Import and Export
I. Overview
In Oinone, the import/export function is processed through Excel files as a medium, which is also a common approach in most management information systems.
During the functional design, we found that any worksheet can be split into non-repeating blocks for independent design, which is one of the design highlights of Oinone's import/export template design.
The Excel import/export template simplifies the complexity of flexibly defining a single worksheet in a business system through multi-block design. When using Oinone's import/export function, the flexible decomposition of worksheets is an essential skill.
The following will start from the concept of Excel template design and step-by-step help readers learn to use the import/export function to meet business needs.
(Ⅰ) Excel Template Design Concepts
1. Noun Explanations
- Workbook: An Excel file is called a workbook.
- Sheet: A workbook contains multiple worksheets.
- Block: A worksheet contains multiple blocks, and the order of blocks is continuous across multiple worksheets.
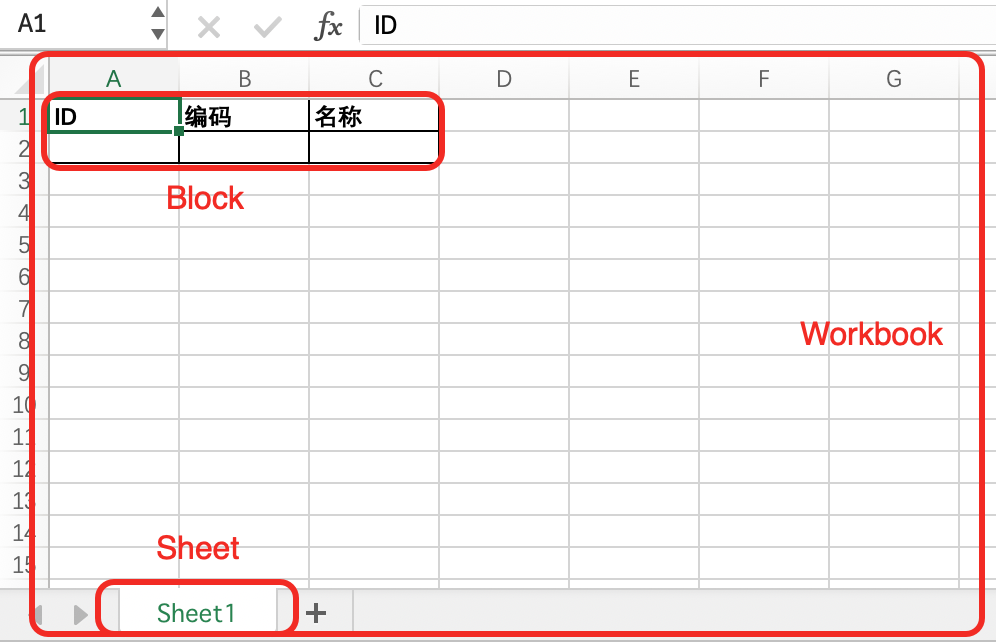
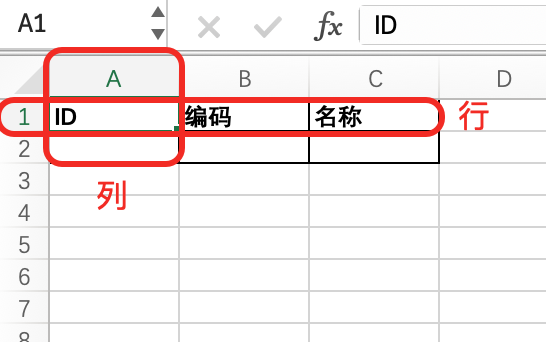
- Row: A collection of all cells in the horizontal direction of a worksheet.
- Col: A collection of all cells in the vertical direction of a worksheet.
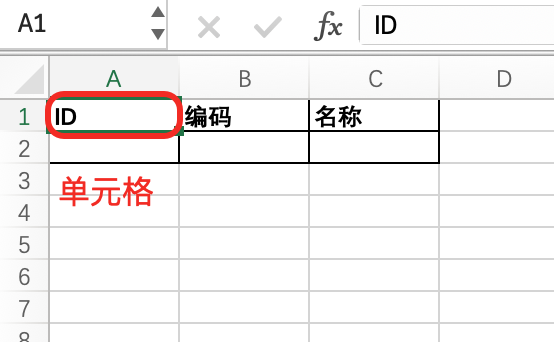
- Cell: The smallest unit for data storage located by coordinates like
A1.
- Analysis Type
- Fixed Header: Similar to a "table", multiple data entries are filled "downward" according to the format defined by the "header".
- Fixed Format: Similar to a "form", a single data entry is filled according to the format defined by "cells".
- Direction
- Horizontal: Sub-elements are arranged horizontally and filled vertically.
- Vertical: Sub-elements are arranged vertically and filled horizontally.
2. Fixed Header
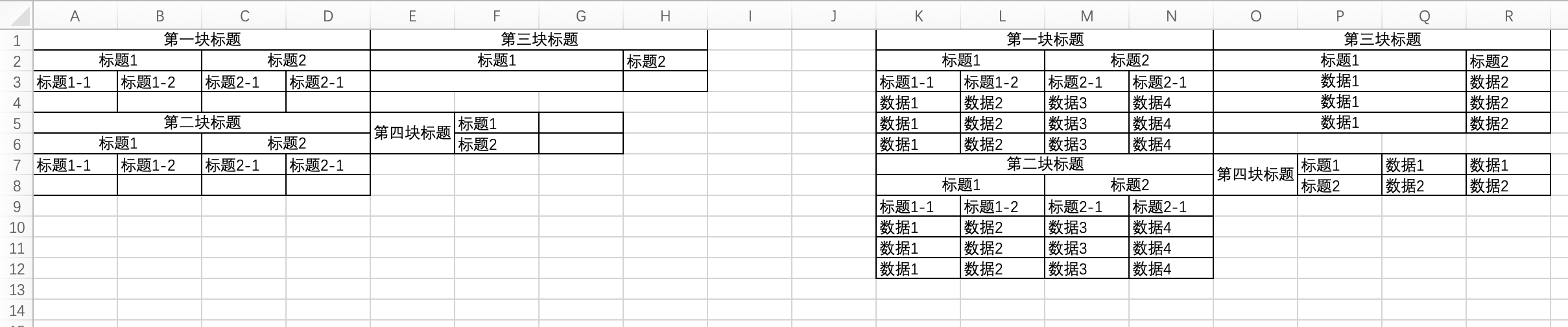
As shown in the figure, the left side is the design area, and the right side is the filled result, consisting of four blocks in total.
- The first block: Allows defining multi-level headers.
- The second block: Two vertically arranged blocks, where the second block will shift downward according to the number of filled contents in the first block.
- The third block: When the "last level row" has a style, the original style will be retained during filling. As shown in the figure, the merged cell style will be retained during filling.
- The fourth block: When the "arrangement direction" is set to vertical, the header will automatically "transpose rows and columns" and perform horizontal filling.
3. Fixed Format
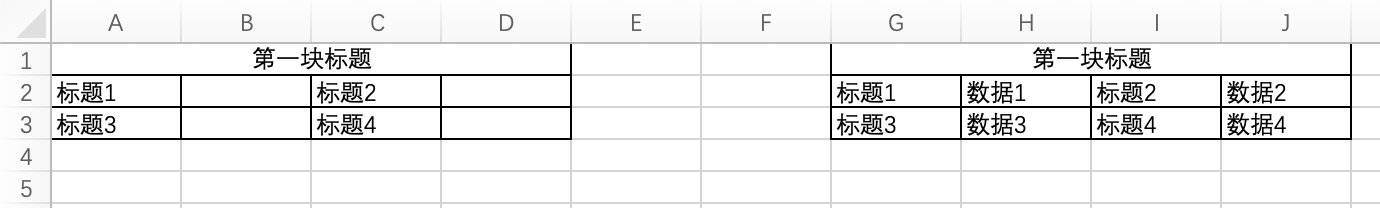
As shown in the figure, the left side is the design area, and the right side is the filled result, with only one block. Obviously, the filling method of the fixed format is much simpler than that of the fixed header, as it only fills the data into the designed positions.
