Development Aid:Configuration Issues and Troubleshooting Paths for O2M, M2O, and M2M Relationship Fields
Ⅰ. M2O Relationship Field Configuration
@Field(displayName = "Teacher Associated Student")
@Field.many2one
@Field.Relation(relationFields = {"studentName"}, referenceFields = {"name"})
private Student students;(Ⅰ) Common Issues
1. Many-to-One Relationship Field Association:
In a many-to-one relationship scenario, studentName is a field in the current model, while name belongs to the Student model. This many-to-one relationship is established through these two fields.
2. Association Relationship Saving Mechanism:
During the saving of this association relationship, the system transfers the value of the name field in the Student model to the studentName field of the current model and stores it in the current model (the many side).
3. Characteristics of the studentName Field:
The studentName field must be set as a stored field because when querying data for the current model (the many side), this field serves as the query criterion.
4. Field Definition Rules:
The name field must be defined in the relationship model, i.e., the Student model (the one side). The studentName field may or may not be defined in the current model. If the studentName field is not yet defined in the current model, the system will automatically create it in the current model.
5. Startup Error Handling:
If an error occurs during startup, make targeted modifications based on the specific error content.
6. Analysis of Saving Errors:
When a "Duplicate entry '******' for key 'PRIMARY'" error occurs during saving, the root cause is that studentName is set as a unique key. When the same name value from the Student model is assigned to the studentName field of the current model, it triggers a unique key conflict. This situation may also occur in other similar relationship operations.
Ⅱ. O2M Relationship Field Configuration
@Field(displayName = "Teacher Associated Pet")
@Field.one2many
@Field.Relation(relationFields = {"id"}, referenceFields = {"teacherId"})
private List<PetShop> studentsCode;Analysis:
- In this one-to-many relationship,
idis a field defined in the current model, andteacherIdis a field in thePetShopmodel. This one-to-many relationship is established through these two fields. - When saving this association relationship, the system transfers the value of
idtoteacherIdand saves it in thePetShopmodel (the many-side model). - Among them,
idmust be defined in the current model (the one-side model). TheteacherIdmay or may not be defined in thePetShopmodel. If theteacherIdfield is not defined in thePetShopmodel, the system will automatically create this association field in thePetShopmodel.
Common Issues:
- Startup error: Make corresponding modifications based on the error content.
- Saving error: Please save the associated relationship model first. If
idis a custom field associated withPetShop, theidmust be assigned a value when saving the association relationship; otherwise, an error will occur.
Ⅲ. M2M Relationship Field Configuration
(Ⅰ) Configuration Example 1
@Field.many2many(through = OrderRelLogistics.MODEL_MODEL, relationFields = {"parentOrderId"}, referenceFields = {"logisticsBillId"})
@Field.Relation(relationFields = {"id"}, referenceFields = {"id"})
@Field(displayName = "Logistics Bill")
private List<LogisticsBill> logisticsBillList;Analysis:
- In this many-to-many relationship scenario, "id (left)" is a field set in the current model, and "id (right)" is a field of the
PetShopmodel.OrderRelLogistics.MODEL_MODELserves as the intermediate table, which maintains the relationship fields of both sides when the association relationship is saved. Specifically, the value of "id (left)" is written to theparentOrderIdfield of the intermediate table, and the value of "id (right)" is written to thelogisticsBillIdfield of the intermediate table.
Common Issues:
- Saving error: Please save the associated relationship model first. If "id (left)" is a custom field in the current model, the custom value needs to be assigned when saving the association relationship to correctly save the association.
