Actions API
In the Oinone platform, Actions serve as the core units for constructing interactive logic. Through standardized definition methods, they enable business functions and data interaction in different scenarios. According to application scenarios and functional characteristics, actions are mainly divided into four types: View Actions, Link Actions, Client Actions, and Server Actions. The functions and applicable scenarios of each type are as follows:
Tip
This document helps you quickly master core concepts and basic logic. In addition to using Ux annotations and XML configuration, we also recommend using the designer for auxiliary development. The designer provides a visual operation interface, simplifies the configuration process, reduces coding complexity, helps you complete development tasks more efficiently and accurately, and significantly improves development efficiency and quality.
I. Server Action
In the Oinone system, Server Actions are core components for implementing backend business logic and data interaction. They define server requests and trigger button actions. Through annotation configuration and validation mechanisms, you can flexibly define request processing rules and data validation logic. The detailed description is as follows:
(Ⅰ) Server Action Configuration
Server actions can be quickly created using the @Action annotation. Here is a configuration example:
@Model.model(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL)
public class Demo {
@Action(
displayName = "Test Server Action",
contextType = ActionContextTypeEnum.CONTEXT_FREE,
bindingType = {ViewTypeEnum.TABLE, ViewTypeEnum.CHART}
)
public TestModel action(TestModel data) {
return data;
}
}Key configuration item analysis:
@ActionAnnotation: The core identifier used to define a method as a server action.contextType(Action Context Type):SINGLE: Suitable for single-row data operations, commonly used in the operation bar of each row in list pages or the top operation area of form pages.BATCH: For multi-row data processing, usually displayed in the batch operation button area above the table in list pages.SINGLE_AND_BATCH: Supports mixed single-row and multi-row operations, used in comprehensive operation scenarios of list pages.CONTEXT_FREE: No specific context restrictions, often used for general operation buttons at the top of list pages.
bindingType(Page Type Where the Button Is Located):TABLE: List page, used to display data lists and corresponding operation buttons.KANBAN: Kanban.FORM: Form page, suitable for data submission or editing operations.DETAIL: Detail page, used to view or modify details of a single piece of data.CALENDAR: CalendarGALLERY: GalleryTREE: Tree viewCUSTOM: Custom page to meet specific business needs.
(Ⅱ) Server Action Validation
In Oinone, data validation can be set not only at the model or field level but also for Server Actions through the @Validation annotation. For example:
@Model.model(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL)
public class Demo {
@Validation(ruleWithTips = {
@Validation.Rule(value = "!IS_BLANK(data.name)", error = "Name is required"),
@Validation.Rule(value = "LEN(data.name) <= 128", error = "Name is too long, cannot exceed 128 characters")
})
@Action(
displayName = "Test Server Action",
contextType = ActionContextTypeEnum.SINGLE,
bindingType = {ViewTypeEnum.FORM}
)
public TestModel action(TestModel data) {
return data;
}
}Built-in functions are used to quickly implement validations such as non-null and length checks. If validation fails, an error is反馈 (fed back) with the预设 (predefined) prompt.
(Ⅲ) Annotation Configuration
@Action
├── displayName Display name
├── summary Summary
├── contextType Action context, optional values see ActionContextTypeEnum
├── bindingType Page types where located, optional values see ViewTypeEnum
├── Advanced More configurations
│ ├── name Technical name, default is Java method name
│ ├── args Parameters, default is Java parameters
│ ├── type Method type, default is UPDATE, optional values see FunctionTypeEnum
│ ├── language Method implementation language, default is JAVA, optional values see FunctionLanguageEnum
│ ├── check Validation check, default is false
│ ├── invisible Hide rule
│ ├── bindingView Bind to specific view
│ └── priority Display order
II. View Action
View Actions play a crucial role in intra-system page navigation, and their routing function is achieved based on model codes and action names.
View Actions can be defined through the button UxRouteButton or the menu UxMenu.