4. Design Scope
For different "analysis types", the design scope varies slightly:
- Fixed Header: The design scope needs to expand one row in the filling direction.
- Fixed Format: The design scope is exactly the same as the Excel-defined scope.
(Ⅱ) Model Topology Diagram
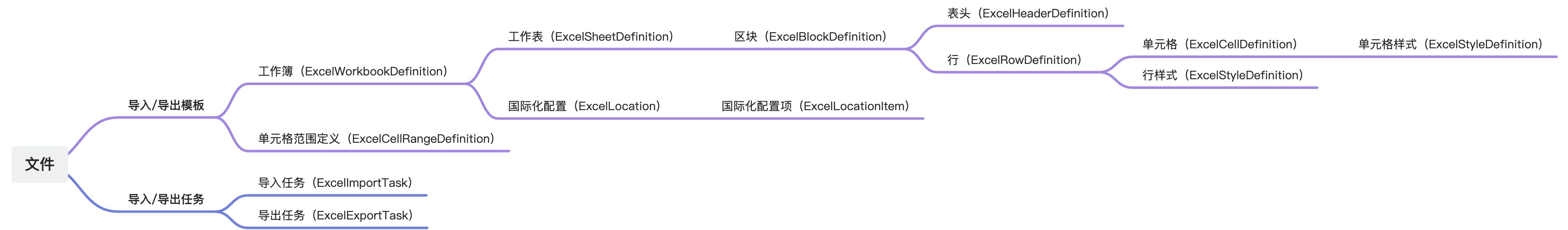
Tip:
For more content about the "file module" related APIs, please refer to: Reference List - Model
II. Preparation
When using the file import/export function, you need to introduce the pamirs-file2-core package dependency in pamirs-demo-boot and add the file module in the startup module.
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.core</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-file2-core</artifactId>
</dependency>pamirs:
boot:
modules:
- fileIf you need to define import/export templates or customize import/export logic in the module, you need to introduce the pamirs-file2-api package dependency in pamirs-demo-api:
<dependency>
<groupId>pro.shushi.pamirs.core</groupId>
<artifactId>pamirs-file2-api</artifactId>
</dependency>In Oinone, in addition to introducing the corresponding dependencies, you also need to declare the corresponding module dependencies in the current module definition:
……
@Module(
name = DemoModule.MODULE_NAME,
displayName = "Demo Module",
version = "1.0.0",
priority = 1,
dependencies = {
……
FileModule.MODULE_MODULE,
……
}
)
……
public class DemoModule implements PamirsModule {
……
}III. Yaml Configuration
pamirs:
boot:
modules:
- file
file:
auto-upload-logo: false # Automatically upload the logo when starting
auto-create-template: true # Automatically generate Excel templates when starting
import-property:
default-each-import: false # Default to import row by row
max-error-length: 100 # Default maximum number of error rows to collect
export-property:
default-clear-export-style: false # Default to use CSV export
excel-max-support-length: 100000 # Excel export supports up to 100,000 rows
csv-max-support-length: 1000000 # CSV export supports up to 1,000,000 rowsIV. Creating Templates
(Ⅰ) Creating Templates with ExcelHelper
In the previous "Tutorial - File Import and Export", we have initially used the ExcelHelper utility class to create a simple fixed-header Excel template. Let's first briefly review it:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(ExcelHelper.fixedHeader(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createBlock("Test Model", TestModel.MODEL_MODEL)
.addColumn("code", "Code")
.addColumn("name", "Name")
.addColumn("user.login", "User Account")
.build());
}
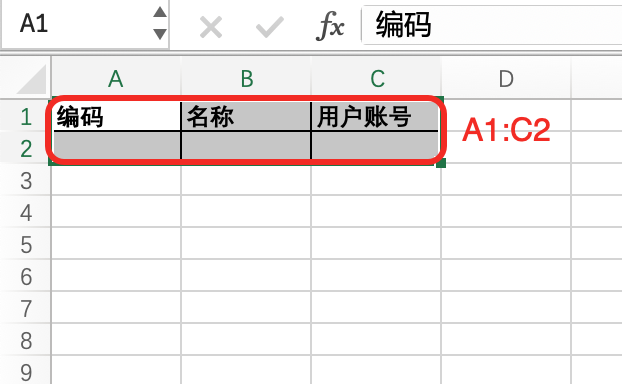
}ExcelHelper#fixedHeader is a simplified way to create fixed-header type templates, which essentially creates templates through WorkbookDefinitionBuilder. It simplifies some common functions:
- createBlock: A combined call to
createSheetandcreateBlock, and the utility class also provides separate call methods. - Automatically calculates the design area. When
addColumnis called, a column is added, and the design area will expand horizontally. - Simplifies the one-to-one correspondence between configuration rows and headers, which can be reflected in the next section.
The content of the Excel template created in this way will be explained in detail in the next section.
Tip:
After calling ExcelHelper#fixedHeader, an ExcelFixedHeadHelper object is created to provide some simple methods to create workbooks. If there are scenarios where settings or definitions are not possible, please use WorkbookDefinitionBuilder to create templates.
Tip:
Here we choose to use the "import template" for demonstration, aiming to quickly see the effect of the Excel file through the "download import template" function. The content of the import template is exactly the same as the design content.
Readers can create "export templates" by themselves to try some of the functions used in the examples. Only examples of "import templates" will be provided in this chapter.
(Ⅱ) Creating Templates with WorkbookDefinitionBuilder
Let's see the corresponding code when using WorkbookDefinitionBuilder to create the same template as in the previous section using ExcelHelper:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$C$2")
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(Boolean.TRUE)
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("User Account").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}We can see that the process of creating an Excel workbook is handled step by step:
- Create a workbook and set properties.
- Create a worksheet.
- Create a block and set properties.
- Create a configuration row for field declaration, which is not displayed in the Excel workbook.
- Create a header row, which is the static content displayed in the Excel workbook.
PS: The and method is used to "return to the upper layer" for construction.
A brief introduction to each method is as follows:
- createSheet combined with and: Create a worksheet and specify the worksheet name.
- createBlock combined with and: Create a block and specify the block's corresponding analysis type, arrangement direction, model, and design area.
- createHeader combined with setIsConfig(true): Create a configuration row, just specify the fields.
- createHeader combined with and: Create a header row, just specify the cell content.
- ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle: Create a default style: full border cells; horizontal normal alignment; vertical center; 11-point font; no bold.
- setBold(true): Set font bold.
The Excel template file created in this way is as follows:
Tip:
- The design scope can be expressed in the syntax format of Excel cell positioning, and the fixed-header type block needs to expand one row in the filling direction.
- The row style set in the header row will use the row style as the cell style when the cell style is not set, which can be understood as the row style being the default style for all cells in this row.
- The row style set in the configuration row will be used by each filled cell during data filling.
Warning:
"Chain calling" is a relatively clear usage provided by the "file module" when designing the API based on the characteristics of the data structure. However, in Java, the stack length of chain calling has certain limitations. If the exception "java: Compilation failed: internal java compiler error" occurs during compilation, you can "break" the chain calling by assigning values to variables to make the program run normally.
(Ⅲ) Creating Fixed Format Templates
Now let's look at the creation method of the "fixed format" template, which is similar to the fixed header template. The only difference is that the title and fields are defined at intervals, and they are created line by line in full accordance with the Excel cell order, as shown in the following code:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_FORMAT, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$D$2")
.createMergeRange("B2:D2")
.createHeader().setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.and()
.createRow().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle())
.createCell().setValue("Code").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.and()
.createRow().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle())
.createCell().setValue("User Account").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}After we create this template, we can see the content of the following Excel file through the "download import template" function:
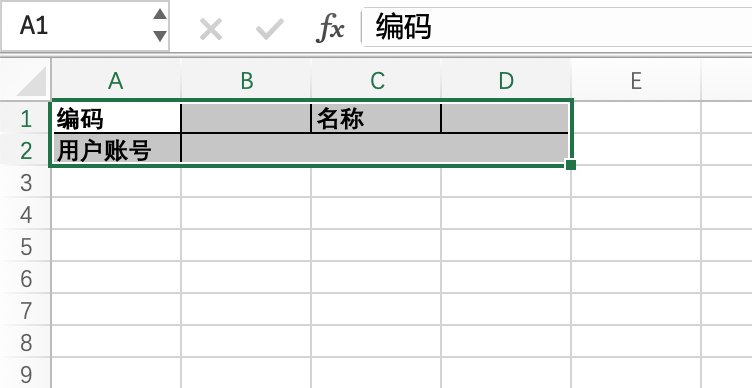
Tip:
In this example, we used createMergeRange to create merged cells, and its coordinate positioning method is exactly the same as that supported by Excel files.
