Module API
I. Overview
A module is the smallest unit divided and managed by business domain, a collection of functions and interfaces. Modularization拆解 (拆解) the program into multiple independent modules, each responsible for implementing a sub-function, ultimately combined into a complete system to meet overall functional requirements. Modules are usually divided by business domain,归集 (归集) data definitions, rule logic, and executable code within the same business scope into the same module.
II. Module
(Ⅰ) Module Definition
Oinone's module definition file declares modules through Java classes and specifies corresponding module metadata. In Oinone, all modules inherit from PamirsModule. Take the expenses module as an example:
package pro.shushi.oinone.trutorials.expenses.api;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import pro.shushi.pamirs.meta.annotation.Module;
import pro.shushi.pamirs.meta.base.PamirsModule;
import pro.shushi.pamirs.meta.common.constants.ModuleConstants;
@Component
@Module(
name = ExpensesModule.MODULE_NAME,
displayName = "Expense Management",
version = "1.0.0",
priority = 1,
dependencies = {ModuleConstants.MODULE_BASE}
)
@Module.module(ExpensesModule.MODULE_MODULE)
@Module.Advanced(selfBuilt = true, application = true)
public class ExpensesModule implements PamirsModule {
public static final String MODULE_MODULE = "expenses";
public static final String MODULE_NAME = "expenses";
@Override
public String[] packagePrefix() {
return new String[]{
"pro.shushi.oinone.trutorials.expenses"
};
}
}- Necessary Class Imports: Introduces Spring's
@Componentannotation and custom module-related annotations and interfaces. - Class Definition: The
ExpensesModuleclass implements thePamirsModuleinterface. - Configuration Annotations
The technical name of the module is configured via the name attribute of @Module, and the frontend-backend interaction protocol uses the technical name to locate the module.
The display name of the module is configured via the displayName attribute of @Module, shown in the product's visual interaction layer.
The module version is configured via the version attribute of @Module, and the system compares version numbers to determine if the module needs an upgrade.
The module priority is configured via the priority attribute of @Module (smaller numbers mean higher priority), and the system uses the highest priority application's homepage as the platform's homepage.
Module dependencies and exclusions are configured via the dependencies and exclusions attributes of @Module, with values as arrays of module codes. If a module inherits models from another module or establishes associations with another module's models, the dependent module list of this module must include the other module's code.
The module code is configured via @Module.module, serving as the unique identifier of the module in the system.
The selfBuilt attribute of @Module.Advanced configures whether the module is a platform-built module.
The application attribute of @Module.Advanced configures whether the module is an application (a module with visual interaction pages). The module switch component can only view applications.
- Constant Definitions: Defines
MODULE_MODULEandMODULE_NAMEconstants representing the module's identifier and name.
| Attribute | Default Value Rule | Naming Convention |
|---|---|---|
| module | No default value Developer-defined specification example: {project name}_ | 1. Use snake_case 2. Only supports numbers, uppercase/lowercase letters, and underscores 3. Must start with a letter 4. Cannot end with an underscore 5. Length must be ≥4 and ≤128 characters |
| name | No default value | 1. Use PascalCase 2. Only supports numbers and letters 3. Must start with a letter 4. Length must be ≤128 characters |
- Method Implementation: The
packagePrefix()method returns the array ofpackageprefixes included in this module.
Note
The Oinone instance always installs the base module, but you must still specify it as a dependency to ensure your module updates when base updates.
Note
The application attribute of @Module.Advanced configures whether the module is an application (with visual interaction pages). Non-application modules have no interaction entry.
Warning
The module package path is returned by the packagePrefix method. If different Oinone modules include the same package path, metadata loading will fail.
Warning
Once installed until uninstalled, the module code cannot be changed; otherwise, the system will recognize it as new metadata.
(Ⅱ) Annotation Configuration
1、@Module
@Module
├── displayName Display name
├── name Technical name
├── version Installation version
├── category Classification code
├── summary Description summary
├── dependencies Dependent module code list
├── exclusions Mutually exclusive module code list
├── priority Sorting
├── module Module code
│ └── value
├── Ds Logical data source name
│ └── value
├── Hook Excluded interceptor list
│ └── excludes
├── Advanced More configurations
│ ├── website Site
│ ├── author Author
│ ├── description Description
│ ├── application Whether it is an application
│ ├── demo Whether it is a demo application
│ ├── web Whether it is a web application
│ ├── toBuy Whether to jump to the website for purchase
│ ├── selfBuilt Whether it is a self-built application
│ ├── license License, default enum: PEEL1
│ ├── maintainer Maintainer
│ ├── contributors Contributors
│ └── url Code repository address
├── Fuse Low-code integration module
2、@UxHomepage
@UxHomepage Module homepage
└── UxRoute
3、@UxAppLogo
@UxAppLogo
└── logo Icon
(Ⅲ) Module Metadata
1、ModuleDefinition
| Element Data Composition | Meaning | Corresponding Annotation | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| displayName | Display name | @Module( displayName="", name="", version="", category="", summary="", dependencies={"",""}, exclusions={"",""}, priority=1L ) | |
| name | Technical name | ||
| latestVersion | Installation version | ||
| category | Classification code | ||
| summary | Description summary | ||
| moduleDependencies | Dependent module code list | ||
| moduleExclusions | Mutually exclusive module code list | ||
| priority | Sorting | ||
| module | Module code | @Module.module("") | |
| dsKey | Logical data source name | @Module.Ds("") | |
| excludeHooks | Excluded interceptor list | @Module.Hook(excludes={"",""}) | |
| website | Site | @Module.Advanced( website="http://www.oinone.top", author="oinone", description="oinone", application=false, demo=false, web=false, toBuy=false, selfBuilt=true, license=SoftwareLicenseEnum.PEEL1, maintainer="oinone", contributors="oinone", url="http://git.com" ) | |
| author | Module author | ||
| description | Description | ||
| application | Whether it is an application | ||
| demo | Whether it is a demo application | ||
| web | Whether it is a web application | ||
| toBuy | Whether to jump to the website for purchase | ||
| selfBuilt | Self-built application | ||
| license | License | Default PEEL1 Optional values: GPL2 GPL2ORLATER GPL3 GPL3ORLATER AGPL3 LGPL3 ORTHEROSI PEEL1 PPL1 ORTHERPROPRIETARY | |
| maintainer | Maintainer | ||
| contributors | Contributor list | ||
| url | Code repository address | ||
| boot | Whether it is an automatically installed boot item | @Boot | Adding this annotation means: It will be automatically installed during startup, regardless of whether the module is configured in the yml file |
| moduleClazz | Class where the module is defined | Only for modules written in code | |
| packagePrefix | Package path for scanning other metadata under this module | ||
| dependentPackagePrefix | Scanning path corresponding to the dependent module list | ||
| state | Status | Automatically calculated by the system, no configuration needed | |
| metaSource | Metadata source | ||
| publishCount | Total number of publications | ||
| platformVersion | Latest platform version | Corresponds to the version of the central platform. Used for remote updates | |
| publishedVersion | Latest published version |
2、UeModule
Inherits from ModuleDefinition and extends metadata related to frontend interaction.