(Ⅰ) Definition via Button UxRouteButton
Here is a detailed example of defining a View Action using the UxRouteButton annotation:
@UxRouteButton(
value = @UxRoute(
model = TestButtonModel.MODEL_MODEL, // Target model, clarifies the target model for navigation
viewType = ViewTypeEnum.TABLE, // Target view type, default is TABLE
viewName = ViewConstants.Name.tableView, // Target view for routing, selects the view of the corresponding type with the highest priority when empty
// Load function-related configurations
load = "newQueryPage", // Can manually specify other functions, such as newQueryPage in the example
// domain as frontend filter condition, the default query condition, users can remove it as needed
domain = "createDate =ge= '${ADD_DAY(NOW_STR(), -7)}' and createDate =lt= '${NOW_STR()}'", // Frontend filter condition, belongs to the default query condition, users can remove it
// filter as backend filter condition, will definitely be added, invisible to users
filter = "name =like= '老'",
// Context passing: data mapping
context = {},
title = "test"
),
action = @UxAction(
name = "customRedirectTablePage", // Name must be unique, otherwise overwriting occurs
label = "Custom Redirect to Table Page",
contextType = ActionContextTypeEnum.SINGLE,
bindingType = ViewTypeEnum.FORM, // On which types of views the button appears, default is TABLE
bindingView = ViewConstants.Name.formView, // In which views the button appears, selects the view of the corresponding type with the highest priority when empty
invisible = ExpConstants.idValueNotExist // Hide condition, !activeRecord.id hides when id exists. For example, hides on the new page without id, does not hide on the edit page with id
)
)
@Model.model(TestButtonModel.MODEL_MODEL)
@Model(displayName = "TestButtonModel Model")
public class TestButtonModel extends IdModel {
public static final String MODEL_MODEL = "test.TestButtonModel";
@Function(openLevel = FunctionOpenEnum.API)
@Function.Advanced(displayName = "Test Load Function", type = {FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY}, category = FunctionCategoryEnum.QUERY_PAGE)
public Pagination<TestButtonModel> newQueryPage(Pagination<TestButtonModel> page, IWrapper<TestButtonModel> queryWrapper) {
if (null == page) {
return null;
}
System.out.println("Test Load Function");
return new TestButtonModel().queryPage(page, queryWrapper);
}
}(Ⅱ) Definition via Menu UxMenu
@UxMenus
public class TestMenus implements ViewActionConstants {
@UxMenu("Test Menu")
class TestMenu {
@UxMenu("TestButtonModel")
@UxRoute(TestButtonModel.MODEL_MODEL)
class TestButtonModelMenu { }
}
}(Ⅲ) Load Function
The load function plays a key role in View Actions. When field mapping DSL is not configured, the load function is executed directly, with both input and output parameters being the target model. The system provides default convention functions, specifically:
- Target view form new: Calls the
constructinterface to load data, used to initialize data for new forms. - Target view form update: Calls the
queryOneinterface to load data, used to obtain the specific record to be updated. - Target view form detail: Calls the
queryOneinterface to load data, used to display detailed information of a specific record. - Target view table query: Calls the
queryPageinterface to load data, and can usedomainandlimitattributes to set query conditions and pagination counts for paginated data queries.
In addition, developers can also manually specify other load functions as needed to meet customized loading requirements. For example, in the above example, the load function is specified as newQueryPage.
(Ⅳ) Data Filtering
Data filtering is divided into frontend filtering (domain) and backend filtering (filter).
- Frontend Filtering (
domain):domainserves as the frontend filter condition, the default query condition, which users can remove as needed. - Backend Filtering (
filter):filterserves as the backend filter condition, which will definitely be added and is invisible to users. In the above example,filter = "name =like= '老'"means the backend will perform fuzzy matching filtering on thenamefield, and users cannot remove this filter condition.
Warning
The operator of frontend filtering (domain) must be consistent with the operator defined by the page search field; otherwise, the configuration is invalid. For example, for the name string field search, the default operator is =like=, and configuring it as another operator will not take effect.
(Ⅴ) Context Passing
Context passing is achieved through data mapping DSL, mainly used in the following two common scenarios:
- Navigation Between the Same Model: The default mechanism only passes the primary key. If other attribute data needs to be used, data mapping context needs to be configured.
- Navigation Between Different Models: The default mechanism attempts to pass the primary key, but if the primary key attribute names are inconsistent, data cannot be obtained. In this case, configuring the data mapping context can not only solve the problem of inconsistent primary key names but also map other attributes with different names for value passing.
In the above example, context = {} means no specific data mapping rules are currently configured and can be set according to actual needs.
Through the detailed introduction of the above configurations, load functions, data filtering, and context passing, developers can flexibly use View Actions to achieve efficient intra-system page navigation and data interaction.