It should be noted that if merged cells are created after createSheet, they will not change according to the block filling. Readers can try using the merged cell function in the "fixed header" export template to see the difference in the merged effect.
(Ⅳ) Creating Import Templates with Preset Rows
1. Creating Preset Empty Rows with the setPresetNumber Method
Based on the example code in the second section, set 10 preset empty rows by setPresetNumber(10). The example code is as follows:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$C$2")
.setPresetNumber(10)
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("User Account").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}The content of the downloaded import template Excel file is as follows:
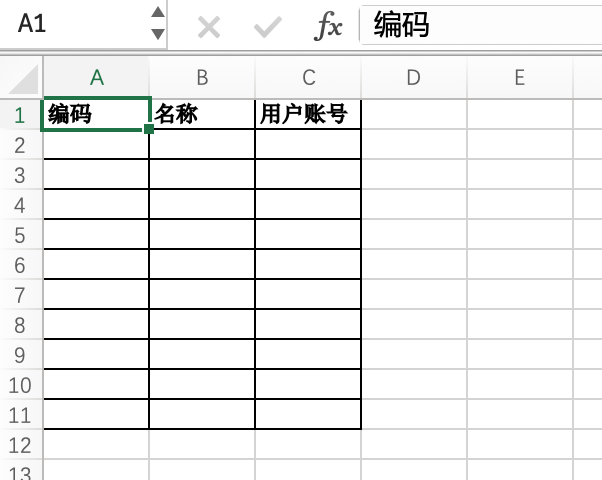
2. Creating Custom Content Preset Rows with the createRow Method
In addition to preset empty rows, we can also use the createRow method to create rows and set corresponding values to customize preset rows. This is very meaningful in import templates with example entries. The example code is as follows:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$C$2")
.setPresetNumber(10)
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("User Account").and()
.and()
.createRow()
.createCell().setValue("This is the code").and()
.createCell().setValue("This is the name").and()
.createCell().setValue("This is the user account").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}The content of the downloaded import template Excel file is as follows:
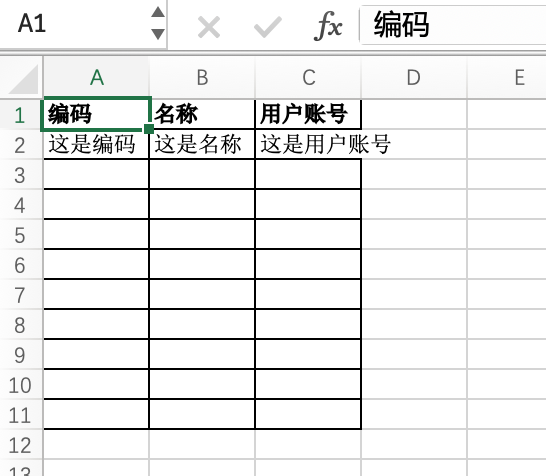
Tip:
The setPresetNumber method sets the total number of preset empty rows. If a preset row is manually created, the insufficient part will be automatically supplemented when adding preset rows. For example, the total number of preset rows in the example is 10. Since a preset row is manually created, only 9 preset empty rows are supplemented in the end.
(Ⅴ) Enabling Auto Column Width
In the example of creating custom preset rows through createRow above, we found that the data in the "This is the user account" cell exceeds the cell. So, how to solve this problem?
We can use the "auto column width" function to automatically calculate the column width according to the content length to handle this problem. Let's enable the "auto column width" function for this column through the setAutoSizeColumn method in the corresponding configuration row field. The example code is as follows:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$C$2")
.setPresetNumber(9)
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("User Account").and()
.and()
.createRow()
.createCell().setValue("This is the code").and()
.createCell().setValue("This is the name").and()
.createCell().setValue("This is the user account").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}The content of the downloaded import template Excel file is as follows:
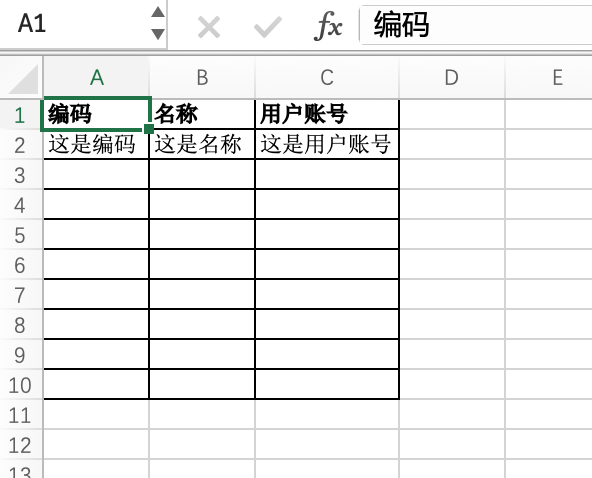
Tip:
When exporting, if the data is particularly long, the auto column width function is not a universal solution. In this case, we need to use fixed column width to solve the problem of abnormal display when the data is too long.
We can change setAutoSizeColumn to the following:
setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle().setWidth(3000))
Unit issue: The width unit provided by POI is different from the unit usually used in Excel, and errors may occur in actual use, which need to be debugged independently.
(Ⅵ) Multi-Level Headers
The example code is as follows:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$C$2")
.createMergeRange("$A1:$B1")
.setPresetNumber(10)
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Basic Information").and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().setValue("User Information").and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("User Account").and()
.and()
.createRow()
.createCell().setValue("This is the code").and()
.createCell().setValue("This is the name").and()
.createCell().setValue("This is the user account").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}The content of the downloaded import template Excel file is as follows:
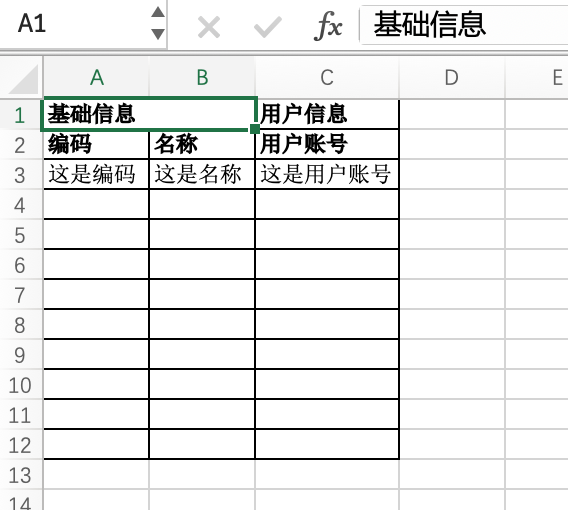
(Ⅶ) Mixed Format
The example code is as follows:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_FORMAT, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$D$2")
.createMergeRange("$B$2:$D$2")
.createHeader().setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.createCell().setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.createCell().setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.createCell().setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.and()
.createRow().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle())
.createCell().setValue("Code").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.and()
.createRow().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle())
.createCell().setValue("User Account").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.and()
.and()
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$3:$D$4")
.setPresetNumber(10)
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setField("partners[*].name").and()
.createCell().setField("partners[*].partnerType").and()
.createCell().setField("partners[*].phone").and()
.createCell().setField("partners[*].email").and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Partner Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("Partner Type").and()
.createCell().setValue("Partner Phone").and()
.createCell().setValue("Partner Email").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}The content of the downloaded import template Excel file is as follows:
Tip:
For the setting properties of Excel rows/columns, if there is a conflict, it will only take effect in the uppermost or leftmost configuration row. For example, the auto column width property is configured in the cell of the configuration row of the first block.