| Element Data Composition | Meaning | Corresponding Annotation | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| homePageModel | Navigation model code | @UxHomepage( @UxRoute( ) ) | Corresponds to a ViewAction. If UxRoute only configures the model, it defaults to the list page of that model |
| homePageName | View action or link action name | ||
| logo | Icon | @UxAppLogo (logo="") |
III. Module Lifecycle
(Ⅰ) Lifecycle Diagram
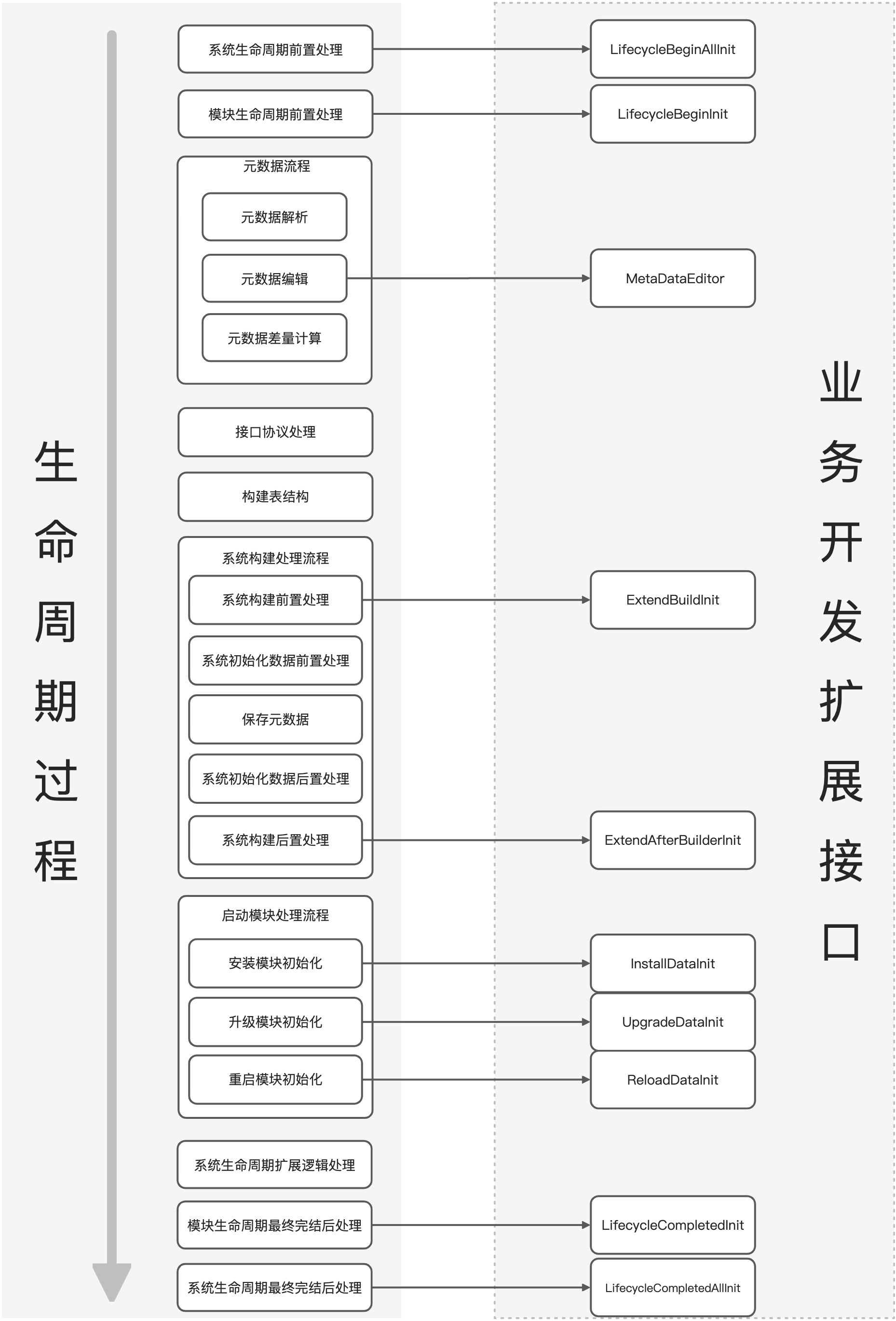
(Ⅱ) Business Extension Description
| Interface | Description | Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| LifecycleBeginAllInit | Pre-logic when the system enters the lifecycle Note: No database operations allowed | System-level information collection and reporting |
| LifecycleCompletedAllInit | Post-logic after the system lifecycle is completed | System-level information collection and reporting, Cleanup of data or context during the lifecycle |
| LifecycleBeginInit | Pre-logic when the module enters the lifecycle Note: No database operations allowed | Reserved, with limited functionality |
| LifecycleCompletedInit | Post-logic after the module lifecycle is completed | Logic where this module needs to initialize after other modules have completed initialization. For example: 1. Initialization of integrated modules 2. Initialization of permission caching …… |
| MetaDataEditor | Metadata editing Note: No database operations allowed | This has been mentioned multiple times in basic tutorials. The core scenario is to actively register metadata such as Actions, Menus, and Views with the system |
| ExtendBuildInit | Pre-processing logic for system construction | Reserved, with limited functionality, used for doing things unrelated to modules |
| ExtendAfterBuilderInit | Post-processing logic for system construction | Reserved, with limited functionality, used for doing things unrelated to modules |
| InstallDataInit | Initialization logic when the module is first installed | Select and execute logic based on module startup instructions, generally used for initializing business data. |
| UpgradeDataInit | Initialization logic when the module is upgraded Note: Executed based on startup instructions; whether to execute once is controlled by the business | |
| ReloadDataInit | Initialization logic when the module restarts Note: Executed based on startup instructions; whether to execute once is controlled by the business |
IV. Module Startup
(Ⅰ) Startup Project
The module startup project is usually independent of the module project, existing as a separate project. It undertakes the important responsibility of organizing and assembling different modules to achieve collaborative startup.

The boot and core projects of each module are independent and do not depend on each other. The boot project depends on the core and api projects, while the core project depends on the api project. The api projects of different modules are allowed to depend on each other. If there is a circular reference, it can be solved by extracting a public api project.
Oinone enables flexible switching between single-node and distributed deployments, providing convenience for enterprise business development. It is suitable for companies of different sizes, helping to effectively save enterprise costs, improve innovation efficiency, and make internet technology more accessible. 
Warning
In Oinone, if cross-module storage models have an inheritance relationship, they must be deployed with the same data source as the dependent module. This feature imposes requirements on module planning. For example, a business-level user extension module must be deployed together with the user module to ensure data consistency and functional integrity.
(Ⅱ) Deployment Parameter pamirs.boot
In Oinone, there are two convenient ways to set startup parameters:
- Command-line configuration: Use
java -jar <your jar name>.jar -Pparameter=Xto quickly set parameters, e.g.,-Plifecycle=INSTALL; - YAML file configuration: Use the
pamirs.bootattribute in the startup YAML file for flexible parameter configuration.
When both methods set the same parameter, the command-line parameter takes precedence to ensure immediate and prioritized configuration.
