Component Lifecycle
In Oinone Kunlun, the component lifecycle is fully implemented following the Vue component lifecycle provided by the Vue framework. Moreover, since Oinone Kunlun is a rendering framework based on DSL Render, its management scope extends beyond just "components." It also needs to handle various data behaviors such as data fetching, rendering, and submission. Therefore, we have extended the component lifecycle to better support the entire system's operation.
I. Vue Component Lifecycle
Before understanding the Widget component lifecycle, let's first review the Vue component lifecycle. Below is a diagram of the lifecycle of a single component instance: (Image source: Vue official documentation - Lifecycle)
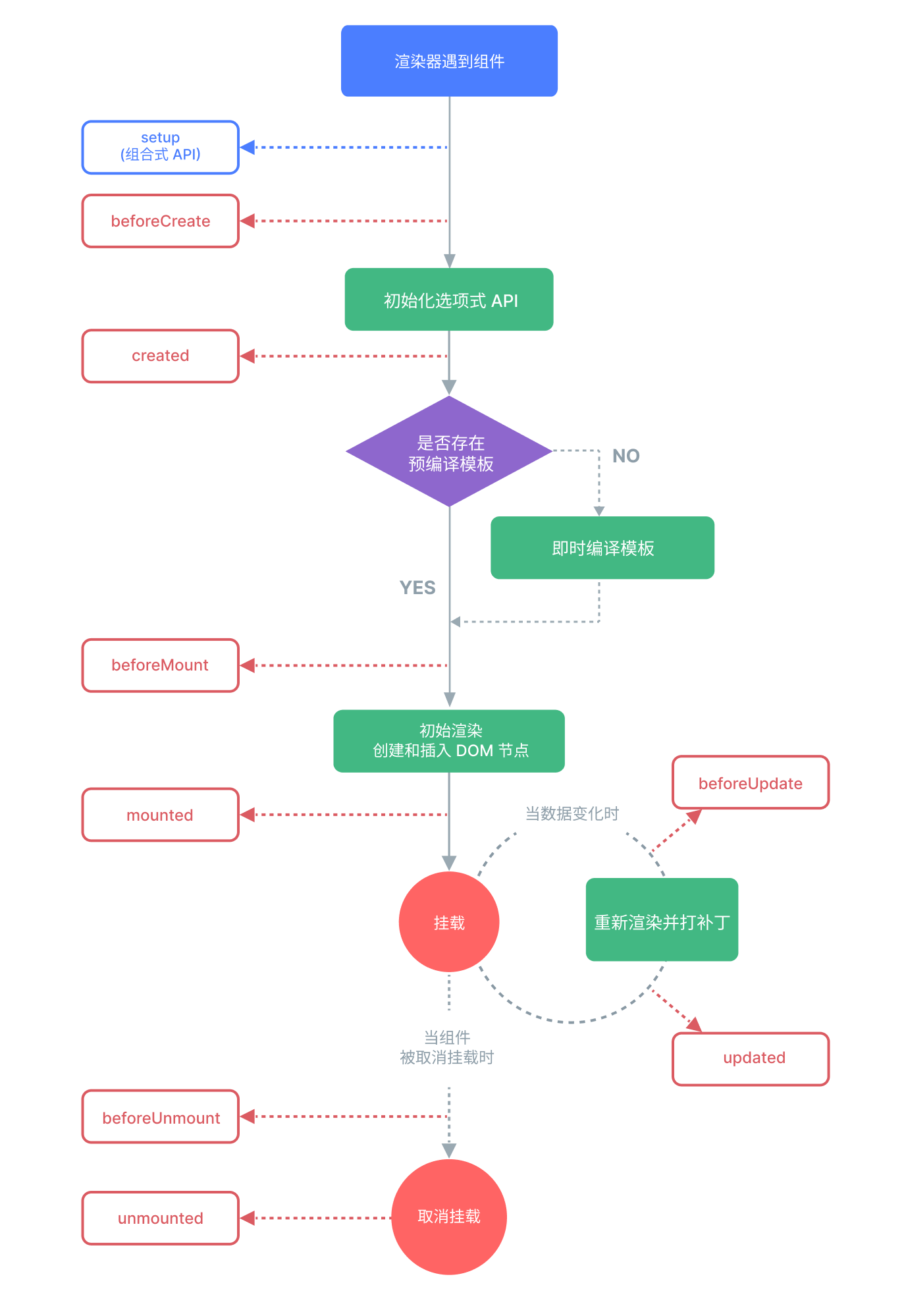
Here we only provide a brief introduction to the Vue component lifecycle for context. The definition of lifecycle hook APIs in Widget components is almost identical. Let's continue.