(Ⅷ) Creating Multi-Worksheet Templates
The example code is as follows:
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(WorkbookDefinitionBuilder.newInstance(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createSheet("Test Model")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_FORMAT, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$D$2")
.createMergeRange("$B$2:$D$2")
.createHeader().setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.and()
.createRow().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle())
.createCell().setValue("Code").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("code").and()
.createCell().setValue("Name").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("name").and()
.and()
.createRow().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle())
.createCell().setValue("User Account").setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true))).and()
.createCell().setField("user.login").and()
.createCell().and()
.createCell().and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.createSheet("Partner List")
.createBlock(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum.FIXED_HEADER, ExcelDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL, "$A$1:$D$2")
.setPresetNumber(10)
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle()).setIsConfig(true)
.createCell().setField("partners[*].name").setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.createCell().setField("partners[*].partnerType").setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.createCell().setField("partners[*].phone").setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.createCell().setField("partners[*].email").setAutoSizeColumn(true).and()
.and()
.createHeader().setStyleBuilder(ExcelHelper.createDefaultStyle(v -> v.setBold(true)))
.createCell().setValue("Partner Name").and()
.createCell().setValue("Partner Type").and()
.createCell().setValue("Partner Phone").and()
.createCell().setValue("Partner Email").and()
.and()
.and()
.and()
.build());
}
}The content of the downloaded import template Excel file is as follows:
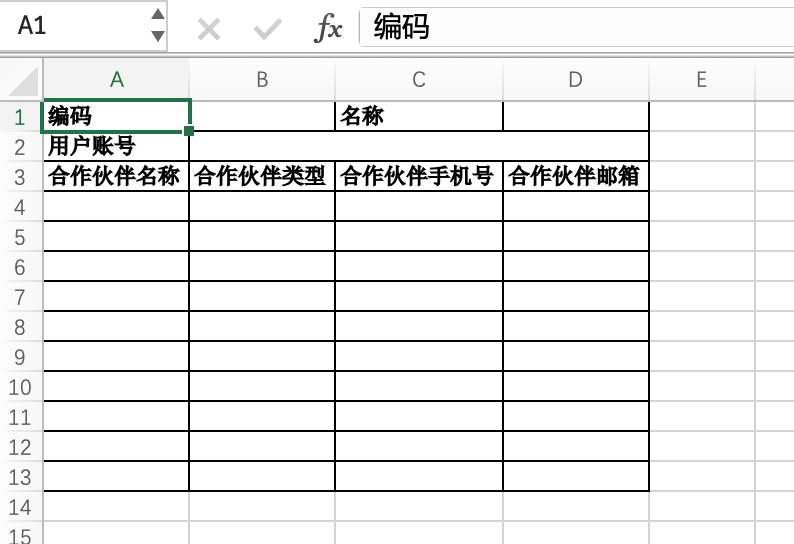
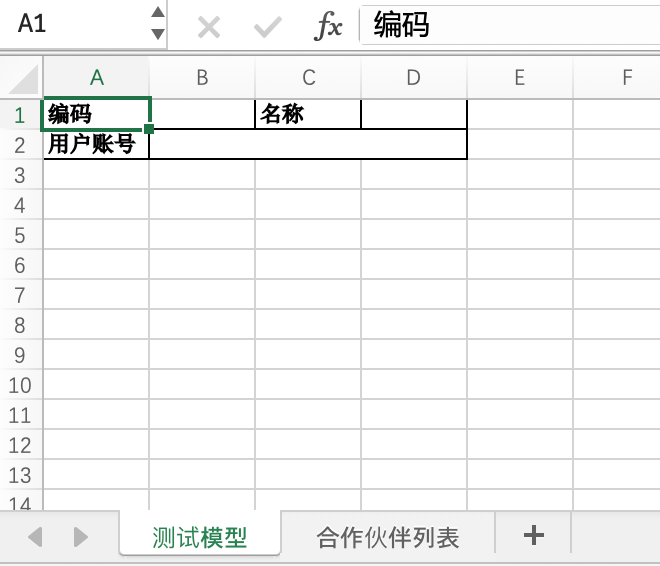
- Test Model Worksheet
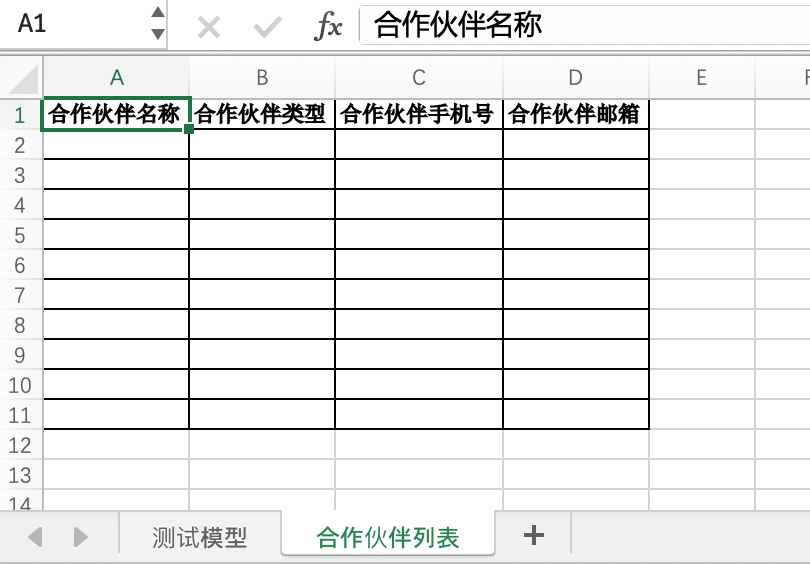
- Partner List
V. Custom Import/Export Logic
Whether it is import logic or export logic, both use "extension points" to process their logic. The following respectively introduce the basic usage and processing methods for common scenarios of import extension points and export extension points.
The extension point uses the expression attribute to configure expressions to determine under what conditions the corresponding extension point is executed. For the usage of expressions, please refer to: Function API - Expression
(Ⅰ) Model Explanation
- Workbook Model: The model code used when selecting a template on the page.
- Block Model: The model code actually used for import/export.
Take the example code in the "Creating Templates with ExcelHelper" section as an example: (To distinguish different models, the following code has been slightly modified)
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(ExcelHelper.fixedHeader(TestModel1.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.createBlock("Test Model", TestModel2.MODEL_MODEL)
.addColumn("code", "Code")
.addColumn("name", "Name")
.addColumn("user.login", "User Account")
.build());
}
}It can be seen that:
- The first parameter of the
ExcelHelper#fixedHeadermethod is:TestModel1.MODEL_MODEL, and this model code is the "workbook model", which is recorded in theExcelWorkbookDefinition#modelfield. - The second parameter of the
createBlockmethod is:TestModel2.MODEL_MODEL, and this model code is the "block model", which is recorded in theExcelBlockDefinition#bindingModelfield.
(Ⅱ) Custom Import Extension Points
Using import extension points by the template's defined name is one of the most basic usages:
@Component
@Ext(ExcelImportTask.class)
public class TestModelImportExtPoint implements ExcelImportDataExtPoint<TestModel> {
@ExtPoint.Implement(expression = "importContext.definitionContext.name==\"" + TestModelImportTemplate.TEMPLATE_NAME + "\"")
@Override
public Boolean importData(ExcelImportContext importContext, TestModel data) {
// do something to import.
return true;
}
}- @Ext(ExcelImportTask.class): Annotation for fixed parameters of import extension points.
- ExcelImportDataExtPoint: Interface definition for import extension points.
- ExcelImportContext: Excel import context, including Excel template definitions and other import所需 information.
- TestModel: The JAVA type corresponding to the "block model".
Tip:
In the expression, importContext is the method parameter name, and the value in the object is obtained by the notation separated by ".". This is the value-taking usage of the expression, and the expression attribute of the extension point requires that the calculation result must be of type Boolean (Boolean). The expression in the example can be stated as: Execute the current extension point when the template name is testModelImportTemplate.