(Ⅱ) Configuration Example 2:
- Add
TalentTypeEnum
@Dict(dictionary = TalentTypeEnum.DICTIONARY,displayName = "Talent Type")
public class TalentTypeEnum extends BaseEnum<TalentTypeEnum,Integer> {
public static final String DICTIONARY ="top.TalentTypeEnum";
public final static TalentTypeEnum DOG =create("DOG",1,"Dog Talent","Dog Talent");
public final static TalentTypeEnum CAT =create("CAT",2,"Cat Talent","Cat Talent");
}- Intermediate Table Definition
@Model.model(PetItemRelPetTalent.MODEL_MODEL)
@Model(displayName = "Intermediate Table", summary = "Intermediate Table")
public class PetItemRelPetTalent extends BaseRelation {
public static final String MODEL_MODEL = "top.PetItemRelPetTalent";
@Field.String
@Field(displayName = "Shop ID")
private String petItemId;
@Field.String
@Field(displayName = "Pet ID")
private String petTalentId;
@Field.String
@Field(displayName = "Pet Type")
private TalentTypeEnum talentType;
}- Relationship Field Definition (In the association relationship, use "##" to enclose the defined constant, here defining the constant "test")
@Field(displayName = "Recommended Talent")
@Field.many2many(
through = PetItemRelPetTalent.MODEL_MODEL,
relationFields = {"petItemId"},
referenceFields = {"petTalentId","talentType"}
)
@Field.Relation(relationFields = {"id"}, referenceFields = {"id", "#2#"})
private List<PetTalent> petTalents;Analysis:
- In this many-to-many relationship, the query first retrieves the fields of the current model to obtain the id (left) of the current model. Then, it queries the intermediate table based on the condition
petItem_id = id (left), from which multiplecategoryIdandtalentTypecan be obtained. Finally, it queries the relationship tablePetTalentbased on the condition(id (right), talentType) IN (categoryId, talentType). - Note: The
talentTypefield must be defined in the relationship tablePetTalentand must be consistent with thetalentTypefield defined in the intermediate table. 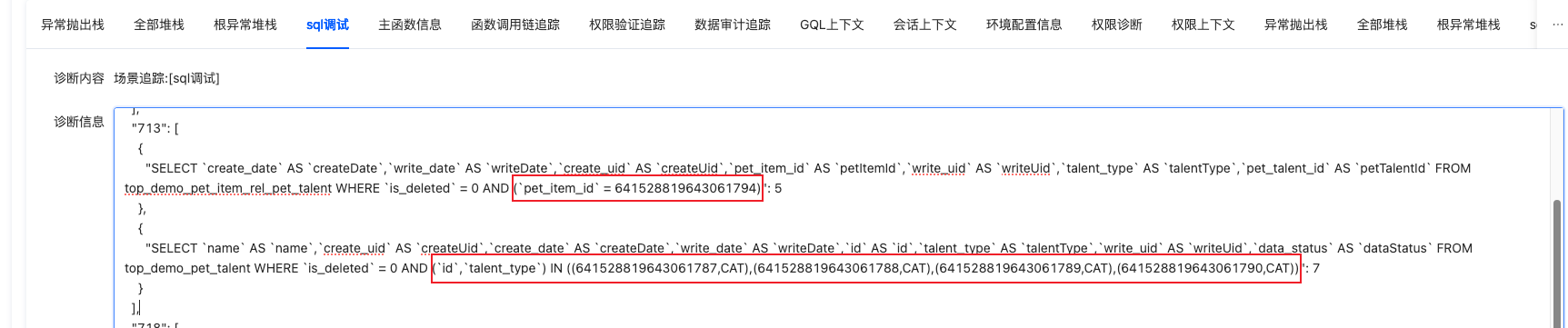
- Common Issues:
- Error: The associated field of the associated model needs to be configured. Reason: The
talentTypefield is not defined inPetTalent.