III. Url Action
Url Actions focus on implementing external link navigation, guiding users to access external web pages, third-party systems, or resource links, providing a convenient channel for interaction between the system and external resources. Url Actions support definition through two methods: the button UxLinkButton and the menu UxMenu.
(Ⅰ) Definition via Button UxLinkButton
The UxLinkButton annotation can be used to create custom external link buttons. An example is as follows:
@UxLinkButton(
value = @UxLink(
// URL supports expressions and can dynamically拼接 (concatenate) parameters
value = "http://www.baidu.com?wd=${activeRecord.name}",
openType = ActionTargetEnum.OPEN_WINDOW,
// In Oinone, the URL calculation function has a higher priority than the value attribute. When both exist, the return value of the function is preferred as the URL
compute = "computeSearchUrl",
// Using context with value adds additional parameters, and with compute, it performs parameter conversion
context = {@Prop(name = "name", value = "activeRecord.name + 'aaa'")}
),
action = @UxAction(
name = "testComputeSearchUrl", // Action name must be unique
label = "Custom External Link",
contextType = ActionContextTypeEnum.SINGLE,
bindingType = ViewTypeEnum.FORM, // On which types of views the button appears, default is TABLE
bindingView = ViewConstants.Name.formView, // In which views the button appears, selects the view of the corresponding type with the highest priority when empty
invisible = ExpConstants.idValueNotExist // Hide condition, !activeRecord.id hides when id exists. For example, hides on the new page without id, does not hide on the edit page with id
)
)
@Model.model(TestButtonModel.MODEL_MODEL)
@Model(displayName = "TestButtonModel Model")
public class TestButtonModel extends IdModel {
public static final String MODEL_MODEL = "test.TestButtonModel";
// Custom URL calculation function
@Function(openLevel = FunctionOpenEnum.API)
@Function.Advanced(displayName = "Calculate Search Url", type = FunctionTypeEnum.QUERY)
public String computeSearchUrl(TestButtonModel data) {
System.out.println(data.getName());
return "https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=" + data.getName();
}
}Note