1. Data Validation
There are two ways to interrupt during data validation:
- Interrupt by "throwing an exception" or "returning false", and data reading will no longer continue at this time.
- Interrupt by returning true, and data reading will continue at this time.
Exception interruption, no longer importing data: (Recommended)
public Boolean importData(ExcelImportContext importContext, TestModel data) {
String code = data.getCode();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(code)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Code is not allowed to be empty");
}
// Other processing logic
return true;
}Tip:
The exception here is not directly interacted with the front end, and any JAVA built-in exception can be used.
"return false" interruption, add error prompt information, and no longer continue reading data:
public Boolean importData(ExcelImportContext importContext, TestModel data) {
String code = data.getCode();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(code)) {
importContext.getImportTask().addTaskMessage(TaskMessageLevelEnum.ERROR, "Code is not allowed to be empty");
return false;
}
// Other processing logic
return true;
}Only add error prompt information and continue reading data:
public Boolean importData(ExcelImportContext importContext, TestModel data) {
String code = data.getCode();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(code)) {
importContext.getImportTask().addTaskMessage(TaskMessageLevelEnum.ERROR, "Code is not allowed to be empty");
return true;
}
// Other processing logic
return true;
}2. Row-by-Row Import
If you need to collect error information and generate the corresponding Excel error file, you need to configure eachImport = true in the template to enable the row-by-row import function.
@Component
public class TestModelImportTemplate implements ExcelTemplateInit {
public static final String TEMPLATE_NAME = "testModelImportTemplate";
@Override
public List<ExcelWorkbookDefinition> generator() {
return Collections.singletonList(ExcelHelper.fixedHeader(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL, TEMPLATE_NAME)
.setDisplayName("Test Model Import")
.setType(ExcelTemplateTypeEnum.IMPORT)
.setEachImport(true)
.createBlock("Test Model", TestModel.MODEL_MODEL)
.addColumn("code", "Code")
.addColumn("name", "Name")
.addColumn("user.login", "User Account")
.build());
}
}Tip:
After enabling the row-by-row import function, only "exception interruption" will collect error information, and other interruption methods will not generate an "import error file".
3. Batch Processing of Imported Data
For business scenarios with requirements for import performance, you can control the access frequency between the import extension point and database operations by yourself. For example, after each row of data enters, we can first save it in the "data buffer" provided by the "read context" and perform batch processing on all data until the last row is reached. The example code is as follows:
public Boolean importData(ExcelImportContext importContext, TestModel data) {
// Data validation
String code = data.getCode();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(code)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Code is not allowed to be empty");
}
// Get/create cache data set
List<TestModel> dataList = importContext.getDataBuffer(0, ArrayList::new);
// Determine if reading is complete
if (importContext.getCurrentListener().hasNext()) {
dataList.add(data);
} else {
new TestModel().createOrUpdateBatch(dataList);
}
return true;
}4. Multi-Block Import Data Processing
Whether a worksheet has multiple blocks or multiple worksheets each have a block, it is generally multi-block processing.
For each block, we have the corresponding block model and the JAVA type corresponding to the model code. We can distinguish these specific JAVA types according to the block model or block index to facilitate us to operate the data in the code. The example code is as follows:
public Boolean importData(ExcelImportContext importContext, Object data) {
if (importContext.getCurrentBlockNumber() == 0) {
TestModel1 testModel1 = (TestModel1) data;
// Test model 1 processing
} else if (importContext.getCurrentBlockNumber() == 1) {
TestModel2 testModel2 = (TestModel2) data;
// Test model 2 processing
}
// Other processing logic
return true;
}(Ⅲ) Custom Export Extension Points
Using export extension points by the template's defined name is one of the most basic usages:
@Component
@Ext(ExcelExportTask.class)
public class TestModelExportExtPoint extends ExcelExportSameQueryPageTemplate implements ExcelExportFetchDataExtPoint {
@ExtPoint.Implement(expression = "context.name==\"" + TestModelExportTemplate.TEMPLATE_NAME + "\"")
@Override
public List<`Object`> fetchExportData(ExcelExportTask exportTask, ExcelDefinitionContext context) {
List<`Object`> dataList = super.fetchExportData(exportTask, context);
// do something to export.
return dataList;
}
}- @Ext(ExcelExportTask.class): Annotation for fixed parameters of export extension points.
- ExcelExportFetchDataExtPoint: Interface definition for export extension points.
- ExcelExportSameQueryPageTemplate: The default implementation for export extension points to obtain data by default, including Hook calls, which is exactly the same as the front-end发起 queryPage request.
- List<
Object>: Block data, defined by block index. For questions about return values, specific explanations can be found in the following text.
1. Export Extension Point Return Value
In order to make the data acquisition function of the export extension point more general, its return value represents block data.
Suppose we have a template with two blocks:
- The first block is of "fixed format" type, and its data structure is "Object".
- The second block is of "fixed header" type, and its data structure is "List".
Then, the pseudocode of its return value can be expressed as:
public List<`Object`> fetchExportData(ExcelExportTask exportTask, ExcelDefinitionContext context) {
// First block data
TestModel data1 = new TestModel();
// Second block data
List<TestModel> data2 = new ArrayList<>();
// Combine into a list in the order defined by the blocks
return Lists.newArrayList(data1, data2);
}2. Using Permission Filtering When Exporting
Since the export function does not go through the front-end request, the Hook function is not used. When we perform custom data acquisition, we need to use the meta-instruction API to make the Hook take effect. For more content about the meta-instruction API, please refer to: Meta-Instruction API
The following code example shows how to achieve exactly the same query logic as the default extension point through custom data acquisition:
@Component
@Ext(ExcelExportTask.class)
public class TestModelExportExtPoint implements ExcelExportFetchDataExtPoint {
@ExtPoint.Implement(expression = "context.name==\"" + TestModelExportTemplate.TEMPLATE_NAME + "\"")
@Override
public List<`Object`> fetchExportData(ExcelExportTask exportTask, ExcelDefinitionContext context) {
// The query logic needs to be wrapped and run through meta-instructions, otherwise the Hook will not take effect
List<TestModel> dataList = Models.directive().run(() -> {
// Concatenate the incoming RSQL expression, which is usually only effective for the first block
IWrapper<TestModel> wrapper = exportTask.temporaryRsql(exportTask.getWorkbookDefinition().getDomain(), () -> Optional.ofNullable(exportTask.getConditionWrapper())
.map(ConditionWrapper::<TestModel>generatorQueryWrapper)
.orElseGet(() -> Pops.<TestModel>query().ge(SqlConstants.ID, 0)));
wrapper.setModel(TestModel.MODEL_MODEL);
// Use the query method with interception
return Models.data().queryListByWrapper(wrapper);
}, SystemDirectiveEnum.BUILT_ACTION, SystemDirectiveEnum.HOOK);
// Other processing logic
return Lists.newArrayList(dataList);
}
}Warning:
Similar to other overridden functions, some built-in export logics will no longer take effect due to overriding extension points. For example: built-in functions such as dataset size verification and automatic query of associated relationship field data. For the query operation of associated relationship fields, you can decide whether to query according to the content defined in the template.
Tip:
If the query logic needs to be customized, only implement the ExcelExportFetchDataExtPoint interface.
If calculation is required after querying, you can use the ExcelExportSameQueryPageTemplate class to assist in querying. Auxiliary query can only be used for the first block.