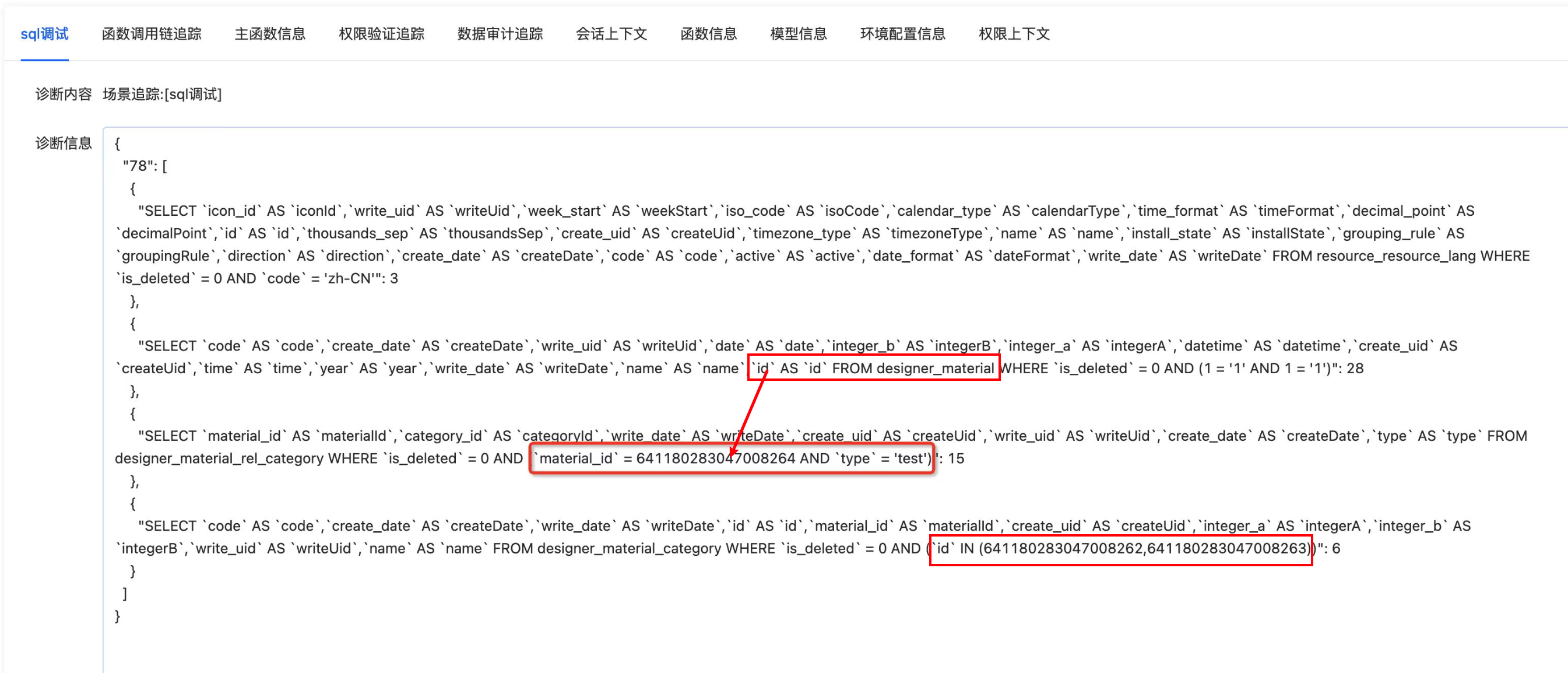
(Ⅲ) Configuration Example 3:
@Field(displayName = "Category")
@Field.many2many(
through = MaterialRelCategory.MODEL_MODEL,
relationFields = {"materialId","type"},
referenceFields = {"categoryId"}
)
@Field.Relation(relationFields = {"id", "#test#"}, referenceFields = {"id"})
private List<MaterialCategory> categoryList;Analysis:
- In this many-to-many relationship, the query first retrieves the fields of the current model to obtain the id (left) of the current model. Then, it queries the intermediate table based on the condition
material_id = id (left) AND type = test, from which multiplecategoryIdcan be obtained. Finally, it queries the relationship tableMaterialCategorybased on the conditionid (right) IN (categoryId).