Chapter 1:Architecture Overview
I. Frontend-Backend Separation Architecture
In software development, the frontend-backend separation architecture is an efficient model that clearly separates the user interface (frontend) from business logic and data processing (backend), allowing them to be developed, tested, and deployed independently.
The frontend is responsible for user interaction, presentation, and input reception, composed of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Complex projects often use frameworks like React or Vue.js to enhance development efficiency. The backend focuses on business logic and data storage, implemented using languages and frameworks such as Python (with Django), Java (e.g., Spring Boot), or Node.js (with Express). The backend interacts with databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL and provides data to the frontend via APIs, typically following RESTful or GraphQL specifications.
This architecture offers significant advantages. Development teams can divide tasks based on expertise, improving efficiency and code quality. Frontend and backend can be deployed and updated independently, reducing maintenance costs and risks while facilitating cross-platform development. E-commerce platforms are typical applications: the frontend displays products and shopping carts, while the backend handles inventory and order logic.
In summary, the frontend-backend separation architecture, with its clear responsibility division, efficient development, and good maintainability, has become a crucial model for modern software construction.
Shushi Oinone employs Vue.js for the frontend, a Java technology stack for the backend, and follows GraphQL specifications for APIs.
Tip: Shushi Oinone framework advances the frontend-backend separation development model
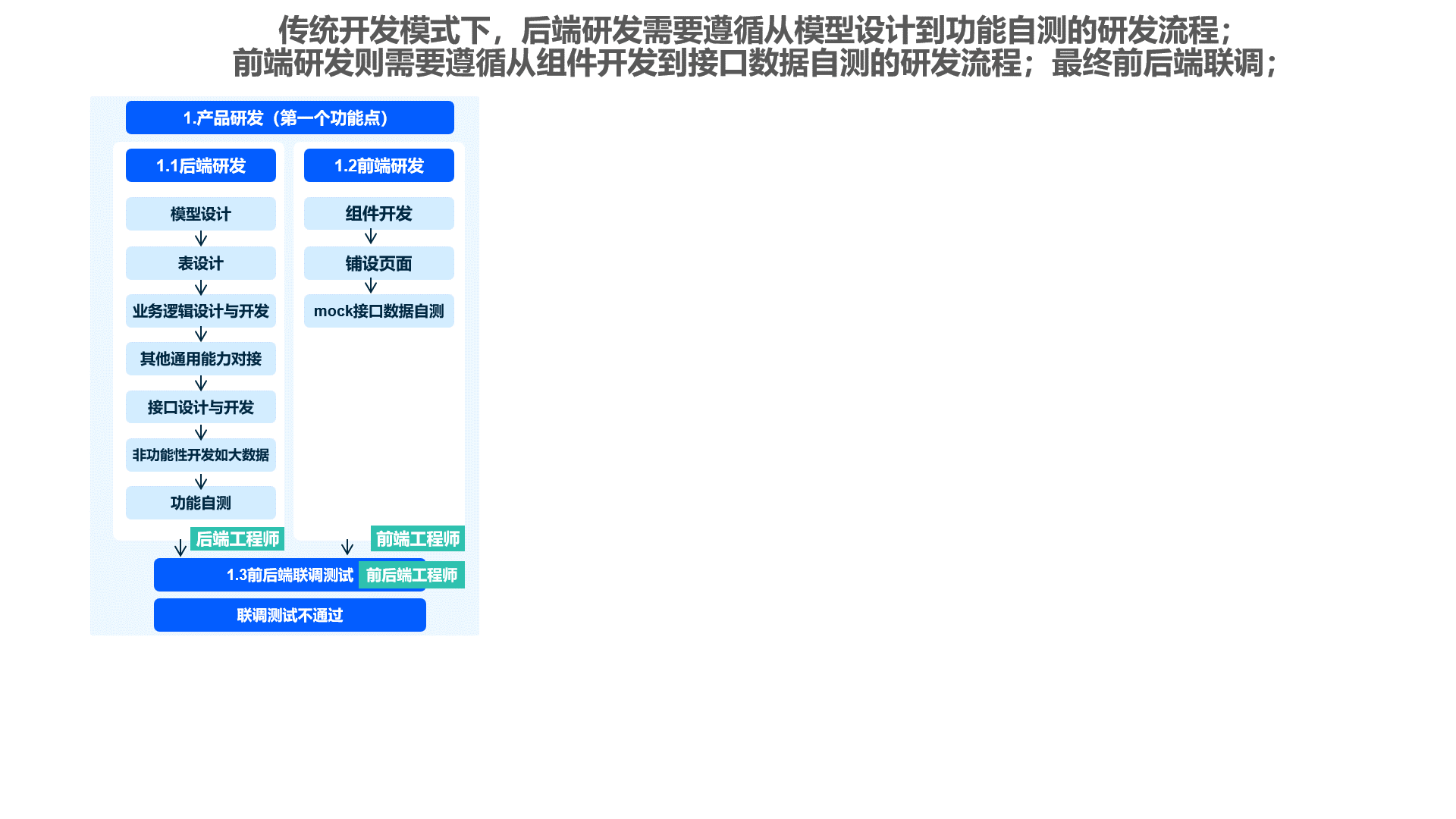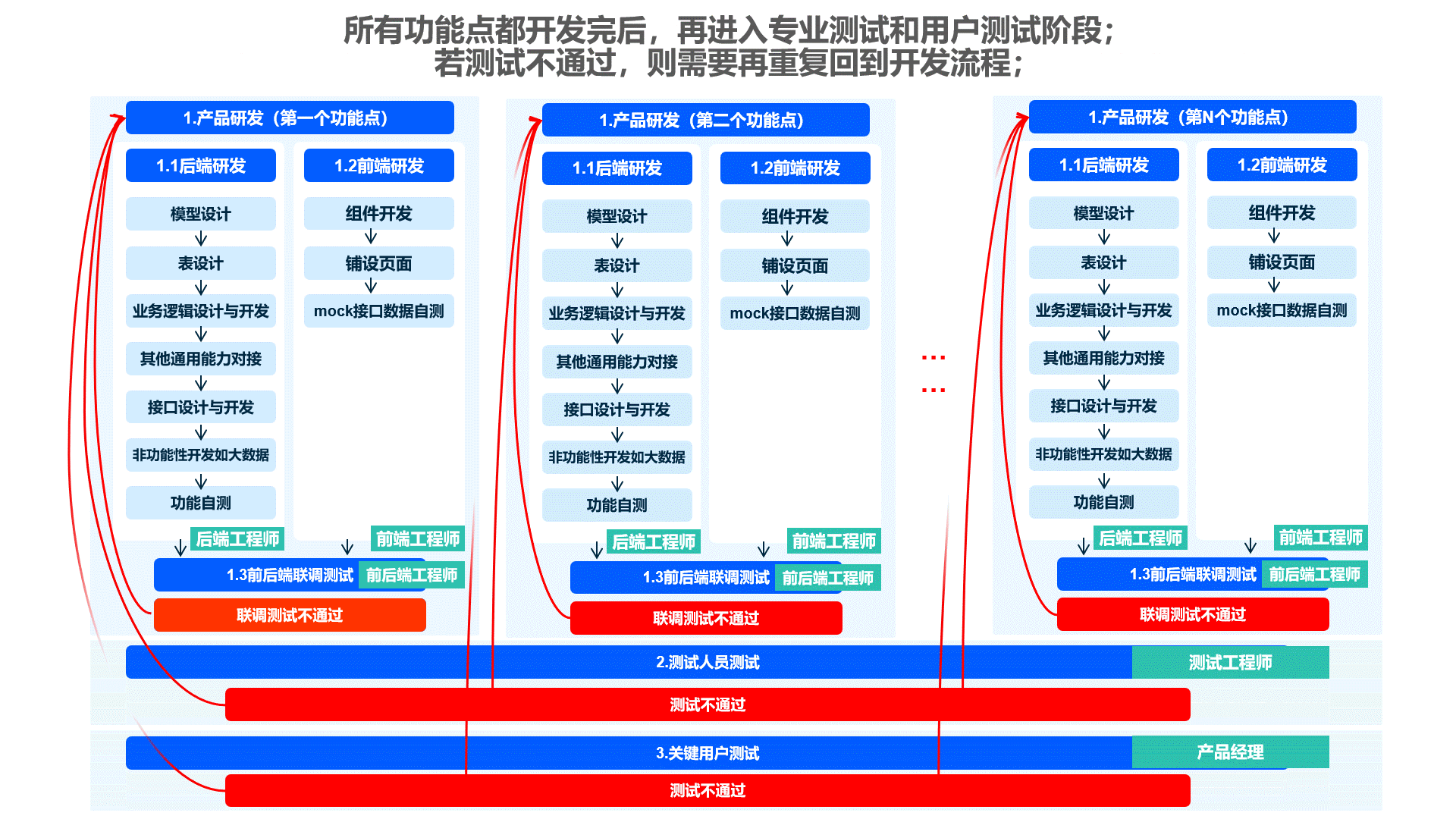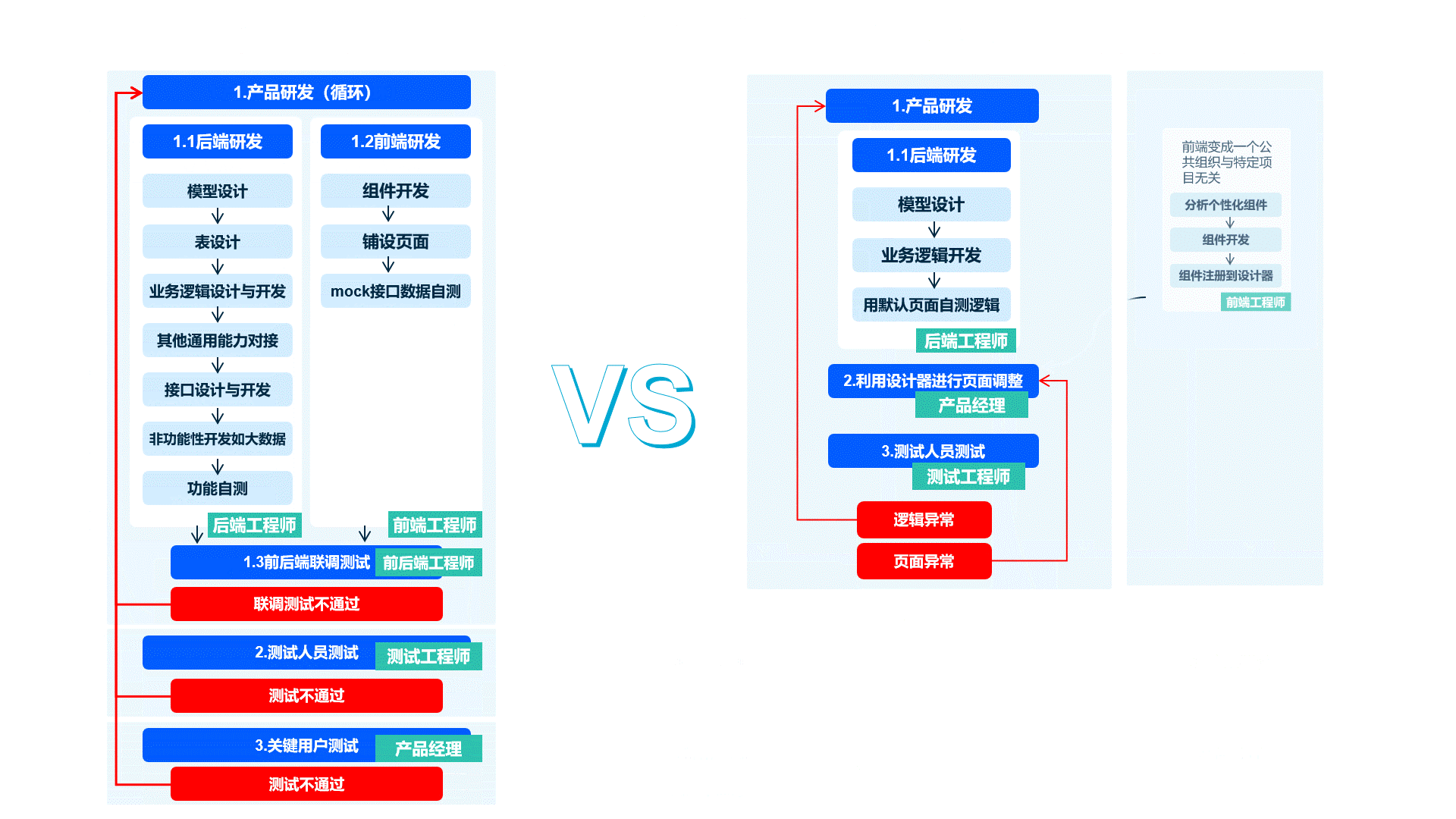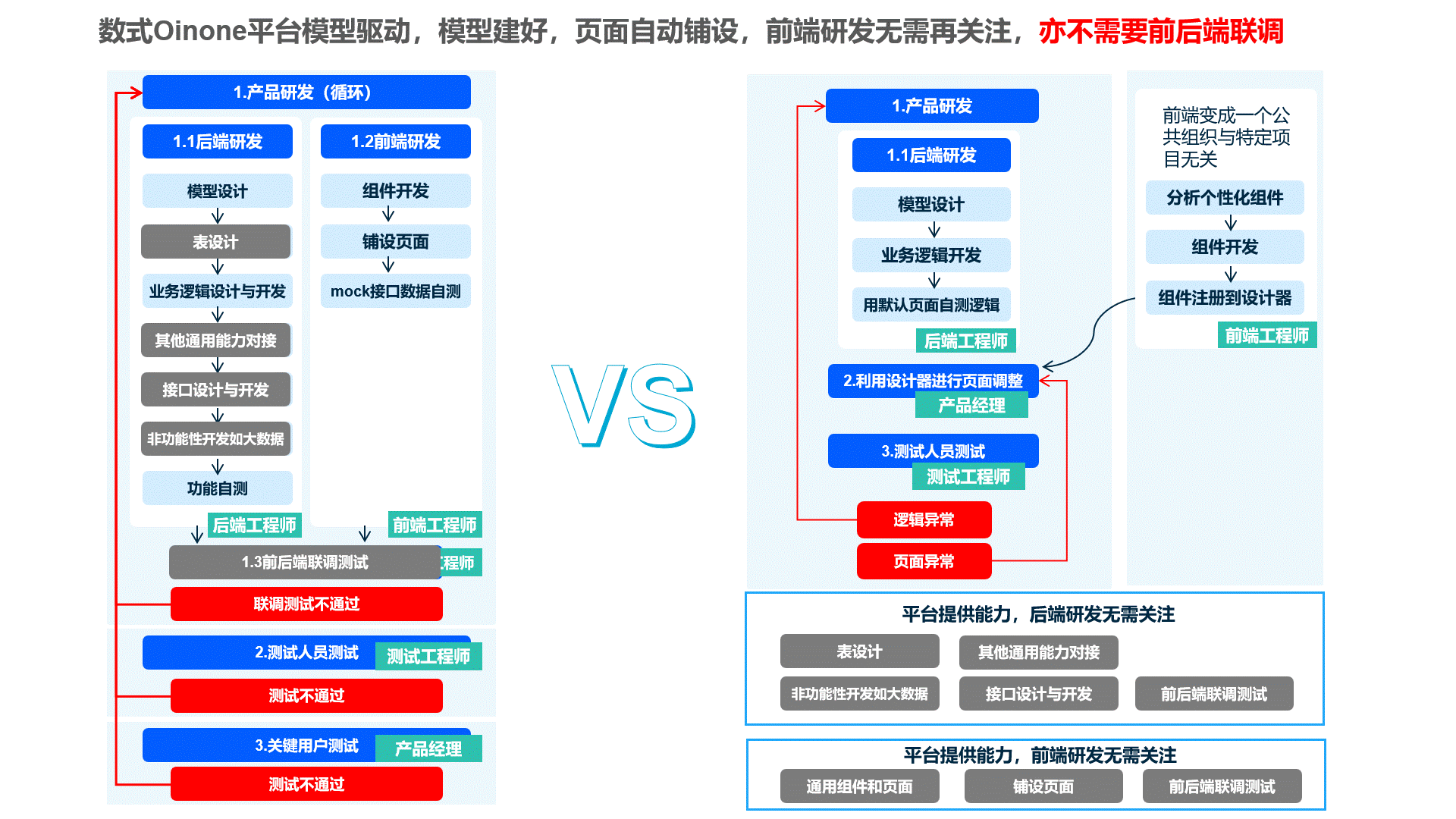
Frontend development is only required when components need customization or special business components need to be built. This retains the benefits of frontend-backend separation while reducing unnecessary communication between front-end and back-end teams during business development, greatly improving efficiency.