1、Command-line Configuration
| Parameter | Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| -Plifecycle | Lifecycle deployment instruction | INSTALL | Options: + INSTALL + CUSTOM_INSTALL + PACKAGE + RELOAD + DDL |
| -PbuildTable | Method for automatically building table structures | None | Options: + NEVER (do not automatically build table structures) + EXTEND (incrementally build table structures) + DIFF (differentially build table structures) |
| -PenableRpc | Whether to enable remote services | None | Options: + true + false |
| -PopenApi | Whether to enable the HTTP API service | None | Options: + true + false |
| -PinitData | Whether to enable the data initialization service | None | Options: + true + false |
| -PgoBack | Set Jar version dependency checking: When configured as true, it enables Jar dependency version downgrading, enhancing deployment flexibility. | None | Options: + true + false |
2、Command-line and Configuration Item对照表
-Plifecycle: Lifecycle Deployment Instruction
| Startup Configuration Item | Default Value | RELOAD | INSTALL | CUSTOM_INSTALL | PACKAGE | DDL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.install | AUTO | READONLY | AUTO | AUTO | AUTO | AUTO |
| pamirs.boot.upgrade | AUTO | READONLY | FORCE | FORCE | FORCE | FORCE |
| pamirs.boot.profile | CUSTOMIZE | READONLY | AUTO | CUSTOMIZE | PACKAGE | DDL |
-PbuildTable: Method for Automatically Building Table Structures
| Startup Configuration Item | Default Value | NEVER | EXTEND | DIFF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.option.diffTable | true | false | false | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.rebuildTable | true | false | true | true |
-PenableRpc: Whether to Enable Remote Services
| Startup Configuration Item | Default Value | false | true |
|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.option.publishService | true | false | true |
-PopenApi: Whether to Enable the HTTP API Service
| Startup Configuration Item | Default Value | false | true |
|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.option.rebuildHttpApi | true | false | true |
-PinitData: Whether to Enable the Data Initialization Service
| Startup Configuration Item | Default Value | false | true |
|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.option.updateData | true | false | true |
-PgoBack: Set Jar Version Dependency Checking
| Startup Configuration Item | Default Value | false | true |
|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.option.goBack | false | false | true |
3、Startup Configuration Items
The startup configuration entry for Oinone is the Java class pro.shushi.pamirs.boot.orm.configure.BootConfiguration. All configuration paths are prefixed with pamirs.boot, and core configuration items include:
install: Installation-related configuration; When there are uninstalled modules in the startup module list, whether to install them automatically, optional values: auto | readonlyupgrade: Upgrade-related configuration; Optional values: auto | force | readonly
| Optional Values | Meaning |
|---|---|
| auto | Automatic upgrade - if the module version number increases, upgrade |
| force | Forced upgrade - upgrade regardless of module version changes |
| readonly | Read-only |
profile: Optional configuration group;options: Custom optional configurations;modules: Module loading configuration;noCodeModule: No-code module configuration.
Profile and Options 对照表
In Oinone, for startup parameters not set via the command line, the custom options under pamirs.boot.options take effect only when the pamirs.boot.profile attribute in the startup YAML file is CUSTOMIZE.
| Option | Description | Default Value | AUTO | READONLY | PACKAGE | DDL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pamirs.boot.option.reloadModule | Whether to load module information stored in the database | false | true | true | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.checkModule | Verify whether dependent modules are installed | false | true | true | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.loadMeta | Whether to scan packages to read module metadata | true | true | false | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.reloadMeta | Whether to load metadata stored in the database | false | true | true | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.computeMeta | Whether to recalculate metadata | true | true | false | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.editMeta | Edit metadata, whether to support programmatic metadata editing | true | true | false | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.diffMeta | Differential calculation of metadata | false | true | false | true | false |
| pamirs.boot.option.refreshSessionMeta | Refresh metadata cache | true | true | true | true | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.rebuildHttpApi | Refresh and rebuild the front-end-backend protocol | true | true | true | false | false |
| pamirs.boot.option.diffTable | Track table structure changes differentially | false | true | false | true | false |
| pamirs.boot.option.rebuildTable | Update and rebuild table structures | true | true | false | true | false |
| pamirs.boot.option.printDDL | Print rebuilt table structure DDL | false | false | false | false | true |
| pamirs.boot.option.publishService | Publish services, whether to publish remote services | true | true | true | false | false |
| pamirs.boot.option.updateData | Initialize and update built-in business data, whether to write changes in built-in business data to the database | true | true | false | true | false |
| pamirs.boot.option.params | Extended parameters | Customizable | Customizable | Customizable | Customizable | Customizable |
Common Problem: No DDL Permission
Example: Management Specifications Conflict: In enterprises with professional DBA teams, due to data security and management specifications, direct DDL operation permissions are strictly prohibited in the production environment.
- Configure the startup custom option:
pamirs.boot.options.rebuildTableasfalseto completely disable the automatic table creation function.
pamirs:
boot:
options:
rebuildTable: falseExample
- Or configure the
pamirs.persistenceconfiguration item to disable the automatic table creation function for部分 (part) data sources. Thepersistenceconfiguration can be global or per-data source.
pamirs:
persistence:
global:
# Global configuration for whether to automatically create the database, default is true
autoCreateDatabase: true
# Global configuration for whether to automatically create data tables, default is true
autoCreateTable: true
<your ds key>:
# Data source configuration for whether to automatically create the database, default is true
autoCreateDatabase: true
# Data source configuration for whether to automatically create data tables, default is true
autoCreateTable: trueExample
- Use
-Plifecycle=DDLto output database change scripts in DDL mode, which can be approved and executed by the company's DBA.
modules Low-code Module Startup List
Through the startup module list, you can specify the modules to be loaded when the boot project starts. If modules are distributed in different boot projects, their mutual calls will automatically trigger the remote communication process to ensure normal cross-project interaction. An example is as follows:
pamirs:
boot:
modules:
- base
- common
- sequence
- resource
- user
- auth
- message
- international
- business
- expensesnoCodeModule No-code Module Startup Configuration
pamirs:
boot:
noCodeModule:
init: true # Whether to load no-code modules on startup. Default is install. After adding a no-code module on the page, it will be loaded on the next startup
modules: # List of no-code modules to start
- nocodeModule1
- nocodeModule2(Ⅲ) Framework Configuration pamirs.framework
Oinone framework's core configuration items are categorized by functional modules as follows:
1、GraphQL Gateway Configuration (pamirs.framework.gateway)
pamirs.framework.gateway.show-doc
Controls whether to enable the Schema document query capability of GraphQL. When set to true, you can view backend interface documents through tools like Insomnia.
pamirs.framework.gateway.statistics
Used to collect runtime status data of DataLoader, including cache hit counts, object loading quantities, error counts, etc., to assist in performance analysis and problem troubleshooting.
2、Hook Function Control Configuration (pamirs.framework.hook)
pamirs.framework.hook.ignoreAll
The default value is false. When set to true, it skips the execution of all Hook functions.
pamirs.framework.hook.excludes
Allows specifying Hook functions to exclude, enabling flexible adjustment of the Hook execution strategy.
3、Data Module Configuration (pamirs.framework.data)
pamirs.framework.data.default-ds-key:
Defines the default database connection identifier for modules, which should correspond to the key in pamirs.datasource configuration.
pamirs.framework.data.ds-map:
Allows specifying independent database connections for specific modules. For example, in the sample scenario of the expense management module, if you need to configure a dedicated database for the expenses module, you can set expenses: biz and define a data source with key biz in pamirs.datasource.
4、Metadata System Configuration (pamirs.framework.system)
pamirs.framework.system.system-ds-key:
Specifies the data source corresponding to the metadata system, which should match the pamirs.datasource configuration item.
pamirs.framework.system.system-models:
Identifies metadata models, which are uniformly stored in the database corresponding to system-ds-key.
pamirs:
framework:
system:
system-ds-key: base
system-models:
- base.WorkerNode
data:
default-ds-key: pamirs
ds-map:
base: base
gateway:
statistics: true
show-doc: true
#hook configuration is as follows
#hook:
#excludes:
#- pro.shushi.pamirs.core.common.hook.QueryPageHook4TreeAfter
#- pro.shushi.pamirs.user.api.hook.UserQueryPageHookAfter
#- pro.shushi.pamirs.user.api.hook.UserQueryOneHookAfter(Ⅳ) Database Dialect pamirs.dialect.ds
Configuration Description of pamirs.datasource Data Source Dialect
- Function Description: Used to define the database dialect information of the data source, with each configuration item identified by a unique
key. - Core Sub-parameters
type: Specifies the database type, with the default valueMySQL. It can be replaced with other database types (such as PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc.).version: Defines the database version number, with the default value8.0, which should match the actual database version.majorVersion: Specifies the database major version number, with the default value8, used to distinguish grammatical features of different major versions.