Tip
For more content about the Vue component lifecycle, please refer to: Vue Lifecycle
II. Widget Lifecycle
A Widget component implemented based on the Vue framework is essentially a Vue component, so its lifecycle must be completely consistent with that of a Vue component. For example:
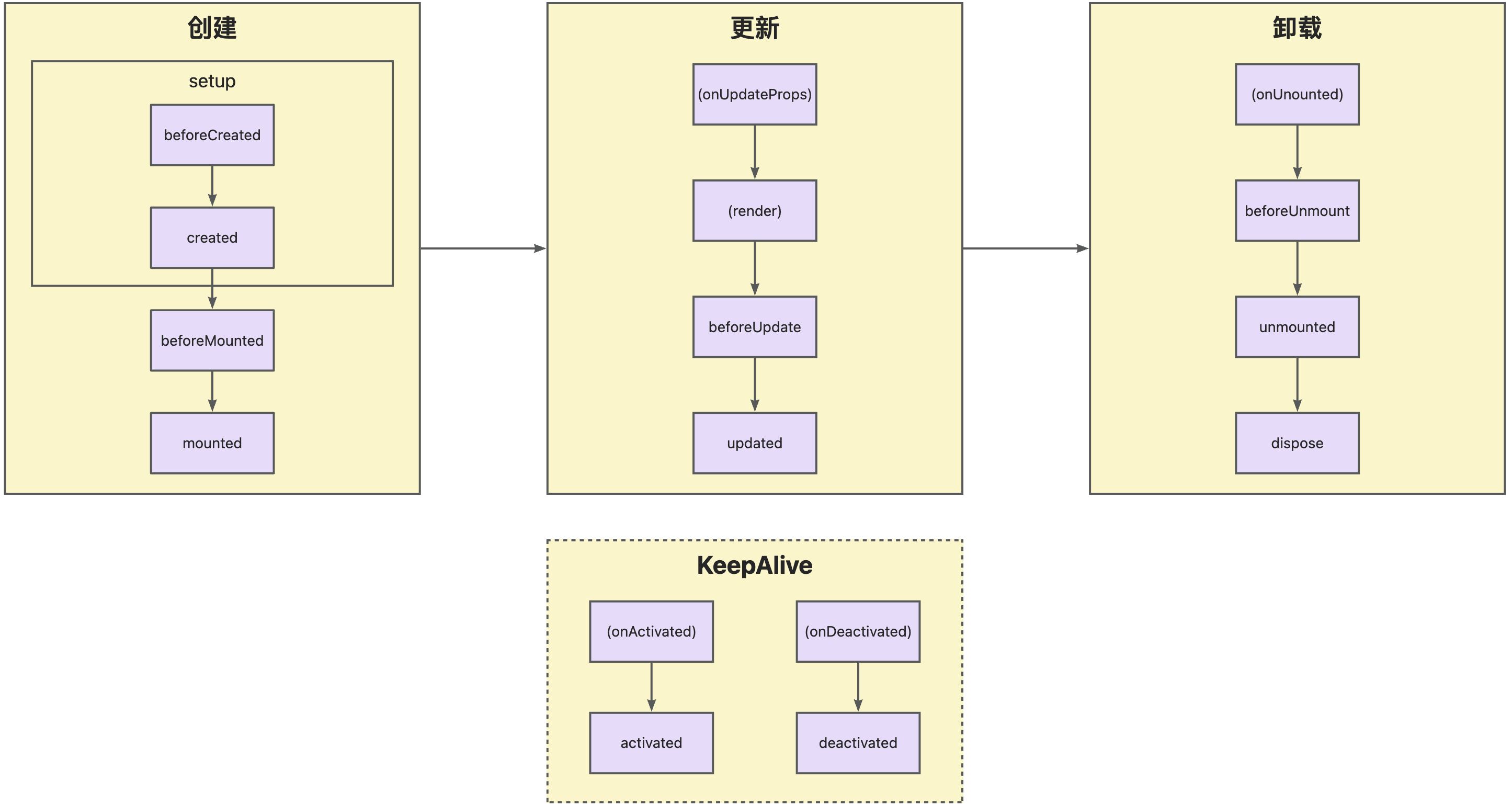
A Widget component goes through many stages: it can be instantiated, rendered, mounted, updated, detached, destroyed... This is the component lifecycle. The diagram above shows the most important events in a component's lifecycle. Generally, a component is first created, then updated (possibly multiple times), and finally destroyed.
