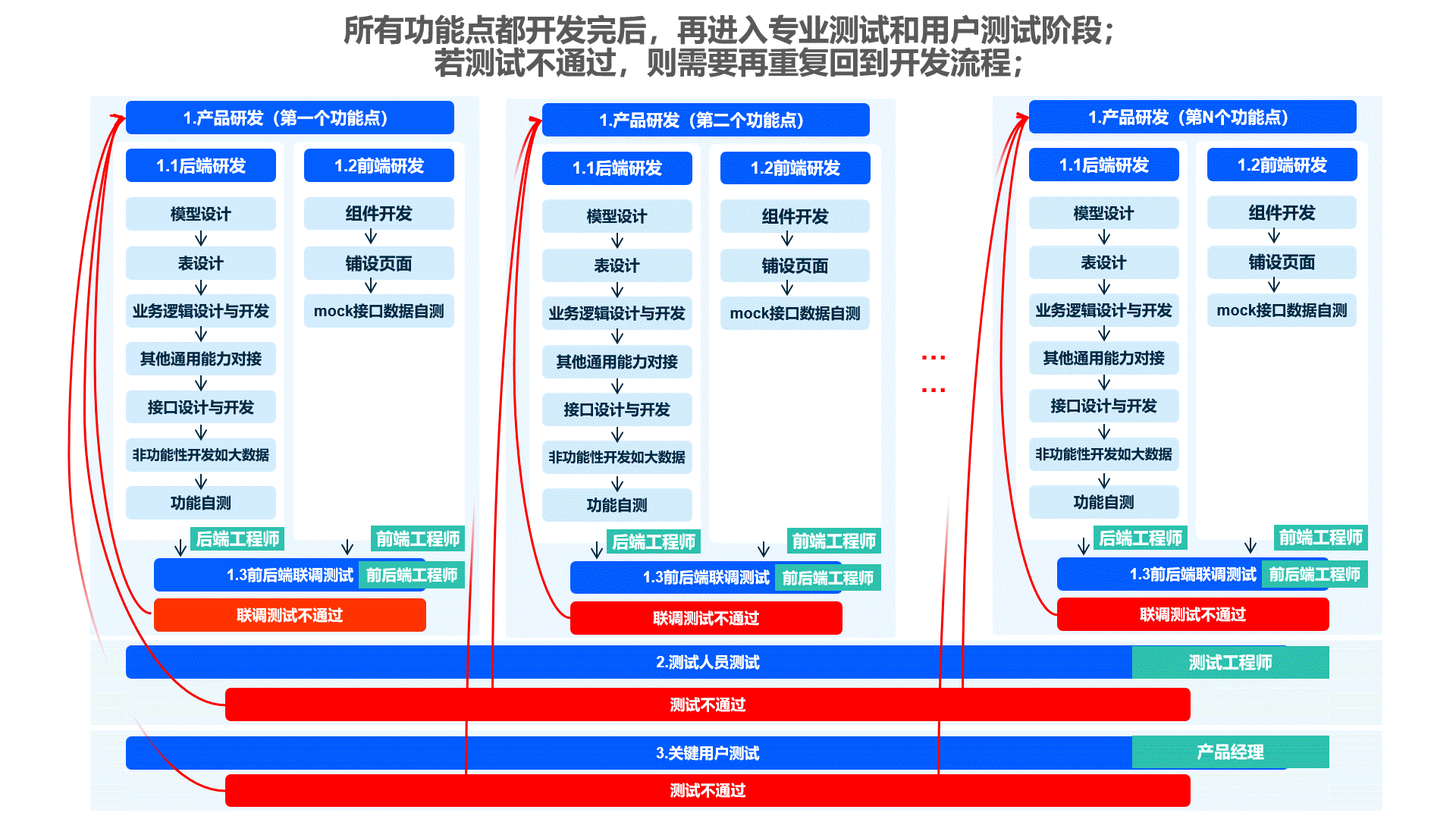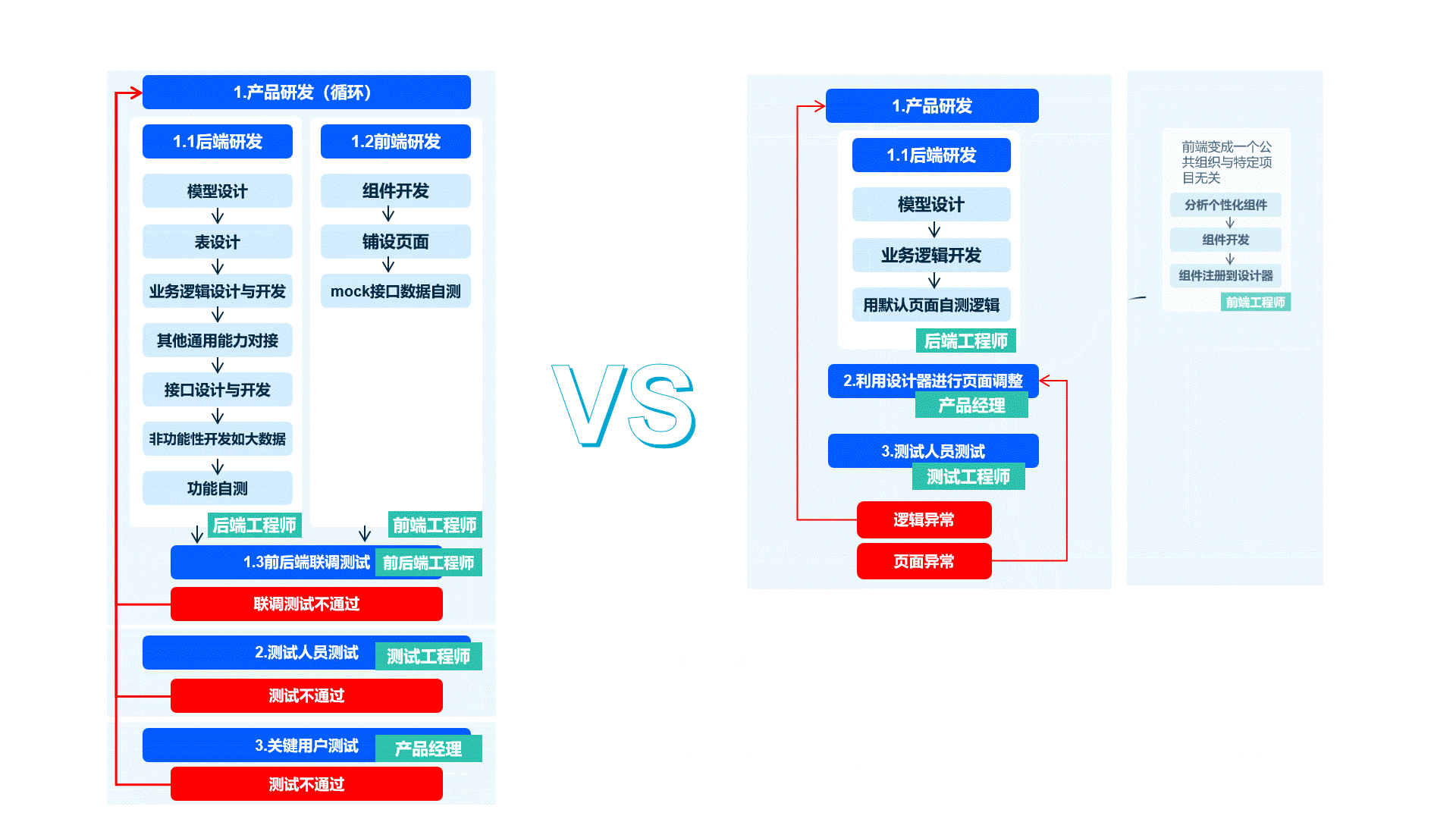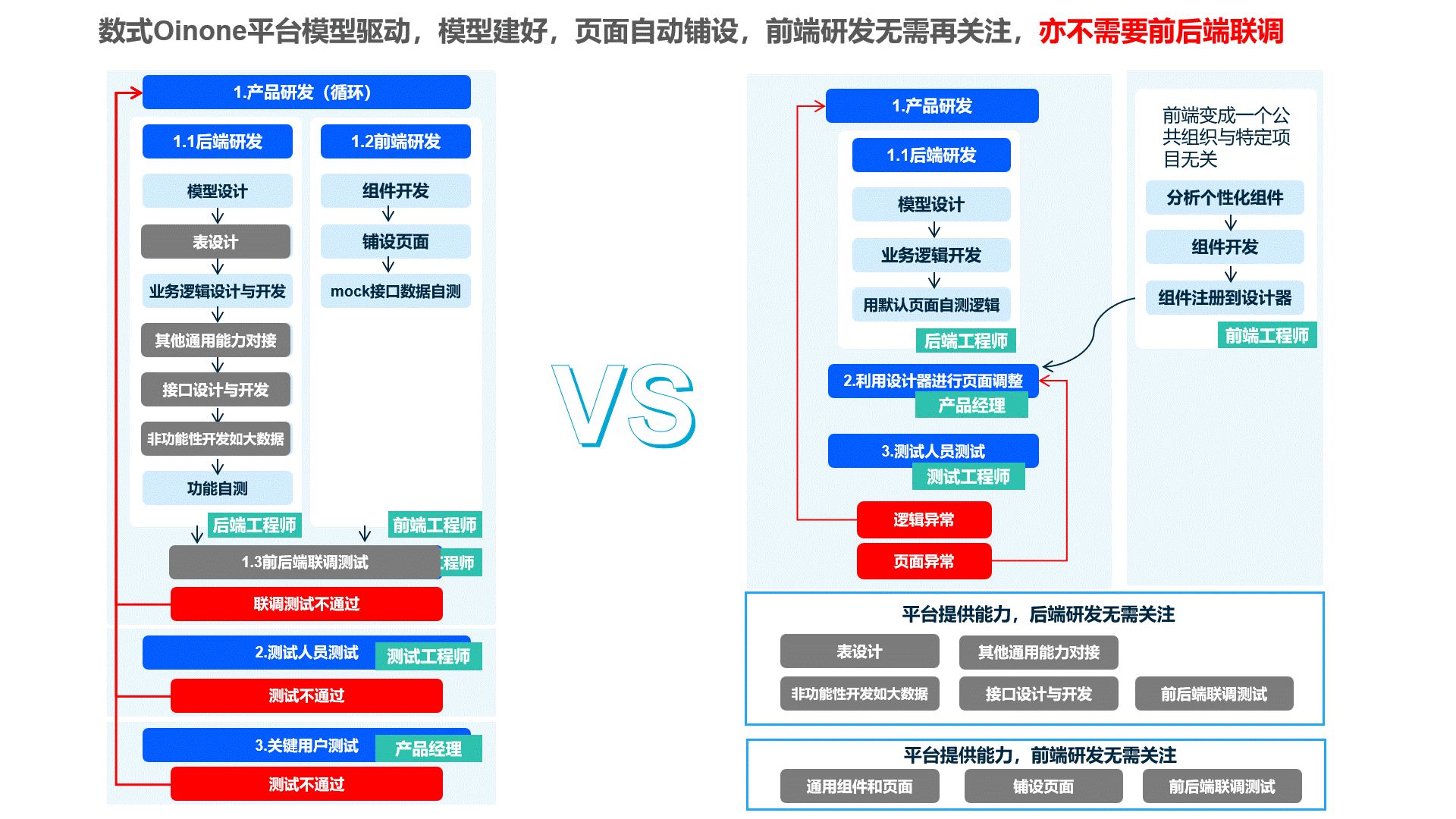
The Shushi Oinone framework optimizes the frontend-backend separation development model. The frontend only intervenes when components are insufficient or when developing specialized business components, reducing communication costs and improving overall efficiency.
- Problems with Traditional Models: Tedious processes, high communication costs, excessive repetitive work, scattered R&D focus, and quality issues at each stage affecting system delivery.
- Advantages of Oinone's New Model: Based on a low-code framework, the backend focuses on business R&D and design, and the frontend focuses on interactive component precipitation. The frontend is decoupled from specific projects, becoming a public organization.
The recommended process is as follows:

III. R&D Efficiency Comparison
(Ⅰ) Original R&D Approach