- Configuration Example
pamirs:
dialect: # MySQL8.0 can be left unconfigured
ds:
base: # Dialect information of the data source in pamirs.datasource, corresponding to the key
type: MySQL
version: 8.0
majorVersion: 8
pamirs: # Dialect information of the data source in pamirs.datasource, corresponding to the key
type: MySQL
version: 8.0
majorVersion: 8For more dialect configurations, refer to: Database Dialect Configuration Topic
(Ⅴ) Data Source Configuration pamirs.datasource
In the application development and deployment process, data storage and interaction are crucial links. pamirs.datasource, as a core configuration item, is mainly used to configure the data source information required for installing modules. It builds a bridge between the application and the database, enabling the application to connect to and operate the database stably and efficiently according to different business needs. Through this configuration, we can independently set multiple data sources to meet the differentiated needs of different modules for database connections, thereby enhancing the flexibility and scalability of the system.
1、General Configuration Items
Under pamirs.datasource, each data source has a series of general configuration items that determine the basic attributes of the data source and the behavior of the connection pool. The following is a detailed explanation of these configuration items:
driverClassName: Specifies the JDBC driver class for the database. Different databases require different driver classes. For example, MySQL usescom.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver, and Oracle usesoracle.jdbc.OracleDriver, etc. This configuration item ensures that the application can correctly load and use the corresponding database driver.type: Defines the type of the connection pool. Common connection pools include HikariCP, Druid, etc. The example usescom.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource, that is, Alibaba's Druid connection pool. The role of the connection pool is to manage database connections, improving connection reusability and performance.url: The connection URL of the database, including the database address, port, database name, and some connection parameters. For example, injdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/trutorials_base?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true,127.0.0.1is the database IP address,3306is the port number,trutorials_baseis the database name, and the following parameters are some connection options, such as whether to use SSL, character encoding, time zone, etc.usernameandpassword: User names and passwords for database authentication to ensure that only authorized users can access the database.initialSize: The initial number of connections in the connection pool, that is, the number of database connections预先 (pre) created by the connection pool when the application starts. An appropriate initial size can reduce the waiting time for the first database access after the application starts.maxActive: The maximum number of active connections in the connection pool, that is, the maximum number of connections allowed to exist simultaneously in the connection pool. When the number of connections required by the application exceeds this limit, new requests will wait until a connection is released.minIdle: The minimum number of idle connections in the connection pool, that is, the minimum number of idle connections that the connection pool always maintains. When the number of idle connections in the connection pool is lower than this value, the connection pool will automatically create new connections.maxWait: The maximum waiting time (in milliseconds) for obtaining a connection. If a connection cannot be obtained within this time, an exception will be thrown. This configuration item can prevent the application from waiting for a connection for too long, improving system response performance.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: Configures how often to perform a detection to close idle connections (in milliseconds). Regular detection can timely release long-idle connections and reduce resource occupation.testWhileIdle: Detects whether the connection is valid when applying for a connection. If set totrue, when fetching a connection from the connection pool, it will first check if the connection is available to avoid fetching invalid connections.testOnBorrow: Detects whether the connection is valid when borrowing a connection. Different fromtestWhileIdle, this configuration item performs detection every time a connection is fetched from the connection pool, which will increase a certain performance overhead.testOnReturn: Detects whether the connection is valid when returning a connection. When set totrue, the validity of the connection will be detected when the connection is returned to the connection pool to ensure that all connections in the connection pool are available.poolPreparedStatements: Whether to cachePreparedStatement.PreparedStatementis a precompiled SQL statement, and caching it can improve SQL execution performance.asyncInit: Whether to asynchronously initialize the connection pool. When set totrue, the initialization of the connection pool will be performed in a background thread without blocking the application startup.
2、Multiple Data Source Configuration
pamirs.datasource supports configuring multiple data sources, each identified by a unique name, such as pamirs and base in the example. This can meet the needs of different modules to access different databases. For example, one module may need to access the business database, and another module may need to access the log database. By independently configuring the connection information of each data source, data access between various modules can be ensured to not interfere with each other.
3、Configuration Example
The following YAML example shows the complete configuration of two data sources (pamirs and base), both using Alibaba Druid connection pool to connect to the MySQL database:
pamirs:
datasource:
pamirs:
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/trutorials_pamirs?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: oinone
initialSize: 5
maxActive: 200
minIdle: 5
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
asyncInit: true
base:
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/trutorials_base?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: oinone
initialSize: 5
maxActive: 200
minIdle: 5
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
asyncInit: trueIn practical applications, you can adjust the data source name, connection parameters, and connection pool configuration according to business needs to flexibly adapt to different database environments. For example, if you need to connect to a PostgreSQL database, you only need to change driverClassName to org.postgresql.Driver and modify the url to the corresponding PostgreSQL connection address. At the same time, according to the performance of the database and the load of the application, reasonably adjusting connection pool parameters such as initialSize and maxActive can further optimize system performance.
(Ⅵ) Database and Table Sharding Configuration pamirs.sharding
pamirs.sharding is the core configuration module in the Oinone framework for implementing database and table sharding, mainly used to define the horizontal splitting strategy and mapping rules of the database. When using the pamirs-trigger-bridge-tbschedule project to enable the built-in scheduling function, this configuration is a required item, which can effectively cope with the data storage and access pressure in high-concurrency scenarios and improve the scalability and performance of the system. Through this configuration, developers can flexibly specify data source mapping relationships, data model sharding rules, and specific database and table sharding strategies to achieve the reasonable distribution of data among multiple databases and tables.
1、Core Configuration Structure Analysis
define: Basic Definition Module
data-sources: Used to declare the mapping relationship of data sources.- Single data source mapping: Such as
ds: pamirsandpamirsSharding: pamirs, indicating that the logical data sourcesdsandpamirsShardingare associated with the actual data sourcepamirs. - Multiple data source mapping: Such as
testShardingDs, which maps the logical data sourcetestShardingDsto the physical data source listtestShardingDs_0andtestShardingDs_1, supporting dynamic data read-write distribution.
- Single data source mapping: Such as
models: Defines the table sharding rules for data models.- The
[trigger.PamirsSchedule]model in the example is configured withtables: 0..13, indicating that this model corresponds to 14 physical tables; - The
[demo.ShardingModel]model, in addition to the table sharding rules, also specifies the table name separator viatable-separator: _; - The
[demo.ShardingModel2]model defines bothds-nodes: 0..1(database sharding rules) andds-separator: _(database name separator) to achieve dual sharding of databases and tables.
- The
rule: Database and Table Sharding Rule Module
For each logical data source, configure specific database and table sharding strategies through the rule sub-item. The configuration syntax is highly compatible with Sharding-JDBC:
actual-ds: Clarifies the list of actual physical data sources corresponding to the logical data source to ensure accurate data read-write positioning.sharding-rules: Defines table-level database and table sharding rules, including:actualDataNodes: Specifies the combination of libraries and tables where data is actually stored (such aspamirs.demo_core_sharding_model_${0..7});tableStrategy/databaseStrategy: Configures the sharding strategy for tables/databases, specifies the sharding key throughshardingColumn, andshardingAlgorithmNameis associated with the specific sharding algorithm;shardingAlgorithms: Defines the sharding algorithm implementation. For example, theINLINEtype calculates the target database and table through thealgorithm-expressionexpression (such asdemo_core_sharding_model_${(Long.valueOf(user_id) % 8)}indicates distributing to 8 tables based on theuser_idmodulo).
replica-query-rules: Defines the master-slave read-write rules, including:- Data Source Definition (
data-sources):pamirsSharding: Data source group name, which can be customized.primaryDataSourceName: Specifies the master database data source (for write operations).replicaDataSourceNames: List of slave database data sources (for read operations, supporting multiple nodes).loadBalancerName: Refers to the load balancing strategy defined inload-balancers.
- Load Balancing Strategy (
load-balancers):round_robin: Load balancer name, which must be consistent withloadBalancerName.type: ROUND_ROBIN: Adopts a round-robin algorithm to distribute read requests, ensuring load balancing of slave databases.
- Data Source Definition (
props: Global attribute configuration, such assql.show: trueto enable SQL execution log printing, which is convenient for debugging and performance analysis.