The Widget framework provides various built-in functions, all declared in the VueWidget base class. For example, if you want to execute some code when the component is mounted, you can override the mounted function in the current component:
protected mounted() {
super.mounted();
// do something.
}Note
The Widget framework uses the object-oriented inheritance feature, so it is unavoidable that some built-in methods are exposed in custom components. To prevent custom components from causing unnecessary impacts on kernel functions, the Widget framework uses a "$$" prefix to declare framework-built methods, which should not be overridden or used by custom components unless specially necessary.
III. Reference List
(Ⅰ) Standard Lifecycle Functions
1. beforeCreated
Function Description
Called before the instance is completely created. (Merged into setup in the new Vue lifecycle)
Function Signature
protected beforeCreated(): voidUsage Example
protected beforeCreated() {
// do something.
}2. created
Function Description
Called after the instance is created. (Merged into setup in the new Vue lifecycle)
Function Signature
protected created(): voidUsage Example
protected created() {
// do something.
}3. beforeMount
Function Description
Called before mounting begins.
Function Signature
protected beforeMount(): voidUsage Example
protected beforeMount() {
// do something.
}4. mounted
Function Description
Called after the component is mounted to the DOM.
Function Signature
protected mounted(): voidUsage Example
protected mounted() {
// do something.
}5. beforeUpdate
Function Description
Called before data updates cause the component to re-render. At this time, the component's state (data, props) has been updated, but the DOM has not been re-rendered yet, allowing access to the pre-update state.
Function Signature
protected beforeUpdate(): voidUsage Example
protected beforeUpdate() {
// do something.
}6. updated
Function Description
Called after the component is re-rendered and the DOM is updated. At this time, updated DOM elements can be accessed to complete operations based on the new DOM.
Function Signature
protected updated(): voidDetails
- Avoid performing repeated rendering operations here; suitable for executing callbacks dependent on DOM updates (such as resetting scrollbar positions).
- If the component updates multiple times,
updatedis called after all child components are updated.
Usage Example
protected updated() {
// do something.
}7. beforeUnmount
Function Description
Called before the component is unmounted. At this time, the component is still mounted, allowing cleanup operations before destruction (such as canceling subscriptions, clearing timers).
Function Signature
protected beforeUnmount(): voidUsage Example
protected beforeUnmount() {
// do something.
}8. unmounted
Function Description
Called after the component is unmounted. At this time, the component's DOM has been removed, the instance is about to be destroyed, and component state or DOM can no longer be accessed.
Function Signature
protected unmounted(): voidUsage Example
protected unmounted() {
// do something.
}9. activated
Function Description
Called when the component is activated (applicable to components cached by keep-alive). For example, triggered when switching back to the component from the cache.
Function Signature
protected activated(): voidDetails
- Used to restore component state or reinitialize resources (such as timers, event listeners).
- Only takes effect when the component is wrapped by
keep-alive.
Usage Example
protected activated() {
// do something.
}10. deactivated
Function Description
Called when the component is deactivated (applicable to components cached by keep-alive). For example, triggered when switching to another component.
Function Signature
protected deactivated(): voidDetails
- Used to release resources to avoid memory leaks (such as clearing timers, unbinding events).
- The component instance is not destroyed, and the state is preserved.
Usage Example
protected deactivated() {
// do something.
}(Ⅱ) Widget Component Extended Functions
1. initialize
Function Description
Component initialization, called when the TypeScript Class is created, prior to the setup lifecycle.
Function Signature
protected initialize(props: VueProps): thisDetails
- Used for DSL editing
- Used for binding Widget components to corresponding Vue components
- Used for obtaining slot parameters (
slotContext)
Usage Example
protected initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
// do something.
return this;
}2. setComponent
Function Description
Binds the Widget component to the corresponding Vue component, can only be used in initialize.
Function Signature
public setComponent(component: WidgetComponent): voidUsage Example
protected initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(RedInput);
return this;
}3. dispose
Function Description
Component destruction, used for scenarios where manually created Widget components need to be manually destroyed.
Function Signature
public dispose(): voidUsage Example
this.formWidget.dispose();