- Repetitive Code Issues: Both frontend and backend have significant repetitive coding work.
- Heavy Debugging Burden: The workload of frontend-backend debugging increases linearly with the number of pages. In case of bugs or functional adjustments, repeated debugging is inevitable.
- Basic Code Risks: The large volume of basic work code leads to frequent basic bugs, requiring continuous collaboration between R&D and testing personnel.
- Implementation Barriers for Specifications: Although coding specifications are formulated, they often remain on paper, making it difficult to implement. This results in inconsistent frontend-backend coding specifications, hindering technical precipitation and team capability improvement.
(Ⅱ) Oinone's R&D Approach

- Efficient Backend R&D: Through in-depth business analysis to design data models and add necessary operations, self-testing of business logic can be completed with default pages, without requiring frontend intervention in advance, effectively enhancing backend development independence and efficiency.
- Targeted Frontend Development: The frontend only engages in professional work when components are insufficient or when developing specialized business components. General components are precipitated to the platform for reuse across all projects, reducing repetitive frontend work and improving component versatility.
- Improved Testing Efficiency: The significant reduction in basic work code enhances testing efficiency.
- Specification Implementation and Capability Enhancement: R&D specifications are solidified through the platform. With continuous precipitation of frontend components and backend industry models, efficiency increases by 40% to 300% compared to the original approach. Intermediate R&D personnel can发挥 (play) the value of senior R&D, while senior R&D continues to precipitate industry capabilities.