2、Configuration Example
Database and Table Sharding Configuration Example
pamirs:
sharding:
define:
data-sources:
ds: pamirs
pamirsSharding: pamirs # Declare that the pamirsSharding database corresponds to the pamirs data source
testShardingDs: # Declare that the testShardingDs database corresponds to the testShardingDs_0\1 data sources
- testShardingDs_0
- testShardingDs_1
models:
"[trigger.PamirsSchedule]":
tables: 0..13
"[demo.ShardingModel]":
tables: 0..7
table-separator: _
"[demo.ShardingModel2]":
ds-nodes: 0..1 # Declare the database creation rules corresponding to the testShardingDs database
ds-separator: _
tables: 0..7
table-separator: _
rule:
pamirsSharding: # Configure the database and table sharding rules for the pamirsSharding database
actual-ds:
- pamirs # Declare that the pamirsSharding database corresponds to the pamirs data source
sharding-rules:
# Configure sharding rules, the following configuration is consistent with sharding-jdbc configuration
- tables:
demo_core_sharding_model:
actualDataNodes: pamirs.demo_core_sharding_model_${0..7}
tableStrategy:
standard:
shardingColumn: user_id
shardingAlgorithmName: table_inline
shardingAlgorithms:
table_inline:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: demo_core_sharding_model_${(Long.valueOf(user_id) % 8)}
props:
sql.show: true
testShardingDs: # Configure the database and table sharding rules for the testShardingDs database
actual-ds: # Declare that the testShardingDs database corresponds to the pamirs data source
- testShardingDs_0
- testShardingDs_1
sharding-rules:
# Configure sharding rules, the following configuration is consistent with sharding-jdbc configuration
- tables:
demo_core_sharding_model2:
actualDataNodes: testShardingDs_${0..1}.demo_core_sharding_model2_${0..7}
databaseStrategy:
standard:
shardingColumn: user_id
shardingAlgorithmName: ds_inline
tableStrategy:
standard:
shardingColumn: user_id
shardingAlgorithmName: table_inline
shardingAlgorithms:
table_inline:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: demo_core_sharding_model2_${(Long.valueOf(user_id) % 8)}
ds_inline:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: testShardingDs_${(Long.valueOf(user_id) % 2)}
props:
sql.show: trueAdjust the data source mapping, sharding strategy, and algorithm expressions according to business needs to achieve efficient data sharding management.
Master-Slave Read-Write Rule Configuration Example
pamirs:
sharding:
define:
data-sources:
pamirsSharding: pamirsMaster # The logical data source pamirsSharding points to the master data source pamirsMaster.
models:
"[trigger.PamirsSchedule]":
tables: 0..13
rule:
pamirsSharding:
actual-ds: # Specify that the logical data source pamirsSharding proxies the data sources pamirsMaster and pamirsSlaver
- pamirsMaster
- pamirsSlaver
# The following configuration is consistent with sharding-jdbc configuration
replicaQueryRules:
data-sources:
pamirsSharding:
primaryDataSourceName: pamirsMaster # **Write database data source**: Master database name
replicaDataSourceNames:
- pamirsSlaver # **Read database data source list**: Slave database name (supports multiple slaves)
loadBalancerName: round_robin # **Load balancer reference**: Associate the load balancing strategy name
load-balancers:
round_robin:
type: ROUND_ROBIN # **Load balancing type**: Round-robin strategy (read requests are evenly distributed to slave databases)Application Scenarios
- Read-Write Separation: Write operations are routed to
pamirsMaster, and read operations are distributed topamirsSlavervia round-robin (multiple slaves can be expanded). - High Availability: Improve read operation performance through load balancing strategies and avoid excessive pressure on a single slave database.
Expansion Instructions
- If you need to add a new slave database, directly add the data source name to the
replicaDataSourceNameslist. - Support switching the load balancing type (such as
RANDOMrandom strategy), just modify thetypefield value.
(Ⅶ) Database-Table Mapping Rules pamirs.mapper
1、Database Configuration
In pamirs.mapper, you can configure the database through the YAML configuration item "pamirs.mapper.<global or ds>". If not configured, the system will automatically use the default value. The specific configuration items, default values, and descriptions are as follows:
| Configuration Item | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
databaseFormat | %s | Database name formatting rule, where %swill be replaced by the actual database name |
tableFormat | %s | Table name formatting rule, where %swill be replaced by the actual table name |
tablePattern | ${moduleAbbr}_%s | Dynamic table name expression for flexible table name generation, %swill be replaced by the actual table name |
columnPattern | %s | Column name formatting rules, %s will be replaced by the actual column name |
tableNameCaseSensitive | false | The table name is case sensitive, toLowerCasewill be automatically converted to all lowercase when false, and true can be used to specify the table name in case format. |
2、Table Configuration
Table configuration can be achieved in two ways: one is to use the YAML configuration item "pamirs.mapper.<global or ds>.table-info"; the other is to use the @Model.Persistence annotation. It should be noted that the annotation takes precedence over the configuration in the YAML configuration file. If not configured, the system will use the default value. The specific configuration items, default values, and descriptions are as follows:
| Configuration Item | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
logicDelete | true | Whether to use logical deletion, where truemeans enabled, and falsemeans disabled |
logicDeleteColumn | is_delete | The field name used for logical deletion |
logicDeleteValue | REPLACE(unix_timestamp(NOW(6)),'.','') | The value assigned to this field during logical deletion |
logicNotDeleteValue | 0 | The value of this field during non-logical deletion |
optimisticLocker | false | Whether to enable the optimistic locking mechanism, where truemeans enabled, and falsemeans disabled |
optimisticLockerColumn | opt_version | The field name used for optimistic locking |
keyGenerator | AUTO_INCREMENT | The rule for primary key auto-increment |
underCamel | true | Whether to enable camel case and underscore conversion, where truemeans conversion is enabled |
capitalMode | false | If case conversion is applied or not, true indicates that the conversion is enabled. The conversion will only take effect if the tableNameCaseSensitive property is enabled. |
columnFormat | %s | The formatting rule for column names, where %swill be replaced by the actual column name |
aliasFormat | %s | The formatting rule for field aliases, where %swill be replaced by the actual field alias |
charset | utf8mb4 | The character set used |
collate | bin | The character set used for sorting |
3、Batch Operation Configuration
Batch operations support batch creation and batch update, and the default submission type of the system is batchCommit. The following is a detailed description of the four submission types:
useAffectRows
- Submission Method: Loop to execute single script submission (process one by one).
- Features:
- Each operation is executed independently, and the actual number of affected rows is returned (such as the number of successfully updated records).
- Suitable for scenarios that require precise tracking of each operation result (such as逐条 (one-by-one) auditing).
useAndJudgeAffectRows
- Submission Method: Also uses loop single script submission.
- Features:
- In addition to returning the actual number of affected rows, it will automatically verify whether the returned value matches the input expected number of rows.
- If they do not match (e.g., expecting to update 1 row but actually affecting 0 rows), an exception will be thrown immediately to terminate subsequent operations.
- Suitable for scenarios with extremely high requirements for data consistency (such as financial transactions, inventory deduction).
collectionCommit
- Submission Method:拼接 (Concatenate) multiple single update scripts into a composite script for submission (such as拼接 (concatenate) multiple
UPDATEstatements). - Features:
- Only supports batch updates, and cannot return the actual number of affected rows for each operation (only returns whether the total operation is successful).
- Reduces database interaction times and improves performance, but sacrifices result details.
batchCommit (Default Value)
- Submission Method: Use the single batch operation script supported by the database (such as parameterized batch statements) for submission.
- Features:
- Supports batch creation and updates, completing multiple data operations through one database interaction.
- Does not return the actual number of affected rows, only confirms whether the operation is successful as a whole.