In Oinone, the compute function has a higher priority than the value attribute. When both are configured, the system preferentially uses the return value of the compute function as the final URL, and the configuration of the value attribute is ignored. For example, in the related example, even if the value attribute value is defined, as long as the compute function exists, the final URL will be dynamically generated by the function.
(Ⅱ) Definition via Menu UxMenu
Menu links can be quickly created through the UxMenu annotation. An example is as follows:
@UxMenus
public class TestMenus implements ViewActionConstants {
// Define a menu link named "Oinone Official Website"
@UxMenu("Oinone Official Website")@UxLink(value = "http://www.oinone.top", openType = ActionTargetEnum.OPEN_WINDOW)
class SsLink{}
}IV. Client Action
Client Actions are used to execute frontend interaction logic and can define trigger buttons through the UxClientButton annotation. A configuration example is as follows:
(Ⅰ) Definition of ClientAction
@UxClientButton(
// Associate with specific client function
value = @UxClient(ClientActionConstants.Import.fun),
action = @UxAction(
name = ClientActionConstants.Import.name, // Unique action identifier
label = ClientActionConstants.Import.label, // Button display name
contextType = ActionContextTypeEnum.CONTEXT_FREE // No context dependency
)
)
@Model.model(TestButtonModel.MODEL_MODEL)
@Model(displayName = "TestButtonModel Model")
public class TestButtonModel extends IdModel {
public static final String MODEL_MODEL = "test.TestButtonModel";
}Example: Corresponding Effect of the Example
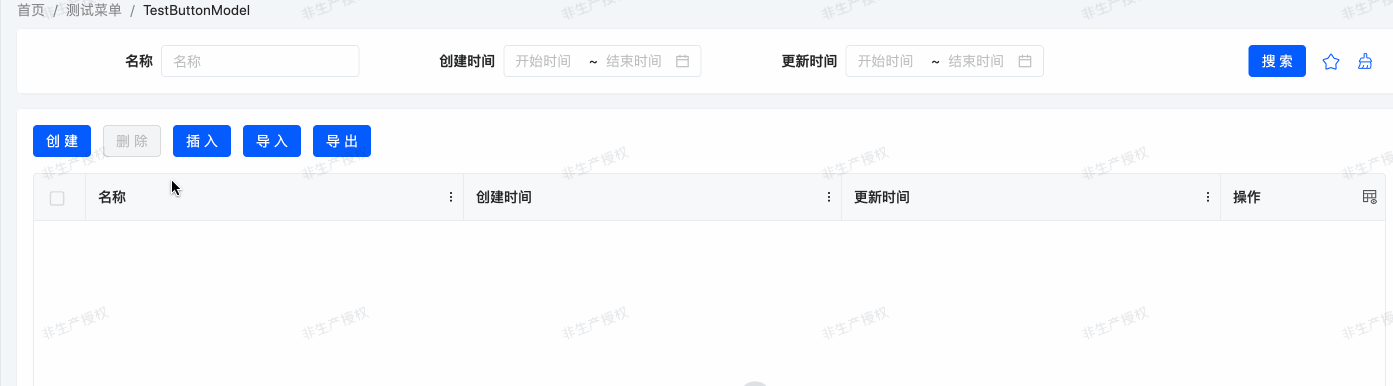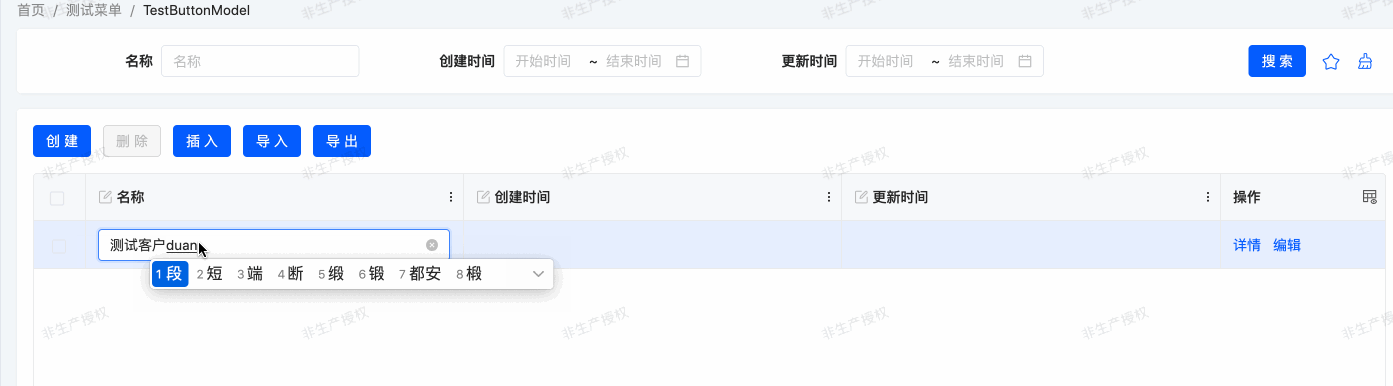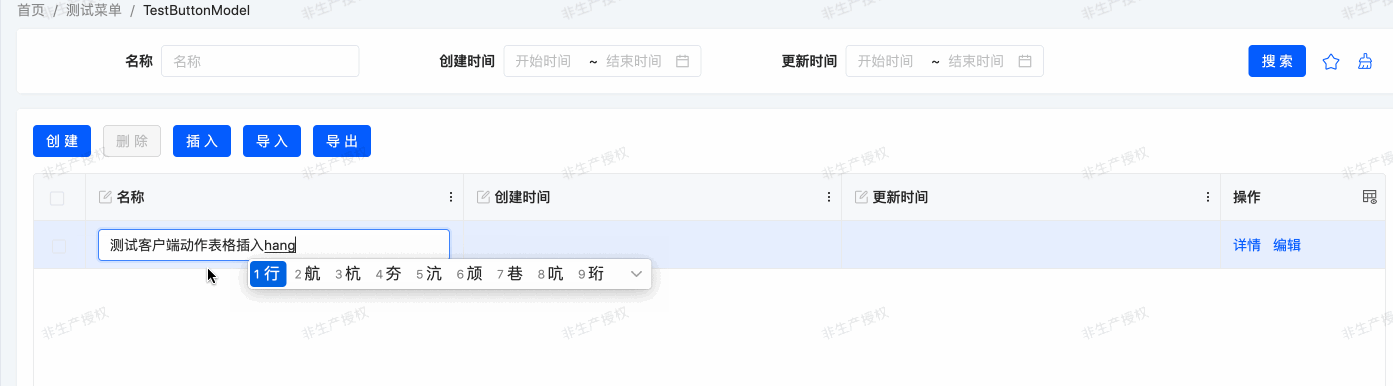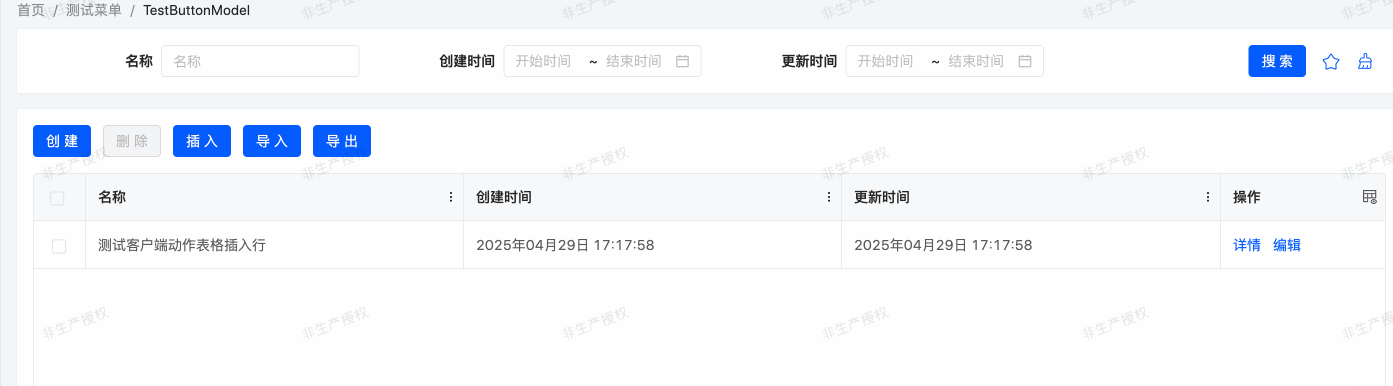
Client Actions use the currently selected row data as method input and return values, suitable for scenarios such as dynamic rendering of page elements, form validation, and pop-up prompts, helping developers efficiently implement frontend interaction functions.
(Ⅱ) Client Function List
| Function Identifier (fun) | Function Description (displayName) | Interface Display Label (label) | Detailed Description | Context Type (ActionContextTypeEnum) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
$$internal_ValidateForm | Form Data Validation | Validate | Validates the legitimacy of form input data | CONTEXT_FREE(No specific context dependency) |