VI. Reference List
(Ⅰ) Models
1. Excel Workbook (ExcelWorkbookDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | Yes | The defined name of the Excel workbook | |
| displayName | String | Yes | The display name of the Excel workbook | |
| filename | String | No | The file name used for export. If not specified, the name is used as the file name by default | |
| model | String | Yes | The model code is used to determine which model's table page the import/export is displayed on, and is not used for model operations | |
| bindingViewName | String | No | When a view is specified, this template is only displayed in the specified view | |
| type | ExcelTemplateTypeEnum | Yes | IMPORT_EXPORT | The template type |
| version | OfficeVersionEnum | Yes | AUTO | The Office version. For import, it is automatically identified by the file name suffix. If there is no suffix, it needs to be manually specified. For export, the new version is used by default |
| sheetList | List<ExcelSheetDefinition> | No | The worksheet list. When the worksheet index is specified, there is one and only one object. Otherwise, it is arranged in order according to the number of sheets in the Excel file | |
| redirectUri | String | No | The redirect address for downloading the import template | |
| sheetDefinitions | String | Yes | The worksheet definition JSON string | |
| definitionContext | String | No | The parsed content of the cached workbook definition | |
| dataStatus | DataStatusEnum | Yes | ENABLED | The data status |
| importStrategy | ExcelImportStrategyEnum | No | STANDARD | The import strategy |
| exportStrategy | ExcelExportStrategyEnum | No | STANDARD | The export strategy |
| hasErrorRollback | Boolean | Yes | false | Rollback when an error occurs |
| maxErrorLength | Integer | Yes | 100 | The maximum number of errors |
| clearExportStyle | Boolean | Yes | false | Clear the export style and use the CSV format for export |
| excelMaxSupportLength | Integer | No | The maximum number of rows supported for Excel format export | |
| csvMaxSupportLength | Integer | No | The maximum number of rows supported for CSV format export | |
| templateSource | ExcelTemplateSourceEnum | No | CUSTOM | The template source |
| locations | List<ExcelLocation> | No | The internationalization configuration | |
| defaultShow | Boolean | No | Whether to display by default | |
| show | Boolean | No | Whether to display | |
| eachImport | Boolean | No | false | Import row by row |
| domain | String | No | The default filtering rule, RSQL expression | |
| excelImportMode | ExcelImportModeEnum | No | MULTI_MODEL | The import mode |
| lang | String | No | The language to which the template belongs |
2. Excel Sheet (ExcelSheetDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | No | Specify the worksheet name. When the worksheet name is not specified, the display name of the model is used by default. When no model is bound and generated, it defaults to using「Sheet + ${index}」as the worksheet name | |
| autoSizeColumn | Boolean | No | true | Auto column width |
| onceFetchData | Boolean | No | This attribute is only valid when it contains a [fixed format] block, and all blocks must have the same bound model | |
| blockDefinitionList | List<ExcelBlockDefinition> | Yes | Block definition | |
| mergeRangeList | List<ExcelCellRangeDefinition> | No | Cell merge range | |
| uniqueDefinitions | List<ExcelUniqueDefinition> | No | Unique definition |
3. Excel Block (ExcelBlockDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bindingModel | String | No | After binding the model, the default template and model parsing functions can be used | |
| fetchNamespace | String | No | The namespace of the acquisition function | |
| fetchFun | String | No | The name of the acquisition function | |
| domain | String | No | The default filtering rule, RSQL expression | |
| analysisType | ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum | Yes | Specify the parsing type used by the worksheet. Different parsing types have different definition methods | |
| direction | ExcelDirectionEnum | Yes | Specify the arrangement direction of the current header row | |
| designRange | ExcelCellRangeDefinition | Yes | The design scope | |
| usingCascadingStyle | Boolean | No | Change the style override to style cascading. Valid for a single block. The priority order is: header row style < data row style < cell style | |
| presetNumber | Integer | No | Use empty strings to fill the cells of the data row | |
| headerList | List<ExcelHeaderDefinition> | No | Header definition | |
| rowList | List<ExcelRowDefinition> | No | Row definition | |
| mergeRangeList | List<ExcelCellRangeDefinition> | No | Cell merge range | |
| uniqueDefinitions | List<ExcelUniqueDefinition> | No | Unique definition |
4. Excel Row (ExcelRowDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cellList | List<ExcelCellDefinition> | No | Cell list | |
| style | ExcelStyleDefinition | No | The global style is used by default in a row. If the cell style is set, it will override the global style. In the header row, the horizontal header row sets the entire column style. The vertical header row sets the entire row style. If the header row and data row set styles at the same time, the style of the data row is the global style |
5. Excel Header Row (ExcelHeaderDefinition)
Inheritance: ExcelRowDefinition
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| isConfig | Boolean | No | false | The configuration row does not participate in calculations and is automatically ignored during export. The application scope specified by the configuration row must be the header scope that needs to be configured |
| isFrozen | Boolean | No | false | The freezing function only takes effect in non-configuration rows and non-hidden rows |
6. Excel Cell (ExcelCellDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | String | No | Cell attribute definition. Fixed header: Only takes effect in the configuration row. Fixed format: Takes effect in any cell | |
| value | String | No | The value of the cell | |
| type | ExcelValueTypeEnum | No | Value type | |
| format | String | No | The formatting method (refer to the user manual) | |
| translate | Boolean | No | Whether to translate. By default, static values, enums, and boolean fields will be automatically translated, and other cases will be processed according to the specified values | |
| isStatic | Boolean | No | false | Whether it is a static value. The static value will use the configuration value during data parsing and will not read the value of the cell |
| isFieldValue | Boolean | No | Mark the content of this cell as an attribute value | |
| autoSizeColumn | Boolean | No | true | Whether to auto column width |
| style | ExcelStyleDefinition | No | Cell style | |
| styleCache | CellStyle( transient ) | No | Style cache (only used at runtime, ignored during serialization) |
7. Excel Unique Definition (ExcelUniqueDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | String | Yes | The associated model code | |
| uniques | List<String> | Yes | List of unique attributes. Multiple attributes combined form a unique identifier |
8. Excel Style (ExcelStyleDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| horizontalAlignment | ExcelHorizontalAlignmentEnum | No | GENERAL | Horizontal alignment |
| verticalAlignment | ExcelVerticalAlignmentEnum | No | Vertical alignment | |
| fillBorderStyle | ExcelBorderStyleEnum | No | Full border style (set top, bottom, left, and right borders at the same time) | |
| topBorderStyle | ExcelBorderStyleEnum | No | Top border style | |
| rightBorderStyle | ExcelBorderStyleEnum | No | Right border style | |
| bottomBorderStyle | ExcelBorderStyleEnum | No | Bottom border style | |
| leftBorderStyle | ExcelBorderStyleEnum | No | Left border style | |
| fillBorderColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Full border color (set top, bottom, left, and right border colors at the same time) | |
| topBorderColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Top border color | |
| rightBorderColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Right border color | |
| bottomBorderColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Bottom border color | |
| leftBorderColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Left border color | |
| fillPatternType | ExcelFillPatternTypeEnum | No | Background fill type (solid color/dots, etc.) | |
| backgroundColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Background color | |
| foregroundColor | Integer(RGB Color Value) | No | Foreground color (pattern color) | |
| wrapText | Boolean | No | false | Whether to wrap text automatically |
| shrinkToFit | Boolean | No | false | Whether to automatically shrink the text to fit the cell width |
| width | Integer | No | Cell width (only valid for the first row, unit: column width unit) | |
| height | Integer | No | Cell height (only valid for the first column, unit: row height unit) | |
| typefaceDefinition | ExcelTypefaceDefinition | No | Font definition (including font name, size, bold, italic, etc.) | |