- The best performance, suitable for routine batch operations that do not require feedback on each result.
| Submission Type | Execution Method | Return Result | Performance | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
useAffectRows | Execute one by one | Single affected row count | Lowest (N interactions) | Fine-grained result tracking |
useAndJudgeAffectRows | Execute one by one + result verification | Single affected row count (exception on interruption) | Low (N interactions) | Strong consistency scenarios |
collectionCommit | Script splicing for one-time submission | Overall success/failure | Medium (1 interaction) | Batch updates (non-strict result requirements) |
batchCommit | Database-native batch statement submission | Overall success/failure | Highest (1 interaction) | Routine batch operations (default recommendation) |
4、Configuration Example
pamirs:
mapper:
static-model-config-locations:
- pro.shushi.pamirs
batch: batchCommit
batch-config:
"[base.Field]":
write: 2000
"[base.Function]":
read: 500
write: 2000
global: # Global configuration
table-info:
logic-delete: true
logic-delete-column: is_deleted
logic-delete-value: REPLACE(unix_timestamp(NOW(6)),'.','')
logic-not-delete-value: 0
optimistic-locker: false
optimistic-locker-column: opt_version
key-generator: DISTRIBUTION
table-pattern: '${moduleAbbr}_%s'
ds:
biz: # Single data source configuration, with higher priority
table-info:
# Configurations identical to the global can be omitted
logic-delete: true
logic-delete-column: is_deleted
logic-delete-value: REPLACE(unix_timestamp(NOW(6)),'.','')
optimistic-locker: false
optimistic-locker-column: opt_version
# ID generation method: 1、DISTRIBUTION:Distributed ID;2、AUTO_INCREMENT:Auto-increment ID
key-generator: AUTO_INCREMENT
table-pattern: '${moduleAbbr}_%s'(Ⅷ) Data Persistence Layer Configuration pamirs.persistence
pamirs.persistence is the core configuration item for implementing automated data persistence management in the Oinone framework, supporting the automatic creation of databases and data tables.
1、Core Configuration Items
pamirs.persistence supports two configuration levels: global and data source levels, as follows:
Global Configuration (global)
Suitable for unified rule setting of all data sources, key parameters:
autoCreateDatabase: Controls whether to automatically create databases globally, with a default value oftrue. When enabled, the system will automatically generate database instances according to the configuration.autoCreateTable: Controls whether to automatically create data tables globally, with a default value oftrue. When enabled, the system will automatically generate corresponding data table structures based on data model definitions.
Data Source-Level Configuration (<your ds key>)
Independently configures specific data sources, with higher priority than global configurations, enabling differentiated management:
autoCreateDatabase: Sets whether to automatically create databases for the specified data source, with a default value oftrue. Used to override global rules to meet the need for部分 (part) data sources that do not require automatic database creation.autoCreateTable: Sets whether to automatically create data tables for the specified data source, with a default value oftrue. Supports independent control of data table automation creation to adapt to complex business scenarios.
2、Configuration Example
pamirs:
persistence:
global:
# Global configuration for whether to automatically create databases, default is true
autoCreateDatabase: true
# Global configuration for whether to automatically create data tables, default is true
autoCreateTable: true
<your ds key>:
# Data source configuration for whether to automatically create databases, default is true
autoCreateDatabase: true
# Data source configuration for whether to automatically create data tables, default is true
autoCreateTable: trueThrough the above configuration, global and local rules can be flexibly combined to balance efficiency and flexibility, ensuring按需 (on-demand) automated deployment of database resources while reducing the risk of misoperations.
(Ⅸ) Event Configuration pamirs.event
1、Core Configuration
pamirs.event is used to manage the basic configuration and distribution strategy of system event messages. The specific configuration is as follows:
pamirs:
event:
enabled: true # Globally control the enable status of the event function, default is true, true for enable, false for disable
topic-prefix: oinone # Uniform prefix for all event topics, facilitating standardized management of topic names
notify-map:
system: ROCKETMQ # Message queue type for system messages,可选 (optional) ROCKETMQ, KAFKA, or RABBITMQ
biz: ROCKETMQ # Message queue type for business messages,可选 (optional) ROCKETMQ, KAFKA, or RABBITMQ
logger: ROCKETMQ # Message queue type for log messages,可选 (optional) ROCKETMQ, KAFKA, or RABBITMQ
schedule:
enabled: true # Trigger switch, default is true
#ownSign: demo # Event isolation key to ensure that two groups of machines only fetch data they generateThrough the above configuration, you can flexibly specify the queue carriers for different types of messages (system, business, log) and achieve unified naming specifications for message topics through topic-prefix, while using the enabled switch to quickly start/stop the event function.
2、Message Queue Connection Configuration
The system supports three message queues: RocketMQ, Kafka, and RabbitMQ. The connection and parameter configuration examples are as follows:
RocketMQ Configuration
spring:
rocketmq:
name-server: 127.0.0.1:9876 # RocketMQ NameServer address, used by producers and consumers to locate the cluster
producer:
enableMsgTrace: true # Enable message trace tracking function, facilitating troubleshooting of message sending issues
customizedTraceTopic: TRACE_PRODUCER # Custom message trace topic
consumer:
enableMsgTrace: true # Enable message trace tracking on the consumer side
customizedTraceTopic: TRACE_CONSUMER # Consumer-side custom trace topicKafka Configuration
spring:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092 # Kafka cluster address for establishing connections
producer:
value-serializer: pro.shushi.pamirs.framework.connectors.event.kafka.marshalling.PamirsKafkaMarshalling # Message serialization class for converting messages into byte streams
consumer:
group-id: ${spring.application.name} # Consumer group ID, consumers within the same group jointly consume Topic partitions
value-deserializer: pro.shushi.pamirs.framework.connectors.event.kafka.marshalling.PamirsKafkaMarshalling # Message deserialization class for parsing byte streams into message objectsRabbitMQ Configuration
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1 # RabbitMQ server host address
port: 5672 # Service port number
username: oinone # Login username
password: oinone # Login password
listener:
direct:
acknowledge-mode: manual # Set the message confirmation mode to manual confirmation, ensuring messages are confirmed only after correct processing to avoid lossThe above configuration needs to be adjusted according to the actual environment for parameters such as address, port, and authentication information. Through the linkage between pamirs.event.notify-map and message queue configuration, efficient distribution and reliable transmission of different types of messages can be achieved.
(Ⅹ) Data Record Configuration pamirs.record.sql
When using the SQL record function of the pamirs framework, you can specify the storage location of the SQL log file through the following configuration. This configuration allows you to record the SQL statements executed by the system and their related information to a specific directory.
pamirs:
record:
sql:
# This path is used to specify the storage directory of the SQL log file and can be modified according to actual needs
store: /oinone/sql/recordYou can modify the store field to a suitable local or remote storage path as needed. If not configured, it defaults to System.getProperty("user.dir"), i.e., the user's home directory.
(Ⅺ) Metadata Path Configuration pamirs.meta
pamirs.meta is used to configure metadata-related path information, where the core configuration item views-package is used to specify the storage suffix of template files. The specific description is as follows:
views-package: Defines the default path suffix for template files, with the default value/pamirs/views. If you need to customize the view file path, you can use the format/pamirs/views/Xas agreed (Xis the module code, no need to manually specify it in the path). The custom path has higher priority than the default configuration, meaning the system preferentially reads template files from the custom path.
meta:
# Template file suffix, default value: /pamirs/views
views-package: /pamirs/views(Ⅻ) Enhanced Model Configuration pamirs.channel
The EnhanceModel enhanced model gives the system powerful full-text search capabilities. To use this function, you need to configure the scan path, search engine-related parameters, and this function depends on the pamirs.event event configuration.