Example: Optimize your front-end and back-end development division with Oinone (optional recommendation)
II. Oinone Module
A module is a division of a program into sub-functions, where each module completes a sub-function, and together they form an integrated whole. It is the smallest unit divided and managed by business domain, a collection of functions and interfaces.
Oinone modules can either add entirely new business logic to the Oinone system or modify and extend existing logic. For example, one module can add business-specific user organization management rules to Oinone's general user organization support, while another can add real-time visualization capabilities.
In Oinone, everything starts and ends with modules.
Terminology: Developers group business functions into Oinone modules. User-facing modules are marked and displayed as applications (Apps), but most modules are not applications.
III. Module Structure
Each module is an independent Java module. The project structure follows Spring's interface-oriented programming specifications, generally including api and core projects. An Oinone module is declared via its XxModule.java file. See Module Definition File Description for details.
(I) Package Scanning Configuration for Each Module
When an Oinone module contains business objects, these files are organized under the module's scanning package path:
- Use the
packagePrefixmethod to configure the package paths where metadata should be scanned.
(II) Simplified Module Directory Structure
Module
├── module-api Module interface project
│ ├── model Models
│ └── Module.java Module definition
└── module-core Module implementation project
├── action Actions
└── init Data initializationIV. Oinone Editions
Oinone has two versions: Oinone Enterprise Edition (requiring a license with shared source code) and Oinone Community Edition (open-source). In addition to technical support or upgrade services, the Enterprise Edition provides additional features, which technically are just new modules installed on top of the Community Edition's modules.
Ready to start? It's time to write your own application!