| styleCache | CellStyle(transient) | No | Style cache (only used at runtime, ignored during serialization, automatically manages Workbook style objects) |
9. Excel Font (ExcelTypefaceDefinition)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| typeface | ExcelTypefaceEnum | No | SONG | Font type (such as Song, Heiti) |
| size | Integer | No | 11 | Font size (unit: point) |
| italic | Boolean | No | false | Whether it is italic |
| strikeout | Boolean | No | false | Whether to add a strikethrough |
| color | Integer(IndexedColors索引值) | No | 0xfff | Font color(such as IndexedColors. RED. GetIndex () in RED) |
| typeOffset | ExcelTypeOffsetEnum | No | NORMAL | Character offset type (normal/superscript/subscript) |
| underline | ExcelUnderlineEnum | No | NONE | Underline type (none/single underline/double underline, etc.) |
| bold | Boolean | No | false | Whether it is bold |
10. Excel Translation (ExcelLocation)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | String | Yes | The associated model code (used to locate the model to which the template belongs) | |
| name | String | Yes | Template name (corresponding to the name field of ExcelWorkbookDefinition) | |
| lang | String | Yes | Language identifier (such as zh-CN、 en-US) | |
| locationItems | List<ExcelLocationItem> | No | Internationalization configuration item list. Stores text mappings in each language and supports JSON format serialization |
11. Excel Translation Item (ExcelLocationItem)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| origin | String | Yes | Original text (untranslated value) | |
| target | String | Yes | Translated target text (value corresponding to the language) |
12. Abstract Excel Task (AbstractExcelTask)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | Yes | Task name | |
| workbookDefinition | ExcelWorkbookDefinition | Yes | Excel workbook definition object (associated entity) | |
| workbookDefinitionId | Long | Yes | Excel workbook definition ID (database storage field) | |
| workbookName | String | No | Excel workbook name (redundant field for quick query) | |
| state | ExcelTaskStateEnum | Yes | Task status (pending/processing/completed/failed, etc.) | |
| messages | List<TaskMessage> | No | Task information list. Stores logs and error information during task execution and supports JSON format serialization | |
| module | String | No | Module code (identifies the module to which the operation belongs, such as order、 customer) | |
| moduleDefinition | ModuleDefinition | No | The application object to which it belongs (associated entity, associated through the module field) | |
| createUserName | String | No | Creator name (non-persistent field, obtained by associating user information) | |
| writeUserName | String | No | Modifier name (non-persistent field, obtained by associating user information) | |
| model | String | No | Model code (identifies the business model corresponding to the operation, such as com.example.Order) |
13. Import Task (ExcelImportTask)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| file | PamirsFile | Yes | Import file object (associated with the file storage system entity, the file needs to be uploaded in advance) | |
| eachImport | Boolean | No | Whether to enable the row-by-row import mode. After enabling, the data will be processed row by row, and an error file can be generated for failed rows | |
| hasErrorRollback | Boolean | No | Whether to roll back the imported data when an error occurs. It needs to be used with maxErrorLength | |
| maxErrorLength | Integer | No | The maximum number of errors allowed. The task will be terminated when this number is exceeded (the default inherits the base class configuration) | |
| errorFile | PamirsFile | No | Import failure file (generated in row-by-row mode, containing failed row data) | |
| importDataList | List<String> | No | Import data list (stored in memory, used for temporary data transfer, not stored in the database) | |
| readCallbackList | List<ExcelReadCallback> | No | Read callback list (callback functions registered at runtime, ignored during serialization) |
14. Export Task (ExcelExportTask)
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| file | PamirsFile | No | Export file object (associated with the file storage system entity) | |
| fileType | ExcelExportFileTypeEnum | No | Export file type (Excel or CSV format) | |
| conditionWrapper | ConditionWrapper | No | Query condition wrapper. Supports RSQL expressions and dynamic condition combinations, and is not persistently stored | |
| rsql | String | No | RSQL filter condition. Automatically synchronizes the rsql field in conditionWrapper for quick query | |
| sync | Boolean | No | false | Whether to execute the export task synchronously. In synchronous mode, it will block and wait for the export to complete. In asynchronous mode, it returns the task ID |
| exportMethod | ExcelExportMethodEnum | No | TEMPLATE | Export method. TEMPLATE: Export based on the template. DIRECT: Export data directly |
| selectedFields | List<ModelField> | No | Selected field list. When exportMethod is DIRECT, specify the model fields to be exported | |
| requestId | String | No | Single request ID. Used to identify temporary data stored in Redis when downloading synchronously |
15. Task Message (TaskMessage)
Inheritance: TransientModel
| Field Name | Type | Mandatory | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Long | No | Message unique identifier (optional, used for paging query or locating specific messages) | |
| level | TaskMessageLevelEnum | Yes | Message level. ERROR: Error. WARNING: Warning. INFO: Prompt | |
| recordDate | Date | No | Message record time (automatically generated, accurate to milliseconds) | |
| rowIndex | Integer | No | Associated Excel row number (used to locate error rows in import tasks, counting from 1) | |
| message | String | Yes | Message content. Supports internationalization translation (translate=true) |
(Ⅱ) Enumerations
1. Template Type (ExcelTemplateTypeEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IMPORT_EXPORT | All | All |
| IMPORT | Import | Only used for import |
| EXPORT | Export | Only used for export |
2. Office Version (OfficeVersionEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding Excel Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUTO | Auto-Identify | Automatically identify the file type and will error if it cannot be identified | XLSX |
| OLD | Old Version | Refers to the office versions released in 2003 and before, using the old file suffix | XLS |
| NEW | New Version | Refers to the office versions released after 2003, using the new file suffix | XLSX |
3. Data Status (DataStatusEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DRAFT | Draft | Draft status |
| NOT_ENABLED | Not Enabled | Not enabled status |
| ENABLED | Enabled | Enabled status |
| DISABLED | Disabled | Disabled status |
4、Import Strategy (ExcelImportStrategyEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| STANDARD | Standard Mode | Standard mode (default), where developers control all import processes |
| EACH | Row-by-Row Import | Automatically collect import errors and generate error files, suitable for step-by-step processing of large data volumes |
| ALL | All Successful | Automatically enable the import transaction, immediately interrupt and roll back if any error occurs to ensure data consistency |
| ALL_EACH | All Successful and Collect Errors | Automatically enable the import transaction while collecting import errors to generate error files, balancing consistency and error positioning |
5、Export Strategy (ExcelExportStrategyEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| STANDARD | Default Fetch | Default to using a single extension point to fetch all data of the entire workbook (suitable for small data volume scenarios) |
| SINGLE | Single Function Fetch | Use the function defined in the workbook to completely fetch all data of the entire workbook (unified data source) |
| BLOCK | Multi-Function Fetch | Use the function defined for each block to fetch data in the corresponding block respectively (suitable for multi-data source block scenarios) |
| STREAM | Streaming Fetch | Fetch data in each block through paging, with data fetching and filling executed alternately (optimizes memory usage) |
6、Template Source (ExcelTemplateSourceEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SYSTEM | System-Generated | Automatically generated by the system when the current model has no template, automatically deleted after creating a new template, and retained after editing |
| INITIALIZATION | Initialization-Generated | Template created during system initialization, not allowing editing or deletion |
| CUSTOM | Custom | Template manually created or edited by the user |
7、Import Mode (ExcelImportModeEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MULTI_MODEL | Multi-Model | One template corresponds to multiple different Sheets, the default mode |
| SINGLE_MODEL | Single-Model | All Sheets share the same data model |
8、Analysis Type (ExcelAnalysisTypeEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FIXED_HEADER | Fixed Header | Fixed header format |