1、Scan Path Configuration
Specify the package paths to be scanned in pamirs.channel.packages. If the definition class of the enhanced model is not under the pro.shushi.pamirs package, this configuration must be performed. The example is as follows:
pamirs:
channel:
packages:
- xx.xx.xx # Scan the enhanced model definition class under the non-pro.shushi.pamirs package, which needs to be configured2、Search Engine Configuration
When using Elasticsearch as the search engine, configure its connection address in pamirs.elastic. The example is as follows:
pamirs:
elastic:
url: 127.0.0.1:9200Note
The EnhanceModel enhanced model function depends on the pamirs.event event configuration. Please ensure that the event configuration is correctly set to ensure the normal operation of the enhanced model.
(XIII) Authorization File Configuration pamirs.license
When using the Oinone enterprise edition, you need to configure the authorization file to ensure the normal operation of the system. The specific configuration is as follows:
pamirs:
license:
# Modify to the path of the certificate provided by the platform and the subject
path: licence/oinone-demo.lic
subject: oinone-demoPlease accurately modify the values of path and subject according to the actual information provided by the platform. path needs to specify the storage path of the certificate file, and subject is the identification information of the certificate. Only after completing the correct configuration can you smoothly use the functions of the Oinone enterprise edition.
(XIV) File Storage Configuration pamirs.file
Oinone currently supports multiple types of OSS services to meet the storage needs of different users. The following is a detailed introduction:
1、Supported OSS Types
| Type | Service |
|---|---|
| OSS | Alibaba Cloud OSS |
| UPYUN | Upyun |
| MINIO | MinIO |
| HUAWEI_OBS | Huawei Cloud OBS |
| LOCAL | Local NGINX file storage |
| TENCENT_COS | Tencent Cloud COS |
2、OSS Generic YAML Configuration
cdn:
oss:
name: # Name
type: # Type
bucket:
uploadUrl: # Upload URL
downloadUrl: # Download URL
accessKeyId:
accessKeySecret:
mainDir: # Main directory
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
referer:
localFolderUrl:
others:
[key]:
name: # Name
type: # Type
bucket:
uploadUrl: # Upload URL
downloadUrl: # Download URL
accessKeyId:
accessKeySecret:
mainDir: # Main directory
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
referer:
localFolderUrl:Note: Use a custom key in others to specify the OSS service for file upload/download functions. Upload and download configurations must match; otherwise, they will not work properly.
3、Configuration Examples for Each OSS
Alibaba Cloud OSS
cdn:
oss:
name: Alibaba Cloud
type: OSS
bucket: pamirs (modify according to actual situation)
uploadUrl: oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
downloadUrl: oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
accessKeyId: Your accessKeyId
accessKeySecret: Your accessKeySecret
# Modify according to actual situation
mainDir: upload/
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
imageResizeParameter:
referer:Huawei Cloud OBS
cdn:
oss:
name: Huawei Cloud
type: HUAWEI_OBS
bucket: pamirs (modify according to actual situation)
uploadUrl: obs.cn-east-2.myhuaweicloud.com
downloadUrl: obs.cn-east-2.myhuaweicloud.com
accessKeyId: Your accessKeyId
accessKeySecret: Your accessKeySecret
# Modify according to actual situation
mainDir: upload/
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
allowedOrigin: http://192.168.95.31:8888,https://xxxx.xxxxx.com
referer:Dependency Addition: To use Huawei Cloud OBS, add the following dependency to the startup project:
<okhttp3.version>4.9.3</okhttp3.version>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
<version>${okhttp3.version}</version>
</dependency>Note: Huawei Cloud OBS has strict referer configuration for anti-leeching, only allowing access with specific referers. The backend logic for Excel import does not carry a referer during anonymous reads, leading to access denial.
MINIO
cdn:
oss:
name: minio
type: MINIO
bucket: pamirs (modify according to actual situation)
uploadUrl: http://192.168.243.6:32190 (modify according to actual situation)
downloadUrl: http://192.168.243.6:9000 (modify according to actual situation)
accessKeyId: Your accessKeyId
accessKeySecret: Your accessKeySecret
# Modify according to actual situation
mainDir: upload/
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
referer:
localFolderUrl:Configuration Without Public IP: For OSS configuration under MINIO without a public IP, refer to File Storage: MINIO OSS Configuration Without Public IP.
Upyun
cdn:
oss:
name: Upyun
type: UPYUN
bucket: pamirs (modify according to actual situation)
uploadUrl: v0.api.upyun.com
downloadUrl: v0.api.upyun.com
accessKeyId: Your accessKeyId
accessKeySecret: Your accessKeySecret
# Modify according to actual situation
mainDir: upload/
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
referer:Tencent Cloud COS
cdn:
oss:
name: TENCENT_COS
type: TENCENT_COS
bucket: cos-dcode-prod-1252296671
uploadUrl: cos.ap-shanghai.myqcloud.com
downloadUrl: cos.ap-shanghai.myqcloud.com
accessKeyId: Your accessKeyId
accessKeySecret: Your accessKeySecret
mainDir: upload/demo/
validTime: 3600000
timeout: 600000
active: true
image-resize-parameter:
allowedOrigin: https://test.oinone.com,http://127.0.0.1:88
referer:4、OSS Configuration Usage Example
To directly upload files to OSS from the backend, obtain the file system client configured by the system through FileClientFactory.getClient().
// Get file client
// 1. Get the default file client
FileClient fileClient = FileClientFactory.getClient();
// 2. Get the file client based on cdnKey (used under multi-CDN configuration)
FileClient fileClient = FileClientFactory.getClient(resourceFileForm.getCdnKey());
// Example 1
CdnFile cdnFile = FileClientFactory.getClient().upload(fileName, data/**byte[]*/);
// Example 2
String fileName = "pathname/" + file.getName();
FileClientFactory.getClient().uploadByFileName(fileName, is/**InputStream*/);The above configurations and examples help you quickly and accurately configure and use OSS services in Oinone.
5、Data Import/Export Configuration
pamirs:
file:
auto-upload-logo: false
import-property:
default-each-import: false # Default line-by-line import
max-error-length: 100 # Default maximum number of error lines collected
export-property:
default-clear-export-style: false # Default CSV export
csv-max-support-length: 1000000 # CSV export maximum support 1,000,000 lines(XV) Permission Configuration pamirs.auth
pamirs.auth is the core configuration item for fine-grained control of permission verification in the system, enabling flexible customization of permission checking rules for different model functions to meet diverse business needs and enhance system security and flexibility.
1、Core Configuration Item Description
pamirs.auth.fun-filter
This configuration item is used to specify that specific functions in the model do not require permission control. In some scenarios, certain functions may not need strict permission verification, and this configuration allows bypassing permission checks to improve system processing efficiency.
pamirs.auth.fun-filter-only-login
This configuration item is used to specify that specific functions in the model only need to verify whether the user is logged in. For functions that only require ensuring the user is logged in, this configuration simplifies the permission verification process.
2、Configuration Example
pamirs:
auth:
fun-filter-only-login:
- namespace: base.ViewAction
fun: homepage # Login
fun-filter:
- namespace: user.PamirsUserTransient
fun: login # LoginIn the above example, the homepage function under the base.ViewAction namespace only requires verifying whether the user is logged in, while the login function under the user.PamirsUserTransient namespace does not require any permission control. Developers can flexibly adjust the configuration content according to actual business needs to achieve precise permission management for different functions.
(XVI) Integration Platform Configuration pamirs.eip
Enable and customize open interface parameters quickly by configuring the open-api module, as specified below:
pamirs:
eip:
open-api:
enabled: true # Enable open interface function, false to disable
test: true # Enable test mode for debugging interface logic
route:
host: 0.0.0.0 # Open interface listening address
port: 9091 # Open interface listening port
aes-key: 6/whOst2CXbxmISUBz9+ayLwmNHsgSqbrNL2xGRMfe8= # AES encryption key for secure data transmission
expires: 7200 # Interface access token validity period (unit: seconds)
delay-expires: 300 # Token delay expiration time (unit: seconds)Through the above configuration, flexibly control the enable status, network listening parameters, and security policies of open interfaces. The enabled and test switches are used for quickly starting/stopping functions and debugging, while parameters under route ensure the security and timeliness of interface access.