$$internal_GotoListTableRouter | Return to Previous Page | Return | Implements page navigation to return to the previous page | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_ReloadData | Refresh Data | Refresh | Reloads data in the current page or table | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_GotoM2MListDialog | Open M2M Table Creation Pop-up | Add | Pops up a window for creating many-to-many relationship data | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_GotoO2MCreateDialog | Open O2M Table Creation Pop-up | Create | Pops up a window for creating one-to-many relationship data | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_GotoO2MEditDialog | Open O2M Table Edit Pop-up | Edit | Pops up a window for editing one-to-many relationship data | SINGLE(Acts on single-row data) |
$$internal_DeleteOne | Delete Selected Data in Bound Table | Delete | Deletes selected single or multiple rows of data in the table | SINGLE_AND_BATCH(Universal for single/multiple rows) |
$$internal_DialogSubmit | Submit Data in Pop-up | Confirm | Submits data filled in the pop-up and executes related operations | SINGLE_AND_BATCH |
$$internal_DialogCancel | Close Pop-up | Cancel | Closes the currently opened pop-up window | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_GotoListImportDialog | Open Import Pop-up | Import | Pops up a window for data import operations | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_GotoListExportDialog | Open Export Pop-up | Export | Pops up a window for data export operations | SINGLE_AND_BATCH |
$$internal_BatchUpdate | Batch Update | Confirm | Batch modifies selected multiple rows of data | SINGLE |
$$internal_AddOne | Add a Row of Data | Insert | Adds a new row of data in the table or list | CONTEXT_FREE |
$$internal_CopyOne | Copy a Row of Data | Copy | Copies the currently selected single row of data | SINGLE |
Description: These predefined functions are suitable for common business scenarios. fun serves as the unique identifier for program calls; displayName is the functional description to help developers understand the logic; label is the button/operation name displayed in the user interface; and ActionContextTypeEnum clarifies the applicable data operation scope of the function (e.g., single row, multiple rows, or no restriction).