| FIXED_FORMAT | Fixed Format | Fixed format |
9、Arrangement Direction (ExcelDirectionEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding EasyExcel Writing Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| HORIZONTAL | Horizontal Arrangement | Sub-elements are arranged horizontally and filled vertically | VERTICAL |
| VERTICAL | Vertical Arrangement | Sub-elements are arranged vertically and filled horizontally | HORIZONTAL |
10、Value Type (ExcelValueTypeEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Default Format (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| STRING | Text | Ordinary text | - |
| INTEGER | Integer | Integer value | 0 |
| NUMBER | Number | Numeric with decimals | 0.00 |
| DATETIME | Date + Time | Combination of date and time | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss(corresponds to DATETIME format) |
| FORMULA | Formula | Excel formula | - |
| BOOLEAN | Boolean | Boolean value (Yes/No) | {"true":"Yes","false":"No"} |
| CALENDAR | Calendar | Date type | - |
| COMMENT | Comment | Cell comment | - |
| HYPER_LINK | Hyperlink | Hyperlink address | - |
| RICH_TEXT_STRING | Rich Text | Rich text content | - |
| ENUMERATION | Enum | Enumeration value | - |
| BIT | Binary Enum | Binary enumeration value | - |
| OBJECT | Object | Complex object | - |
11、Horizontal Alignment (ExcelHorizontalAlignmentEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding POI Enum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| GENERAL | Default | Text left-aligned; numbers, dates, and times right-aligned; booleans centered | HorizontalAlignment.GENERAL |
| LEFT | Left-Aligned | Content left-aligned | HorizontalAlignment.LEFT |
| CENTER | Center-Aligned | Content center-aligned | HorizontalAlignment.CENTER |
| RIGHT | Right-Aligned | Content right-aligned | HorizontalAlignment.RIGHT |
| FILL | Fill-Aligned | Content repeats to fit cell width | HorizontalAlignment.FILL |
| JUSTIFY | Justified | Content aligned at both ends, automatically adjusting word spacing (suitable for multi-line text) | HorizontalAlignment.JUSTIFY |
| CENTER_SELECTION | Center Selection | Content centered within the selected area (requires combined use with cell merging) | HorizontalAlignment.CENTER_SELECTION |
| DISTRIBUTED | Distributed | Content evenly distributed, aligned with cell borders at both ends | HorizontalAlignment.DISTRIBUTED |
12、Vertical Alignment (ExcelVerticalAlignmentEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding POI Enum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TOP | Top-Aligned | Content aligned with the top of the cell | VerticalAlignment.TOP |
| CENTER | Center-Aligned | Content vertically center-aligned | VerticalAlignment.CENTER |
| BOTTOM | Bottom-Aligned | Content aligned with the bottom of the cell | VerticalAlignment.BOTTOM |
| JUSTIFY | Justified | Content aligned at both ends, automatically adjusting line spacing (suitable for multi-line text) | VerticalAlignment.JUSTIFY |
| DISTRIBUTED | Distributed | Content evenly distributed, aligned with cell borders at top and bottom | VerticalAlignment.DISTRIBUTED |
13、Border Style (ExcelBorderStyleEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding POI Enum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NONE | No Border | No border | BorderStyle.NONE |
| THIN | Thin Border | Thin solid border | BorderStyle.THIN |
| MEDIUM | Medium Border | Medium solid border | BorderStyle.MEDIUM |
| THICK | Thick Border | Thick solid border | BorderStyle.THICK |
| DASHED | Dashed Border | Dashed border | BorderStyle.DASHED |
| DOTTED | Dotted Border | Dotted border | BorderStyle.DOTTED |
| DOUBLE | Double Border | Double solid border | BorderStyle.DOUBLE |
| HAIR | Hair Border | Extremely thin solid border (hairline) | BorderStyle.HAIR |
| MEDIUM_DASHED | Medium Dashed Border | Medium dashed border | BorderStyle.MEDIUM_DASHED |
| DASH_DOT | Dash-Dot Border | Dash-dot border | BorderStyle.DASH_DOT |
| MEDIUM_DASH_DOT | Medium Dash-Dot Border | Medium dash-dot border | BorderStyle.MEDIUM_DASH_DOT |
| DASH_DOT_DOT | Dash-Dot-Dot Border | Dash-dot-dot border | BorderStyle.DASH_DOT_DOT |
| MEDIUM_DASH_DOT_DOT | Medium Dash-Dot-Dot Border | Medium dash-dot-dot border | BorderStyle.MEDIUM_DASH_DOT_DOT |
| SLANTED_DASH_DOT | Slanted Dash-Dot Border | Slanted dash-dot border | BorderStyle.SLANTED_DASH_DOT |
14、Fill Pattern (ExcelFillPatternTypeEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding POI Enum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO_FILL | No Fill | No background fill | FillPatternType.NO_FILL |
| SOLID_FOREGROUND | Solid Fill | Solid color background fill | FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND |
| FINE_DOTS | Fine Dots | Dense dotted background fill | FillPatternType.FINE_DOTS |
| ALT_BARS | Alternating Bars | Horizontal alternating stripe background fill | FillPatternType.ALT_BARS |
| SPARSE_DOTS | Sparse Dots | Sparse dotted background fill | FillPatternType.SPARSE_DOTS |
| THICK_HORZ_BANDS | Thick Horizontal Bands | Thick horizontal stripe background fill | FillPatternType.THICK_HORZ_BANDS |
| THICK_VERT_BANDS | Thick Vertical Bands | Thick vertical stripe background fill | FillPatternType.THICK_VERT_BANDS |
| THICK_BACKWARD_DIAG | Thick Backward Diagonal | Thick diagonal (top-left to bottom-right) background fill | FillPatternType.THICK_BACKWARD_DIAG |
| THICK_FORWARD_DIAG | Thick Forward Diagonal | Thick diagonal (top-right to bottom-left) background fill | FillPatternType.THICK_FORWARD_DIAG |
| BIG_SPOTS | Big Spots | Large dotted background fill | FillPatternType.BIG_SPOTS |
| BRICKS | Bricks | Brick texture background fill | FillPatternType.BRICKS |
| THIN_HORZ_BANDS | Thin Horizontal Bands | Thin horizontal stripe background fill | FillPatternType.THIN_HORZ_BANDS |
| THIN_VERT_BANDS | Thin Vertical Bands | Thin vertical stripe background fill | FillPatternType.THIN_VERT_BANDS |
| THIN_BACKWARD_DIAG | Thin Backward Diagonal | Thin diagonal (top-left to bottom-right) background fill | FillPatternType.THIN_BACKWARD_DIAG |
| THIN_FORWARD_DIAG | Thin Forward Diagonal | Thin diagonal (top-right to bottom-left) background fill | FillPatternType.THIN_FORWARD_DIAG |
15、Font Type (ExcelTypefaceEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SONG | Song | Song typeface (common Chinese body text font) |
| REGULAR_SCRIPT | Regular Script | Regular script (handwriting-style font) |
| BOLDFACE | Boldface | Boldface (bold sans-serif font) |
| YAHEI | Microsoft YaHei | Microsoft YaHei (clear and readable sans-serif font) |
16、Character Offset Type (ExcelTypeOffsetEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding POI Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NORMAL | Normal | Display normally | Font.SS_NONE (0) |
| SUPER | Superscript | Text displayed above the baseline | Font.SS_SUPER (1) |
| SUB | Subscript | Text displayed below the baseline | Font.SS_SUB (2) |
17、Underline Type (ExcelUnderlineEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Corresponding POI Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NONE | None | No underline | Font.U_NONE (0) |
| SINGLE | Single | Single solid underline | Font.U_SINGLE (1) |
| DOUBLE | Double | Double solid underline | Font.U_DOUBLE (2) |
| SINGLE_ACCOUNTING | Single Accounting | Single underline adapted for accounting reports (same width as cell) | Font.U_SINGLE_ACCOUNTING (3) |
| DOUBLE_ACCOUNTING | Double Accounting | Double underline adapted for accounting reports (same width as cell) | Font.U_DOUBLE_ACCOUNTING (4) |
18、Task Status (ExcelTaskStateEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PROCESSING | Processing | Task is executing (performing data reading/writing or conversion) |
| SUCCESS | Success | Task completed successfully (all data processed without errors) |
| FAILURE | Failure | Task execution failed (terminated due to errors, requires checking logs or error files) |
19、Export File Type (ExcelExportFileTypeEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EXCEL | Excel Format | Export Excel format file (.xlsx) |
| CSV | CSV Format | Export CSV format file (comma-separated values) |
20、Export Method (ExcelExportMethodEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TEMPLATE | Export by Template | Use predefined Excel template for data filling and export |
| SELECT_TEMPLATE_FIELD | Export by Selected Template Fields | Export after filtering data based on selected fields from the template |
| SELECT_FIELD | Export by Model Fields | Directly select fields from the data model to generate Excel export |
21、Message Level (TaskMessageLevelEnum)
| Value | Display Name | Description | Processing Logic |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIP | Tip | Routine prompt information output to console | Only printed to console, not stored |
| INFO | Info | Detailed task execution information | Stored in the info list for traceability |
| WARNING | Warning | Non-blocking warning (does not affect task main process) | No rollback, requires manual attention |
| ERROR | Error | Error information causing task failure | Triggers rollback and terminates task execution |