(XVII) Distributed Cache Configuration pamirs.distribution
The configuration entry for Oinone's distributed cache is the Java class pro.shushi.pamirs.distribution.session.config.DistributionSessionConfig. All configuration paths are prefixed with pamirs.distribution.session, and core configuration items include:
- allMetaRefresh
- ownSign
The core configuration entry for Oinone's distributed cache is the Java class pro.shushi.pamirs.distribution.session.config.DistributionSessionConfig. All configuration paths are prefixed with pamirs.distribution.session, and core configuration items are as follows:
allMetaRefresh: In the distributed cache metadata refresh strategy configuration,allMetaRefreshhas a default value offalse, and the system automatically enables the delta update Redis mechanism; when this configuration item is set totrue, the system switches to the full update mode to ensure complete data synchronization.ownSign: Used to set a unique identifier for cached data, ensuring data uniqueness and traceability, avoiding local metadata pollution of the public environment in the R&D collaboration environment, and automatically merging dual-path caches when the request URL contains this parameter.
pamirs:
distribution:
session:
allMetaRefresh: true
ownSign: devUser1(XVIII) Middleware-Related Configurations
1、Message Queue Connection Configuration
Reference: Message Queue Connection Configuration in Event Configuration
2、Elasticsearch Configuration
Reference: Search Engine Configuration in Enhanced Model
3、Configuration Center pamirs.zookeeper
ZooKeeper serves as the configuration center for managing and storing the system's configuration information. By reasonably configuring related parameters, ensure stable connection and data interaction between the system and ZooKeeper services. The detailed configuration item descriptions and examples are as follows:
Configuration Item Description
zkConnectString: The connection string of the ZooKeeper server, specifying the address and port of the ZooKeeper cluster. Multiple server addresses are separated by commas.zkSessionTimeout: The timeout period for ZooKeeper sessions, in milliseconds. If there is no effective interaction with the ZooKeeper server within this time, the session is closed.rootPath: The root path for storing configuration information in ZooKeeper, where all configuration data is stored.
Configuration Example
pamirs:
zookeeper:
zkConnectString: 127.0.0.1:2181
zkSessionTimeout: 60000
rootPath: /trutorialsThrough the above configuration, the system connects to the local ZooKeeper server and manages configuration information under the /trutorials path. You can modify these configuration items according to the actual environment to adapt to different production environments.
4、Redis Configuration
When Oinone uses Redis, configure it through the Spring framework. The following is a detailed Redis configuration example, which you can flexibly adjust according to actual conditions.
spring:
redis:
database: 1
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
timeout: 5000
# password: Abc@1234
jedis:
pool:
# Maximum idle connections in the connection pool, default 8
max-idle: 16
# Minimum idle connections in the connection pool, default 0
min-idle: 4
# Maximum number of connections in the connection pool, default 8 (negative value means no limit)
max-active: 16
# Maximum blocking wait time for the connection pool (negative value means no limit), default -1
max-wait: 5000The above configuration sets Redis connection information and connection pool parameters. Among them, database can specify the database to use; host and port determine the address and port of the Redis server; timeout avoids long waits for connections; connection pool-related parameters (such as max-idle, min-idle, max-active, and max-wait) optimize the use and management of Redis connections to improve system performance.
5、RPC Configuration - Dubbo
Dubbo is a high-performance, lightweight open-source RPC framework. The following configuration enables remote service invocation and management based on Dubbo. The configuration example below covers core parameters such as service application information, registry, communication protocol, service consumers, and providers, which can be flexibly adjusted according to actual needs:
dubbo:
application:
# Current application name, used to identify the service's所属 (affiliated) application in the registry
name: trutorials-boot
# Current application version number, facilitating service version management and compatibility control
version: 1.0.0
registry:
# Registry address, using Zookeeper as the registry, connecting to the local port 2181
address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
protocol:
# Communication protocol uses Dubbo protocol
name: dubbo
# When the service port is set to -1, an available port is automatically allocated
port: -1
# Data serialization method, using pamirs serialization scheme here
serialization: pamirs
consumer:
# Timeout for service consumers to invoke services, in milliseconds, set to 5000 milliseconds
timeout: 5000
provider:
# Timeout for service providers to process requests, in milliseconds, set to 5000 milliseconds
timeout: 5000
scan:
# Automatically scan Dubbo service annotations under the specified package path, scanning pro.shushi and its sub-packages here
base-packages: pro.shushi
cloud:
subscribed-services: # Reserved configuration item for subscribed services, can be used to configure the list of cloud services to subscribe toWarning
In Oinone, the exclusive pamirs serialization scheme is uniformly used for serialization operations. If the configuration does not match this scheme, a serialization exception will be triggered during remote invocation.
(XIX) Environment Protection
The Oinone platform launches an environment protection function for partners, ensuring the secure execution of deployment operations such as configuration file modification and multi-JVM startup within the same environment through strict security protection.
1、Command-Line Configuration
-PenvProtected=${value}
The environment protection function of the Oinone platform is enabled by default (default value is true). This function compares the current configuration with the latest data stored in the base_platform_environment table in the database, combined with the configuration characteristics of each parameter for judgment. During system startup, if there is incorrect configuration content, it is printed in the startup log to help developers quickly locate and troubleshoot problems.
In addition, the environment protection function provides optimization suggestions for production configurations based on the comparison results. Developers can pay attention to relevant log content when starting the system to optimize production environment configurations.
-PsaveEnvironments=${value}
Whether to save the environment parameters of this startup to the database, default is true.
In some special cases, to avoid unnecessary changes to protection parameters in the public environment, we can choose not to save the configuration parameters of this startup to the database, which will not affect other JVMs from failing to start due to verification errors.
-PstrictProtected=${value}
Whether to use strict verification mode, default is false
It is generally recommended to enable strict verification mode in the public environment to maximally protect the public environment's metadata from interference by other environments.
Note
When enabling strict verification mode, avoid scenarios where different connection addresses are used for internal and external networks. If unavoidable, strict verification mode cannot be enabled.
2、Common Problems
How to migrate the database and change the database connection address?
- Migrate the original database to the new database.
- Modify the database connection address in the configuration file.
- Add
-PenvProtected=falseto the startup script to disable environment protection. - Start the JVM service, where error log prompts will be visible without interrupting the current startup.
- Remove
-PenvProtected=falsefrom the startup script or change the value totrue, and environment protection checks will continue at the next startup. - Check that the corresponding database connection configuration in the
base_platform_environmenttable has been modified. If other JVMs do not modify it correctly before startup, they will fail to start.
How to modify the Redis connection address to local during local development without affecting the public environment?
PS: Since the metadata cache in Redis is synchronized based on database deltas, this operation will cause the public environment to fail to correctly refresh the metadata cache in Redis during startup, requiring coordination with the pamirs.distribution.session.allMetaRefresh parameter. Unless specially necessary, we do not recommend using this form for collaborative development, as multiple configuration modifications increase the probability of errors.
- When starting the local environment for the first time, in addition to modifying Redis-related configurations, also configure
pamirs.distribution.session.allMetaRefresh=trueto initialize the newly connected local Redis. - When starting locally, add startup parameters
-PenvProtected=false -PsaveEnvironments=falseto ensure local startup does not modify public environment configurations and can pass environment protection checks normally. - After the local environment starts successfully and develops functions normally, when publishing to the public environment for testing, first modify the business project configuration
pamirs.distribution.session.allMetaRefresh=truein the public environment, then start the business project. - After starting the business project once, restore the configuration to
pamirs.distribution.session.allMetaRefresh=false.